Why can decreasing the probability of a type I error cause an increase in the probability of a type Il error? Choose the correct answer below. O A. Decreasing a decreases the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis. This increases the probability of the complement, not rejecting the null hypothesis, which could increase the probability of failing to reject the null hypothesis when it is false, a type Il error. O B. Decreasing a increases the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis. This decreases the probability of the complement, failing to reject the null hypothesis, which could increase the probability of failing to reject the alternative hypothesis when it is false, a type Il error. OC. Decreasing a increases the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis, which increases the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true, a type II error. O D. Decreasing a decreases the probability of failing to reject the null hypothesis. This increases the probability of the complement, rejecting the null hypothesis, which could increase the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true, a type II error.
Why can decreasing the probability of a type I error cause an increase in the probability of a type Il error? Choose the correct answer below. O A. Decreasing a decreases the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis. This increases the probability of the complement, not rejecting the null hypothesis, which could increase the probability of failing to reject the null hypothesis when it is false, a type Il error. O B. Decreasing a increases the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis. This decreases the probability of the complement, failing to reject the null hypothesis, which could increase the probability of failing to reject the alternative hypothesis when it is false, a type Il error. OC. Decreasing a increases the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis, which increases the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true, a type II error. O D. Decreasing a decreases the probability of failing to reject the null hypothesis. This increases the probability of the complement, rejecting the null hypothesis, which could increase the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true, a type II error.
Chapter9: Sequences, Probability And Counting Theory
Section9.7: Probability
Problem 1SE: What term is used to express the likelihood of an event occurring? Are there restrictions on its...
Related questions
Question
64
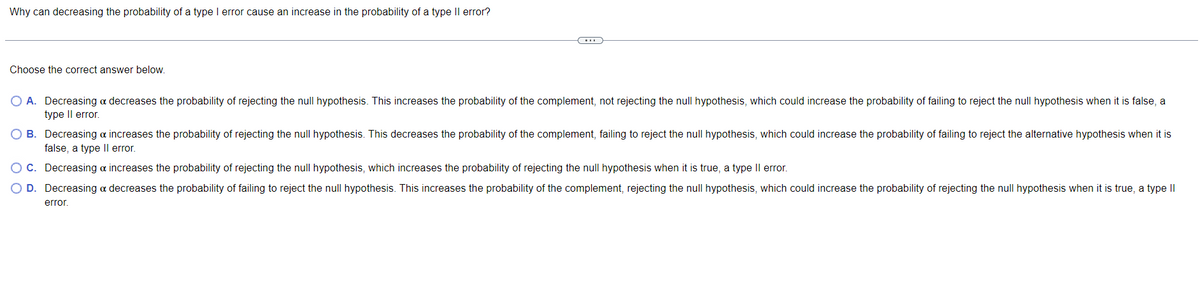
Transcribed Image Text:Why can decreasing the probability of a type I error cause an increase in the probability of a type Il error?
(...)
Choose the correct answer below.
O A. Decreasing a decreases the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis. This increases the probability of the complement, not rejecting the null hypothesis, which could increase the probability of failing to reject the null hypothesis when it is false, a
type II error.
B. Decreasing a increases the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis. This decreases the probability of the complement, failing to reject the null hypothesis, which could increase the probability of failing to reject the alternative hypothesis when it is
false, a type II error.
Decreasing & increases the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis, which increases the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true, a type II error.
C.
O D.
Decreasing a decreases the probability of failing to reject the null hypothesis. This increases the probability of the complement, rejecting the null hypothesis, which could increase the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true, a type II
error.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

