Weber's law, a concept taught in most Introduction to Psychology courses, states that the ratio of the intensity of a stimulus to the "just noticeable" increment in intensity is constant, that is, the ratio doesn't depend on the intensity of the stimulus. The ratio is called the "Weber fraction," so a concise statement of Weber's law is that "the Weber fraction is constant, regardless of the stimulus intensity." It turns out that Weber's law is not so much a law as it is a rule of thumb, since it is violated in many situations. For instance, for some auditory stimuli, the Weber fraction does depend systematically on the stimulus intensity. Espaio The following bivariate data are the experimental data obtained for one listener in an auditory intensity discrimination task. For each of the ten stimulus intensities x (in decibels), the Weber fraction y (in decibels) is shown. Figure 1 is a scatter plot of the data. Also given is the product of the stimulus intensity and the Weber fraction for each of the ten stimuli. (These products, written in the column labelled "xy", may aid in calculations.) Stimulus Weber intensity, x fraction, y xy (in decibels) (in decibels) 35 -0.45 -15.75 40 -0.43 -17.2 45 -1.39 -62.55 14 50 -1.07 -53.5 -24 55 -2.15 -118.25 60 -2.76 -165.6 65 -3.2 -208 70 -3 -210 75 -4.27 -320.25 Stimulus intensity (in decibels) 80 -4.48 -358.4 Figure 1 Send data to calculator Send data to Excel What is the sample correlation.coefficient for these data? Carry your intermediate computations to at least four decimal places and round your answer to at least three decimal places. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.) Weber fraction (in decibels) 回 日 B回回
Weber's law, a concept taught in most Introduction to Psychology courses, states that the ratio of the intensity of a stimulus to the "just noticeable" increment in intensity is constant, that is, the ratio doesn't depend on the intensity of the stimulus. The ratio is called the "Weber fraction," so a concise statement of Weber's law is that "the Weber fraction is constant, regardless of the stimulus intensity." It turns out that Weber's law is not so much a law as it is a rule of thumb, since it is violated in many situations. For instance, for some auditory stimuli, the Weber fraction does depend systematically on the stimulus intensity. Espaio The following bivariate data are the experimental data obtained for one listener in an auditory intensity discrimination task. For each of the ten stimulus intensities x (in decibels), the Weber fraction y (in decibels) is shown. Figure 1 is a scatter plot of the data. Also given is the product of the stimulus intensity and the Weber fraction for each of the ten stimuli. (These products, written in the column labelled "xy", may aid in calculations.) Stimulus Weber intensity, x fraction, y xy (in decibels) (in decibels) 35 -0.45 -15.75 40 -0.43 -17.2 45 -1.39 -62.55 14 50 -1.07 -53.5 -24 55 -2.15 -118.25 60 -2.76 -165.6 65 -3.2 -208 70 -3 -210 75 -4.27 -320.25 Stimulus intensity (in decibels) 80 -4.48 -358.4 Figure 1 Send data to calculator Send data to Excel What is the sample correlation.coefficient for these data? Carry your intermediate computations to at least four decimal places and round your answer to at least three decimal places. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.) Weber fraction (in decibels) 回 日 B回回
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter5: Inverse, Exponential, And Logarithmic Functions
Section5.6: Exponential And Logarithmic Equations
Problem 52E
Related questions
Question
100%
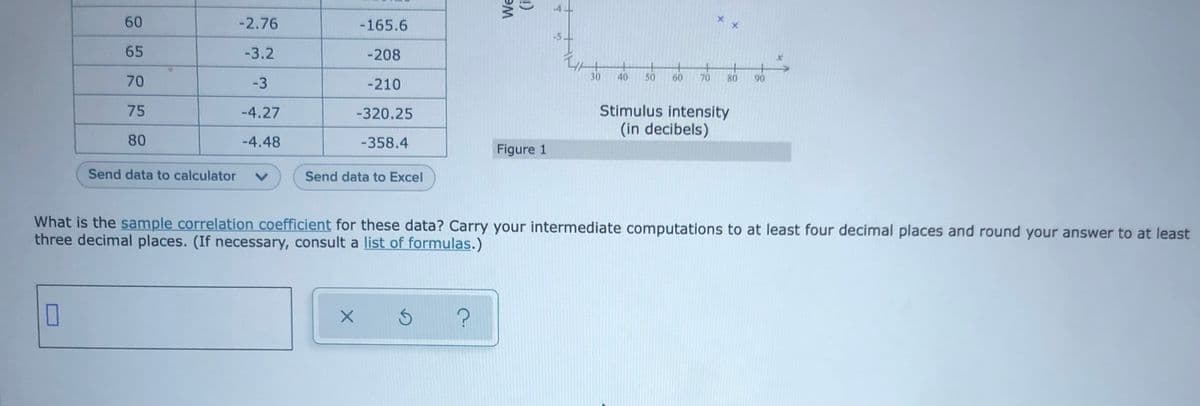
Transcribed Image Text:60
-2.76
-165.6
65
-3.2
-208
70
-3
-210
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
Stimulus intensity
(in decibels)
75
-4.27
-320.25
80
-4.48
-358.4
Figure 1
Send data to calculator
Send data to Excel
What is the sample correlation coefficient for these data? Carry your intermediate computations to at least four decimal places and round your answer to at least
three decimal places. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.)
We
!)
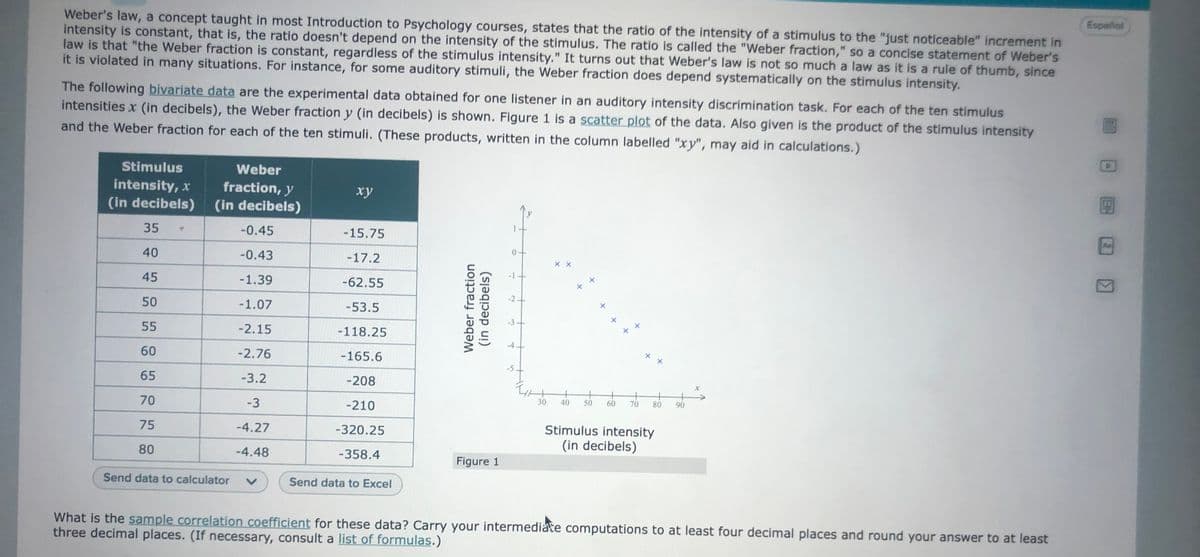
Transcribed Image Text:Español
Weber's law, a concept taught in most Introduction to Psychology courses, states that the ratio of the intensity of a stimulus to the "just noticeable" increment in
intensity is constant, that is, the ratio doesn't depend on the intensity of the stimulus. The ratio is called the "Weber fraction," so a concise statement of Weber's
law is that "the Weber fraction is constant, regardless of the stimulus intensity." It turns out that Weber's law is not so much a law as it is a rule of thumb, since
it is violated in many situations. For instance, for some auditory stimuli, the Weber fraction does depend systematically on the stimulus intensity.
The following bivariate data are the experimental data obtained for one listener in an auditory intensity discrimination task. For each of the ten stimulus
intensities x (in decibels), the Weber fraction y (in decibels) is shown. Figure 1 is a scatter plot of the data. Also given is the product of the stimulus intensity
and the Weber fraction for each of the ten stimuli. (These products, written in the column labelled "xy", may aid in calculations.)
Stimulus
Weber
intensity, x
fraction, y
ху
(in decibels) (in decibels)
35
-0.45
-15.75
0+
40
-0.43
-17.2
-1+
45
-1.39
-62.55
-2+
50
-1.07
-53.5
-3+
55
-2.15
-118.25
60
-2.76
-165.6
65
-3.2
-208
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
70
-3
-210
75
-4.27
-320.25
Stimulus intensity
(in decibels)
80
-4.48
-358.4
Figure 1
Send data to calculator
Send data to Excel
What is the sample correlation coefficient for these data? Carry your intermediače computations to at least four decimal places and round your answer to at least
three decimal places. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.)
Weber fraction
(in decibels)
EN
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill


Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning