When the Euro coin was introduced in 2002, two math professors had their statistics students test whether the Belgian one Euro coin was a fair coin. They spun the coin rather than tossing it and found that out of 250 spins, 160 showed a head (event H) while 90 showed a tail (event T). On that basis, they claimed that it is not a fair coin. O Part (a) Based on the given data, find P(H) and P(T). (Round your answers to two decimal places.) P(H) = 0.6 P(T) = 0.4 O Part (b) Use a tree diagram to find the probabilities of each possible outcome for the experiment of spinning the coin twice. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) H. Н. 0.6400 TT TH, d.2304 HT H O Part (c) Use the tree diagram to find the probability of obtaining exactly one head in two spins of the coin. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
When the Euro coin was introduced in 2002, two math professors had their statistics students test whether the Belgian one Euro coin was a fair coin. They spun the coin rather than tossing it and found that out of 250 spins, 160 showed a head (event H) while 90 showed a tail (event T). On that basis, they claimed that it is not a fair coin. O Part (a) Based on the given data, find P(H) and P(T). (Round your answers to two decimal places.) P(H) = 0.6 P(T) = 0.4 O Part (b) Use a tree diagram to find the probabilities of each possible outcome for the experiment of spinning the coin twice. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) H. Н. 0.6400 TT TH, d.2304 HT H O Part (c) Use the tree diagram to find the probability of obtaining exactly one head in two spins of the coin. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section11.8: Probabilities Of Disjoint And Overlapping Events
Problem 2C
Related questions
Question
100%
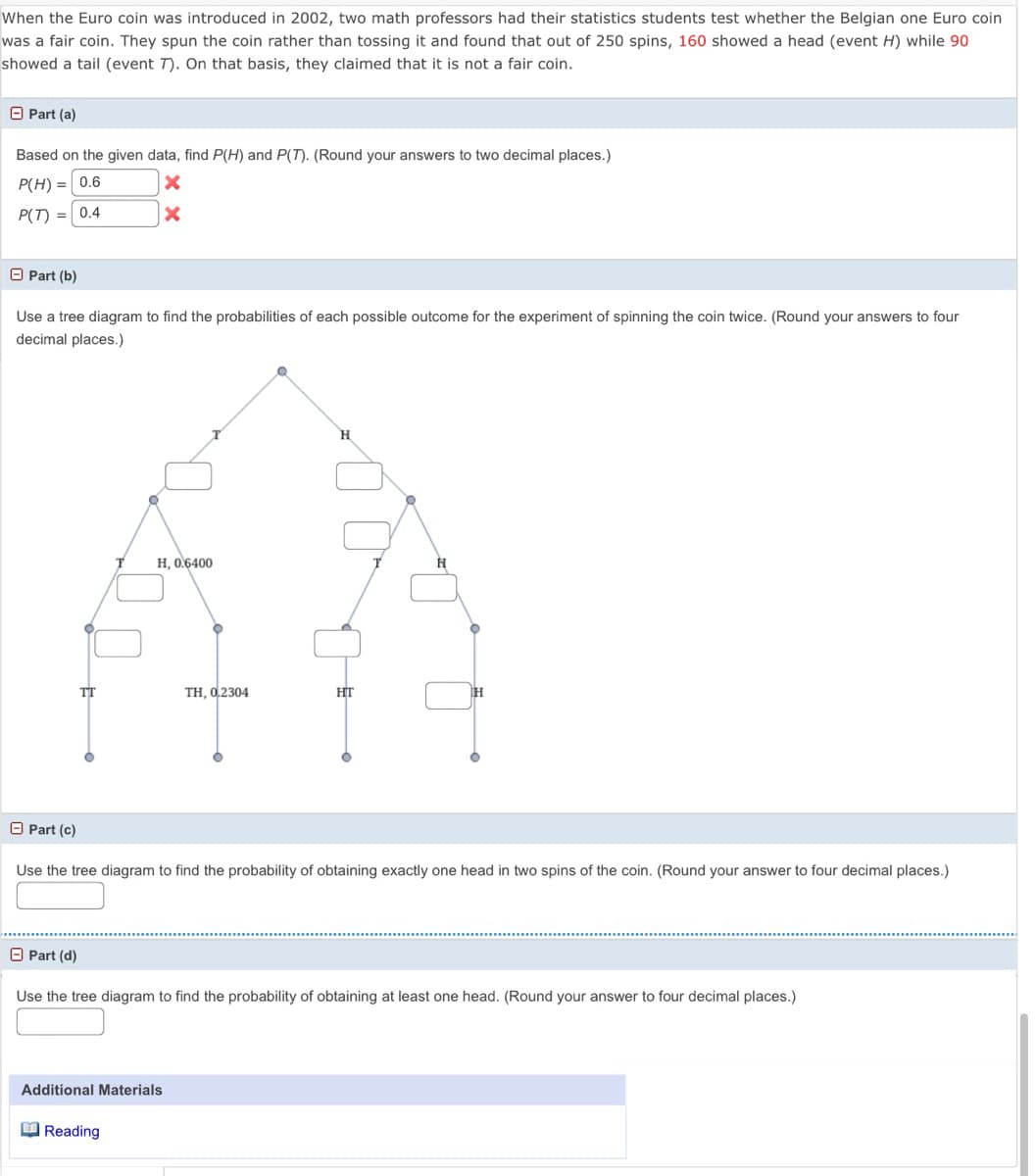
Transcribed Image Text:When the Euro coin was introduced in 2002, two math professors had their statistics students test whether the Belgian one Euro coin
was a fair coin. They spun the coin rather than tossing it and found that out of 250 spins, 160 showed a head (event H) while 90
showed a tail (event T). On that basis, they claimed that it is not a fair coin.
O Part (a)
Based on the given data, find P(H) and P(T). (Round your answers to two decimal places.)
P(H) = 0.6
P(T) = 0.4
O Part (b)
Use a tree diagram to find the probabilities of each possible outcome for the experiment of spinning the coin twice. (Round your answers to four
decimal places.)
H
H, 0.6400
TT
TH, 0,2304
HT
O Part (c)
Use the tree diagram to find the probability of obtaining exactly one head in two spins of the coin. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
O Part (d)
Use the tree diagram to find the probability of obtaining at least one head. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
Additional Materials
O Reading
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning