When a catalyst is added to a reaction, the reaction rate is increased because the catalyst 1) increases activation energy 2) decreases activation energy 3) increases potential energy of the reactants 4) decreases potential energy of the reactants
When a catalyst is added to a reaction, the reaction rate is increased because the catalyst 1) increases activation energy 2) decreases activation energy 3) increases potential energy of the reactants 4) decreases potential energy of the reactants
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Chapter13: Rates Of Reaction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13.143QP
Related questions
Question
FYI: #5-8 is like a),b),c) and d)
Thank you.
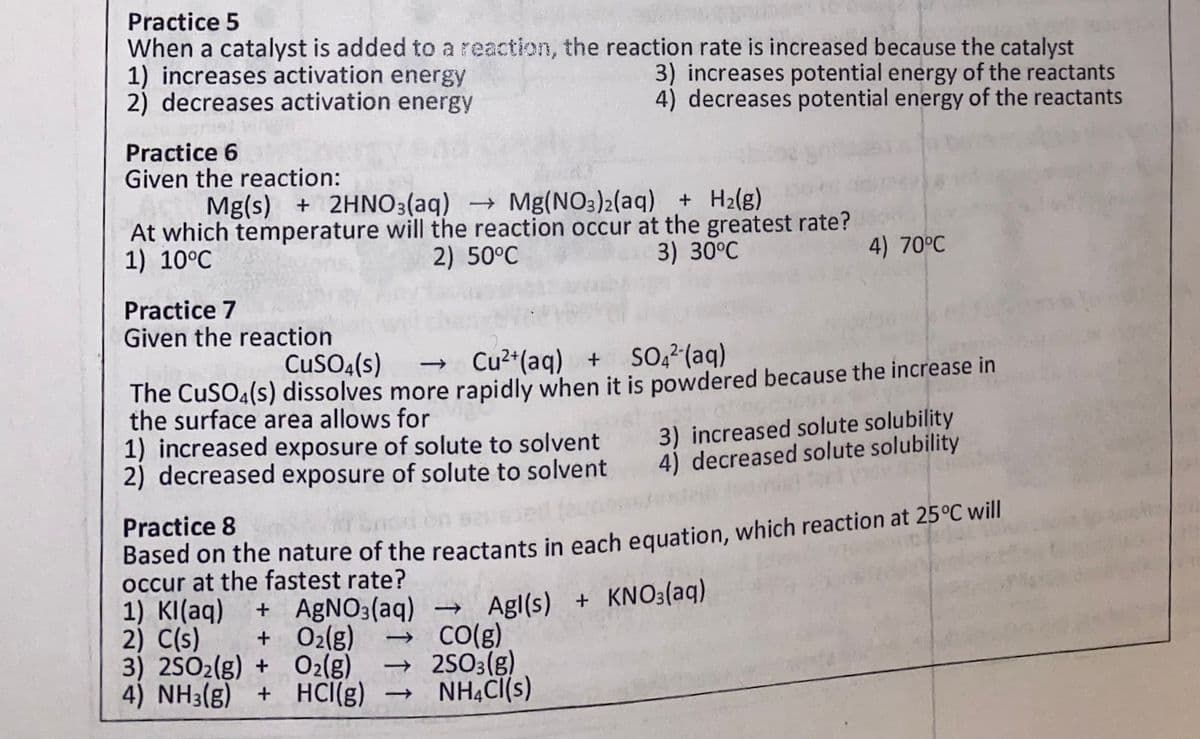
Transcribed Image Text:Practice 5
When a catalyst is added to a reaction, the reaction rate is increased because the catalyst
1) increases activation energy
2) decreases activation energy
3) increases potential energy of the reactants
4) decreases potential energy of the reactants
Practice 6
Given the reaction:
Mg(s) + 2HNO3(aq) Mg(NO3)2(aq) + H2(g)
At which temperature will the reaction occur at the greatest rate?
2) 50°C
1) 10°C
3) 30°C
4) 70°C
Practice 7
Given the reaction
CuSO4(s)
→ Cu²*(aq) + SO, (aq)
The CuSO4(s) dissolves more rapidly when it is powdered because the increase in
the surface area allows for
1) increased exposure of solute to solvent
2) decreased exposure of solute to solvent
3) increased solute solubility
4) decreased solute solubility
Practice 8
Based on the nature of the reactants in each equation, which reaction at 25°C will
occur at the fastest rate?
1) KI(aq)
2) C(s)
3) 2SO2(g) + O2(g)
4) NH3(g) + HCI(g) → NH4CI(s)
+ A£NO3(aq) → Agl(s) + KNO3(aq)
→ CO(g)
→ 2SO3(g)
+ 02(g)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning