xy 1 2 -w+z 2y - w³. z w³+ z³ - 2zw = 0 = 0 = 0
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter4: Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors
Section4.6: Applications And The Perron-frobenius Theorem
Problem 69EQ: Let x=x(t) be a twice-differentiable function and consider the second order differential equation...
Related questions
Question
help me please
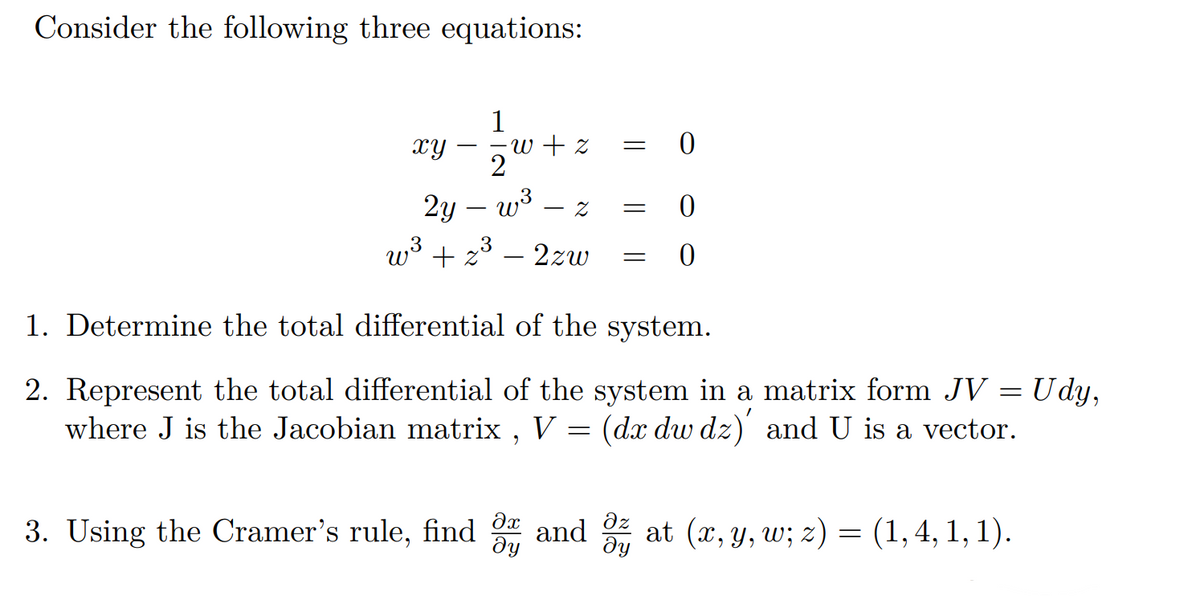
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following three equations:
1
xy
∙w + z
= 0
2
2y — w³
Z
=
0
w³ + z³ – 2zw
=
0
1. Determine the total differential of the system.
2. Represent the total differential of the system in a matrix form JV = Udy,
where J is the Jacobian matrix, V = (dx dw dz)' and U is a vector.
3. Using the Cramer's rule, find 3 and ² at (x, y, w; z) = (1,4, 1, 1).
дz
ду
ду
-
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning