You are working for a big engineering company. The company has a project on building a channel, and you are a junior engineer in that project. The designed channel has a rectangular cross-section (B=20m and H=10m as shown in the Figure 1) and carries water from a hill to a valley which produces a flow rate of 5 m/sec of rainwater. The steady-state flow rate equation is given by 0.48(20h)5/3 (20+2h)²/3 V(t)= a) Use the bisection method of finding roots of equations to find the height of the water in the channel in order to get a flow rate of 5 m/sec. b) Use the secant method of finding roots of equations to find the height of the water in the channel in order to get a flow rate of 5 m³/sec. c) What is your observation on both methods ** The calculation is in 2 decimal point and given e=0.1 H=10 m h B =20 m
You are working for a big engineering company. The company has a project on building a channel, and you are a junior engineer in that project. The designed channel has a rectangular cross-section (B=20m and H=10m as shown in the Figure 1) and carries water from a hill to a valley which produces a flow rate of 5 m/sec of rainwater. The steady-state flow rate equation is given by 0.48(20h)5/3 (20+2h)²/3 V(t)= a) Use the bisection method of finding roots of equations to find the height of the water in the channel in order to get a flow rate of 5 m/sec. b) Use the secant method of finding roots of equations to find the height of the water in the channel in order to get a flow rate of 5 m³/sec. c) What is your observation on both methods ** The calculation is in 2 decimal point and given e=0.1 H=10 m h B =20 m
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
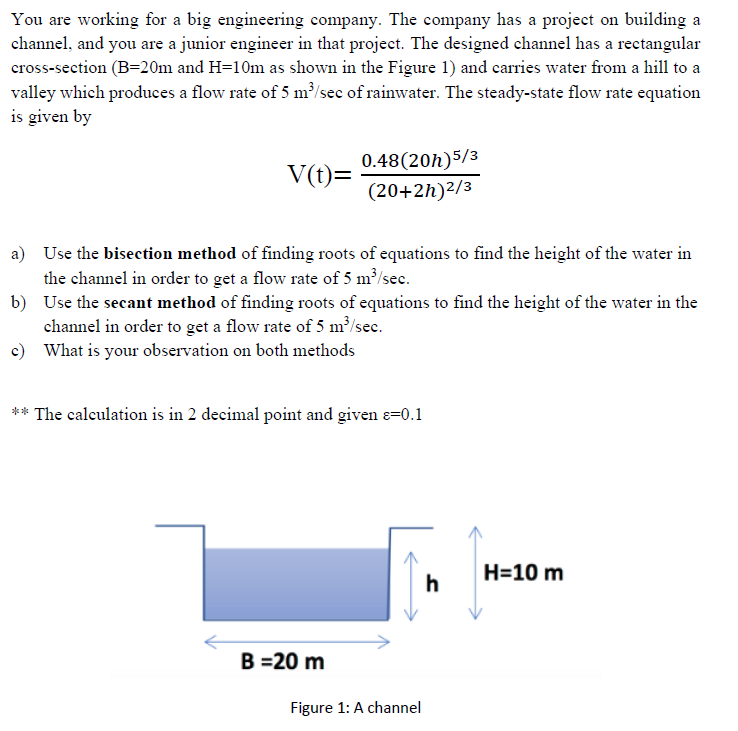
Transcribed Image Text:You are working for a big engineering company. The company has a project on building a
channel, and you are a junior engineer in that project. The designed channel has a rectangular
cross-section (B=20m and H=10m as shown in the Figure 1) and carries water from a hill to a
valley which produces a flow rate of 5 m³/sec of rainwater. The steady-state flow rate equation
is given by
0.48(20h)5/3
V(t)=
(20+2h)²/3
a) Use the bisection method of finding roots of equations to find the height of the water in
the channel in order to get a flow rate of 5 m³/sec.
b) Use the secant method of finding roots of equations to find the height of the water in the
channel in order to get a flow rate of 5 m³/sec.
c) What is your observation on both methods
** The calculation is in 2 decimal point and given e=0.1
H=10 m
h
B =20 m
Figure 1: A channel
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780073398006
Author:
Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning