What do the ions that gave a precipitate with (NH),CO, and Na, PO, have in common? 3. 4. Which test ions were spectator ions throughout part A? What do these ions have i common? 5. Which ONE of the following ions is mostly likely to give a precipitate with PO,? Explain F CH,O, NO, Mg Cs NH, H* 31 Nameouusa Oluarens aluareng Part A 1. Place 9 clean small test tubes in a test tube rack. The test tubes should be clean but do not have to be dry because aqueous solutions will be used. 2. To each test tube add 5 drops of the solution (0.1 M) indicated in the data table. 3. Next add 5 drops of silver nitrate (0.5 M) to each of the 9 test tubes. If there is no apparent change be sure to gently swirl the test tube to mix the reagents (a stirring rod can be used). If the contents of the test tube are cloudy, a solid precipitate was formed. If the contents of the test tube are clear, no reaction occurred. Record the results in the data table writing "ppt" and their color for precipitates and "NR" for no reaction. 4. Your instructor will inform you of where to dispose of the chemicals used. Rinse the test tubes and repeat the procedure two more times first using ammonium carbonate (0.5 M) in step 3 and then again using sodium phosphate (0.5 M) in step 3. coibane chsprote Slver Ag* C. Test Tube Solution Test Ion Co,2 PO 1 Barium nitrate Ba2 eheve Per Ppt clod 2 Ammonium CI chloride we Calcium nitrate e 3 Ca2 unte 4 Lithium nitrate Li* NR NR Ne PPT ualow Ammonium iodide I NO NK 6 Potassium nitrate K* UK 7 Sodium nitrate Na NK NK N2 8 Strontium nitrate Sr2t Pptunide nte PPT yeloce NK Ammonium Br Ne bromide 30
What do the ions that gave a precipitate with (NH),CO, and Na, PO, have in common? 3. 4. Which test ions were spectator ions throughout part A? What do these ions have i common? 5. Which ONE of the following ions is mostly likely to give a precipitate with PO,? Explain F CH,O, NO, Mg Cs NH, H* 31 Nameouusa Oluarens aluareng Part A 1. Place 9 clean small test tubes in a test tube rack. The test tubes should be clean but do not have to be dry because aqueous solutions will be used. 2. To each test tube add 5 drops of the solution (0.1 M) indicated in the data table. 3. Next add 5 drops of silver nitrate (0.5 M) to each of the 9 test tubes. If there is no apparent change be sure to gently swirl the test tube to mix the reagents (a stirring rod can be used). If the contents of the test tube are cloudy, a solid precipitate was formed. If the contents of the test tube are clear, no reaction occurred. Record the results in the data table writing "ppt" and their color for precipitates and "NR" for no reaction. 4. Your instructor will inform you of where to dispose of the chemicals used. Rinse the test tubes and repeat the procedure two more times first using ammonium carbonate (0.5 M) in step 3 and then again using sodium phosphate (0.5 M) in step 3. coibane chsprote Slver Ag* C. Test Tube Solution Test Ion Co,2 PO 1 Barium nitrate Ba2 eheve Per Ppt clod 2 Ammonium CI chloride we Calcium nitrate e 3 Ca2 unte 4 Lithium nitrate Li* NR NR Ne PPT ualow Ammonium iodide I NO NK 6 Potassium nitrate K* UK 7 Sodium nitrate Na NK NK N2 8 Strontium nitrate Sr2t Pptunide nte PPT yeloce NK Ammonium Br Ne bromide 30
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
3rd Edition
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Chapter4: Chemical Reactions In Solution
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4.80QE: What is the solid that precipitates, and how much of it forms, when an excess of sodium chloride...
Related questions
Question
Question 4

Transcribed Image Text:What do the ions that gave a precipitate with (NH),CO, and Na, PO, have in common?
3.
4. Which test ions were spectator ions throughout part A? What do these ions have i
common?
5. Which ONE of the following ions is mostly likely to give a precipitate with PO,?
Explain
F CH,O,
NO,
Mg
Cs
NH,
H*
31
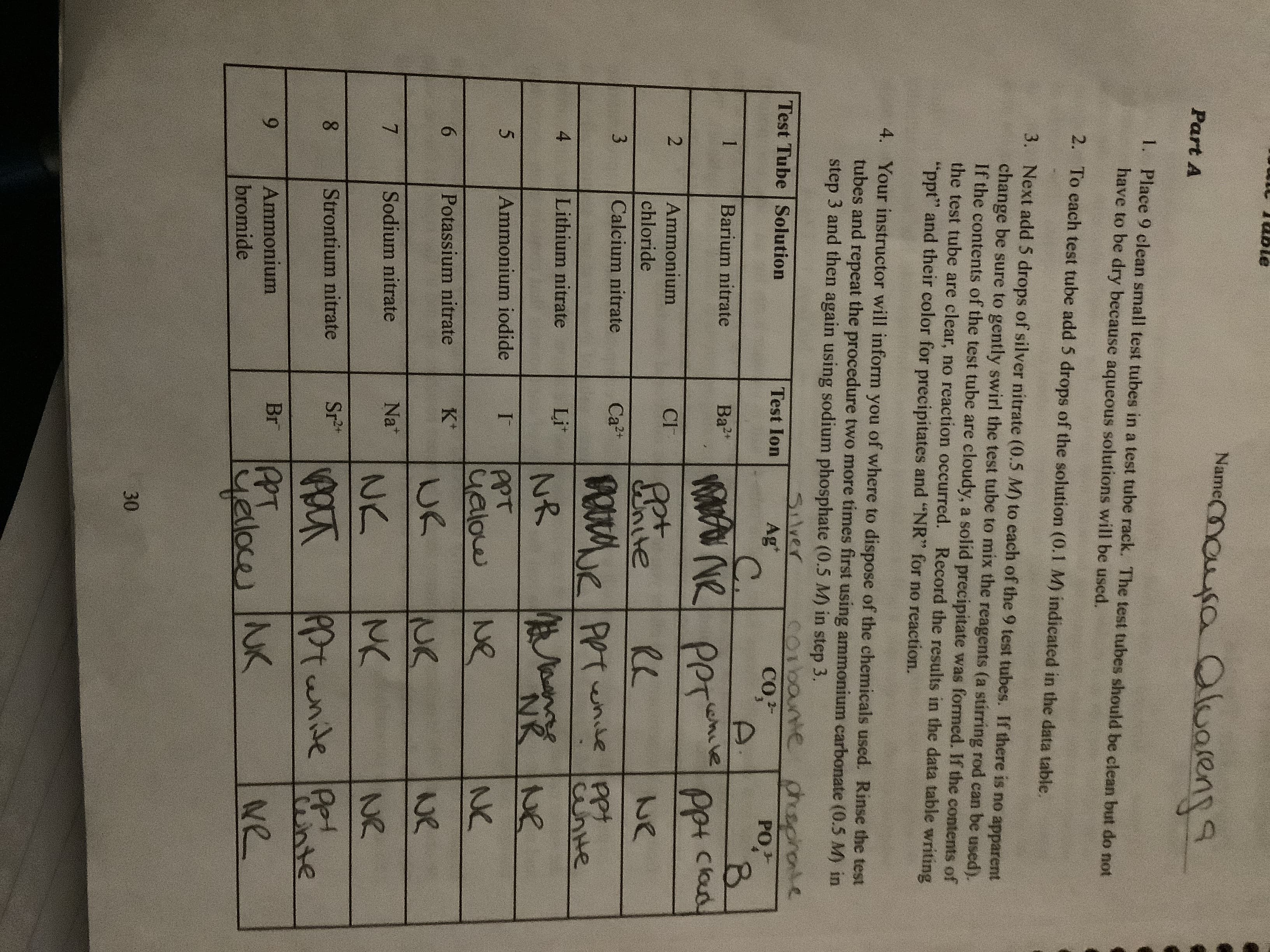
Transcribed Image Text:Nameouusa Oluarens
aluareng
Part A
1.
Place 9 clean small test tubes in a test tube rack. The test tubes should be clean but do not
have to be dry because aqueous solutions will be used.
2.
To each test tube add 5 drops of the solution (0.1 M) indicated in the data table.
3. Next add 5 drops of silver nitrate (0.5 M) to each of the 9 test tubes. If there is no apparent
change be sure to gently swirl the test tube to mix the reagents (a stirring rod can be used).
If the contents of the test tube are cloudy, a solid precipitate was formed. If the contents of
the test tube are clear, no reaction occurred. Record the results in the data table writing
"ppt" and their color for precipitates and "NR" for no reaction.
4. Your instructor will inform you of where to dispose of the chemicals used. Rinse the test
tubes and repeat the procedure two more times first using ammonium carbonate (0.5 M) in
step 3 and then again using sodium phosphate (0.5 M) in step 3.
coibane chsprote
Slver
Ag*
C.
Test Tube Solution
Test Ion
Co,2
PO
1
Barium nitrate
Ba2
eheve
Per
Ppt clod
2
Ammonium
CI
chloride
we
Calcium nitrate
e
3
Ca2
unte
4
Lithium nitrate
Li*
NR
NR Ne
PPT
ualow
Ammonium iodide
I
NO
NK
6
Potassium nitrate
K*
UK
7
Sodium nitrate
Na
NK
NK
N2
8
Strontium nitrate
Sr2t
Pptunide
nte
PPT
yeloce NK
Ammonium
Br
Ne
bromide
30
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning