Which one of the these primary protein structures is most likely to form an alpha helix that would would cross a plasma membrane from the extracellular side to the cytoplasmic side? Use the diagram provided to decode the one letter amino acid abbreviations. Nonpolar side chains H HN*-C CH H,N* H,N -C C. H,C -CH O CH, H,N*- H,N* - -C- C CH CH, CH H,C CH, H,C CH, CH, Glycine (G) Gly Alanine (A) Ala Valine (V) Val Leucine (L) Leu Isoleucine () lle H H. H,N*. CH, CH, H,N* No charged or electro- negative atoms to form hydrogen bonds; not soluble in CH, H,N-c- CH, H,C CH, CH2 NH CH, water Methionine (M) Met Phenylalanine (F) Phe Tryptophan (W) Trp Proline (P) Pro H H Polar side H. chains H HN* -C-C H,N*-C- H,N* -C CH, CH, H,N* -C- H,N* -C- -C, CH2 CH, Partial charges ô*CH, CH2 CH can form но CH, SH C. hydrogen bonds; soluble in water 6 OH H,N OH он H,N Serine (S) Ser Threonine (T) Thr Cysteine (C) Сys Tyrosine (Y) Tyr Asparagine (N) Asn Glutamine (Q) Gin Electrically charged side chains Acidic Basic H H H,N* -C CH H,N* -C H,N* H,N*- CH, CH, CH, Charged side chains form hydrogen bonds; highly soluble in CH, CH, CH2 CH, NH CH, CH, CH, "NH, NH NH water c='NH, NH2 Aspartate (D) Asp Glutamate (E) Glu Lysine (K) Lys Arginine (R) Arg Histidine (H) His O 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. O N-DTNLVLLRAGLLIRHKKE - COOH O N-DTNLRRSIAGLLIRHKKE - COOH O N-DTNLVLLIAGLLIRHKKE - COOH
Which one of the these primary protein structures is most likely to form an alpha helix that would would cross a plasma membrane from the extracellular side to the cytoplasmic side? Use the diagram provided to decode the one letter amino acid abbreviations. Nonpolar side chains H HN*-C CH H,N* H,N -C C. H,C -CH O CH, H,N*- H,N* - -C- C CH CH, CH H,C CH, H,C CH, CH, Glycine (G) Gly Alanine (A) Ala Valine (V) Val Leucine (L) Leu Isoleucine () lle H H. H,N*. CH, CH, H,N* No charged or electro- negative atoms to form hydrogen bonds; not soluble in CH, H,N-c- CH, H,C CH, CH2 NH CH, water Methionine (M) Met Phenylalanine (F) Phe Tryptophan (W) Trp Proline (P) Pro H H Polar side H. chains H HN* -C-C H,N*-C- H,N* -C CH, CH, H,N* -C- H,N* -C- -C, CH2 CH, Partial charges ô*CH, CH2 CH can form но CH, SH C. hydrogen bonds; soluble in water 6 OH H,N OH он H,N Serine (S) Ser Threonine (T) Thr Cysteine (C) Сys Tyrosine (Y) Tyr Asparagine (N) Asn Glutamine (Q) Gin Electrically charged side chains Acidic Basic H H H,N* -C CH H,N* -C H,N* H,N*- CH, CH, CH, Charged side chains form hydrogen bonds; highly soluble in CH, CH, CH2 CH, NH CH, CH, CH, "NH, NH NH water c='NH, NH2 Aspartate (D) Asp Glutamate (E) Glu Lysine (K) Lys Arginine (R) Arg Histidine (H) His O 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. O N-DTNLVLLRAGLLIRHKKE - COOH O N-DTNLRRSIAGLLIRHKKE - COOH O N-DTNLVLLIAGLLIRHKKE - COOH
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Lauralee Sherwood
Chapter2: Cell Physiology
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11RE
Related questions
Question
The selected answer is incorrect
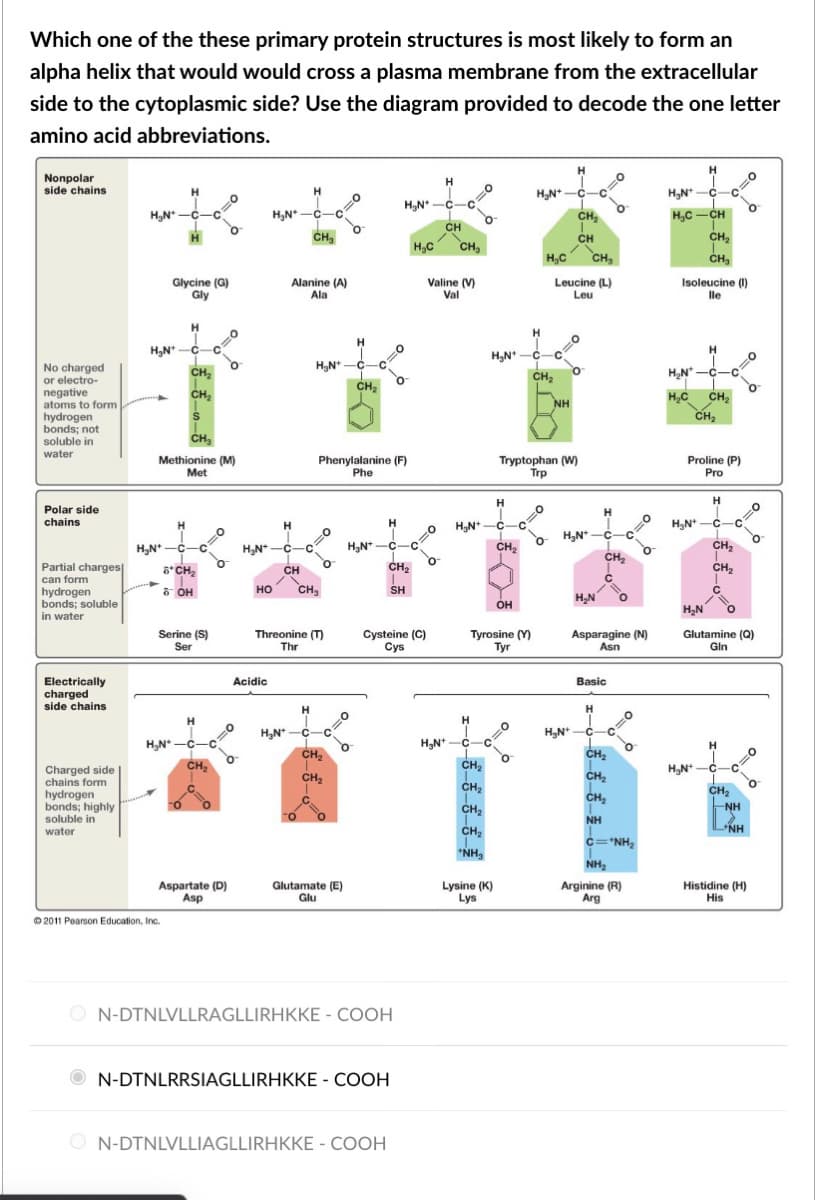
Transcribed Image Text:Which one of the these primary protein structures is most likely to form an
alpha helix that would would cross a plasma membrane from the extracellular
side to the cytoplasmic side? Use the diagram provided to decode the one letter
amino acid abbreviations.
Nonpolar
side chains
H
HN*-C
H,N*
C.
H,C -CH
CH,
H,N*-
H,N* -
-C-
CH,
-
CH
CH,
CH
H,C
CH,
H,C
CH,
CH,
Glycine (G)
Gly
Alanine (A)
Ala
Valine (V)
Val
Leucine (L)
Leu
Isoleucine (I)
lle
H
H.
H,N*
CH.
H,N -C
H,N*
No charged
or electro-
negative
atoms to form
hydrogen
bonds; not
soluble in
CH,
CH,
CH,
H,C CH,
NH
CH2
CH
water
Methionine (M)
Met
Phenylalanine (F)
Phe
Tryptophan (W)
Trp
Proline (P)
Pro
H
H
Polar side
H.
H,N* -C
chains
H
HN*
-C
-C-C
H,N*-C-
H,N* -C
CH2
H,N* -C-
H,N*-C-
CH,
CH2
-C,
CH,
Partial charges
6*CH,
CH2
CH
can form
C.
но
CH
SH
C.
hydrogen
bonds; soluble
in water
6 OH
H,N
OH
H,N
Serine (S)
Ser
Threonine (T)
Thr
Cysteine (C)
Сys
Tyrosine (Y)
Tyr
Asparagine (N)
Asn
Glutamine (Q)
Gin
Electrically
charged
side chains
Acidic
Basic
H
H
H,N* -C
H,N* -C
H,N*
CH.
CH,
CH,
CH,
Charged side
chains form
hydrogen
bonds; highly
soluble in
CH,
CH,
CH
CH,
CH2
NH
CH,
CH,
*NH,
NH
NH
water
c="NH,
NH2
Aspartate (D)
Asp
Glutamate (E)
Glu
Lysine (K)
Lys
Arginine (R)
Arg
Histidine (H)
His
O 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
O N-DTNLVLLRAGLLIRHKKE - COOH
O N-DTNLRRSIAGLLIRHKKE - COOH
O N-DTNLVLLIAGLLIRHKKE - COOH
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781285866932
Author:
Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781285866932
Author:
Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168116
Author:
Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:
OpenStax College