Von capacitor +q 0.632E Switch O r= RC 21 3r 4r (a) (b) Figure 21.38 (a) An RC circuit with an initially uncharged capacitor. Current flows in the direction shown (opposite of electron flow) as soon as the switch is closed. Mutual repulsion of like charges in the capacitor progressively slows the flow as the capacitor is charged, stopping the current when the capacitor is fully charged and Q = C· emf . (b) A graph of voltage across the capacitor versus time, with the switch closing at time t = 0. (Note that in the two parts of the figure, the capital script E stands for emf, q stands for the charge stored on the capacitor, and t is the RC time constant.)
Von capacitor +q 0.632E Switch O r= RC 21 3r 4r (a) (b) Figure 21.38 (a) An RC circuit with an initially uncharged capacitor. Current flows in the direction shown (opposite of electron flow) as soon as the switch is closed. Mutual repulsion of like charges in the capacitor progressively slows the flow as the capacitor is charged, stopping the current when the capacitor is fully charged and Q = C· emf . (b) A graph of voltage across the capacitor versus time, with the switch closing at time t = 0. (Note that in the two parts of the figure, the capital script E stands for emf, q stands for the charge stored on the capacitor, and t is the RC time constant.)
Related questions
Question
When charging a capacitor, as discussed in conjunction as shown, how long does it take for the voltage on the capacitor to reach emf? Is this a problem?
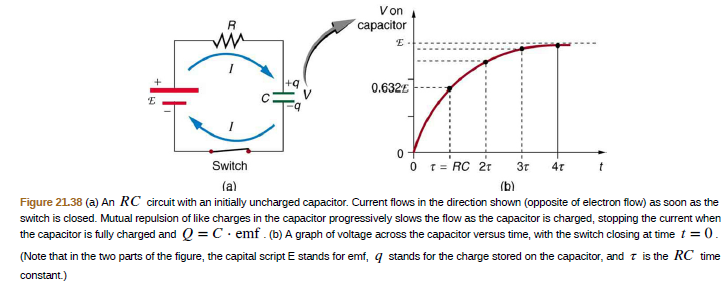
Transcribed Image Text:Von
capacitor
+q
0.632E
Switch
O r= RC 21
3r
4r
(a)
(b)
Figure 21.38 (a) An RC circuit with an initially uncharged capacitor. Current flows in the direction shown (opposite of electron flow) as soon as the
switch is closed. Mutual repulsion of like charges in the capacitor progressively slows the flow as the capacitor is charged, stopping the current when
the capacitor is fully charged and Q = C· emf . (b) A graph of voltage across the capacitor versus time, with the switch closing at time t = 0.
(Note that in the two parts of the figure, the capital script E stands for emf, q stands for the charge stored on the capacitor, and t is the RC time
constant.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images
