You are on the roof of a Physics Building, 19 m above the ground. Your physics professor, who is 1.87 m tall, is approaching the building at constant speed of 2.28 m/s. If you wish to drop an egg on his head, how far should your professor be when you release the egg?
You are on the roof of a Physics Building, 19 m above the ground. Your physics professor, who is 1.87 m tall, is approaching the building at constant speed of 2.28 m/s. If you wish to drop an egg on his head, how far should your professor be when you release the egg?
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter1: Units, Trigonometry. And Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1CQ: Estimate the order of magnitude of the length, in meters, of each of the following; (a) a mouse, (b)...
Related questions
Question
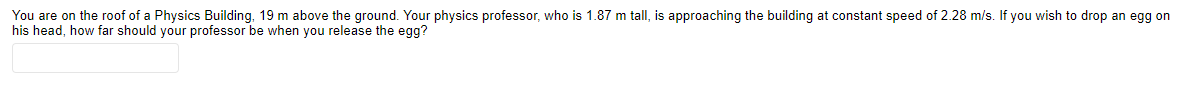
Transcribed Image Text:You are on the roof of a Physics Building, 19 m above the ground. Your physics professor, who is 1.87 m tall, is approaching the building at constant speed of 2.28 m/s. If you wish to drop an egg on
his head, how far should your professor be when you release the egg?
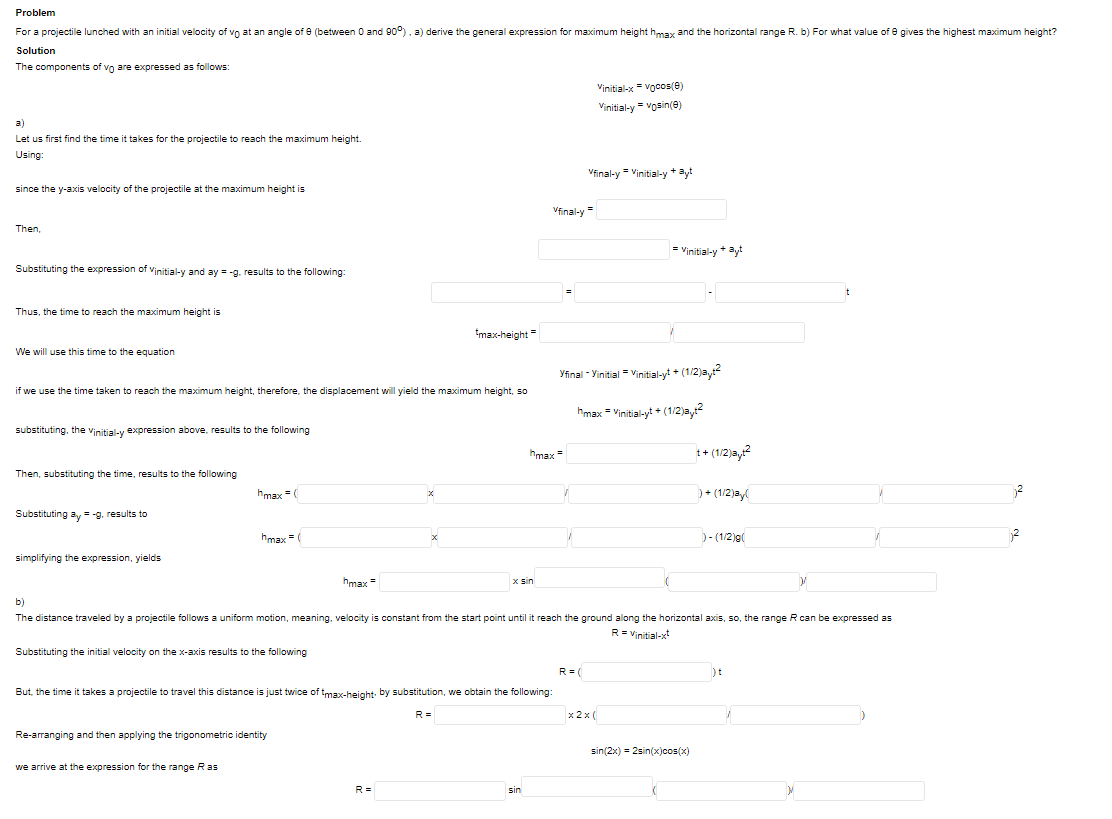
Transcribed Image Text:Problem
For a projectile lunched with an initial velocity of vo at an angle of e (between O and 90°). a) derive the general expression for maximum height hmax and the horizontal range R. b) For what value of e gives the highest maximum height?
Solution
The components of vo are expressed as follows:
Vinitial-x = vocos(e)
Vinitial-y= Vosin(e)
a)
Let us first find the time it takes for the projectile to reach the maximum height.
Using:
Vfinal-y = Vinitial-y + ayt
since the y-axis velocity of the projectile at the maximum height is
Vfinal-y=
Then,
= Vinitial-y * ayt
Substituting the expression of Vinitial-y and ay = -g. results to the following:
Thus, the time to reach the maximum height is
tmax-height =
We will use this time to the equation
Yfinal - Yinitial = Vinitial-yt + (1/2)a,
if we use the time taken to reach the maximum height, therefore, the displacement will yield the maximum height, so
hmax = Vinitial-yt + (1/2)ay?
substituting, the vinitial-y expression above, results to the following
hmax =
1+ (1/2)a,?
Then, substituting the time, results to the following
hmax
)+ (12)ay(
= (
Substituting ay = -g, results to
hmax =
)- (1/2)g(
simplifying the expression, yields
hmax=
X sin
b)
The distance traveled by a projectile follows a uniform motion, meaning, velocity is constant from the start point until it reach the ground along the horizontal axis, so, the range R can be expressed as
R= Viritial-x
Substituting the initial velocity on the x-axis results to the following
R= (
)t
But, the time it takes a projectile to travel this distance is just twice of tmax-height by substitution, we obtain the following:
R =
x 2x(
Re-arranging and then applying the trigonometric identity
sin(2x) = 2sin(x)cos(x)
we arrive at the expression for the range Ras
R =
sin
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:
9780133969290
Author:
Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:
9781107189638
Author:
Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:
Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:
9780321820464
Author:
Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:
Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio…
Physics
ISBN:
9780134609034
Author:
Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:
PEARSON