You have been asked to determine if two different production processes have different mean numbers of units produced per hour. Process 1 has a mean defined as μ₁ and process 2 has a mean defined as μ2. The null and alternative hypotheses are H₂: μ₁ −μ₂ ≤0 and H₁: ₁-₂ > 0. The process variances are unknown but assumed to be equal. Using random samples of 36 observations from process 1 and 49 observations from process 2, the sample means are 60 and 50 for populations 1 and 2 respectively. Complete parts a through d below. Click the icon to view a table of critical values for the Student's t-distribution. a. Can you reject the null hypothesis, using a probability of Type I error x = 0.05, if the sample standard deviation from process 1 is 28 and from process 2 is 23? The test statistic is t=. (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
You have been asked to determine if two different production processes have different mean numbers of units produced per hour. Process 1 has a mean defined as μ₁ and process 2 has a mean defined as μ2. The null and alternative hypotheses are H₂: μ₁ −μ₂ ≤0 and H₁: ₁-₂ > 0. The process variances are unknown but assumed to be equal. Using random samples of 36 observations from process 1 and 49 observations from process 2, the sample means are 60 and 50 for populations 1 and 2 respectively. Complete parts a through d below. Click the icon to view a table of critical values for the Student's t-distribution. a. Can you reject the null hypothesis, using a probability of Type I error x = 0.05, if the sample standard deviation from process 1 is 28 and from process 2 is 23? The test statistic is t=. (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Calculus For The Life Sciences
2nd Edition
ISBN:9780321964038
Author:GREENWELL, Raymond N., RITCHEY, Nathan P., Lial, Margaret L.
Publisher:GREENWELL, Raymond N., RITCHEY, Nathan P., Lial, Margaret L.
Chapter1: Functions
Section1.2: The Least Square Line
Problem 5E
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:You have been asked to determine if two different production processes have different mean numbers of units produced per hour.
Process 1 has a mean defined as µ₁ and process 2 has a mean defined as µ2. The null and alternative hypotheses are Hỏ: µ₁ −µ₂ ≤0
and H₁: ₁-₂ > 0. The process variances are unknown but assumed to be equal. Using random samples of 36 observations from
process 1 and 49 observations from process 2, the sample means are 60 and 50 for populations 1 and 2 respectively. Complete parts a
through d below.
Click the icon to view a table of critical values for the Student's t-distribution.
a. Can you reject the null hypothesis, using a probability of Type I error x = 0.05, if the sample standard deviation from process 1 is 28
and from process 2 is 23?
The test statistic is t =
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:You have been asked to determine if two different production processes have different mean numbers of units produced per hour. Process 1 has a mean
defined as μ₁ and process 2 has a mean defined as µ₂. The null and alternative hypotheses are H₂: μ₁ −μ₂ ≤0 and H₁ : µ₁ − µ₂ > 0. The process variances
are unknown but assumed to be equal. Using random samples of 36 observations from process 1 and 49 observations from process 2, the sample means are
60 and 50 for populations 1 and 2 respectively. Complete parts a through d below.
Click the icon to view a table of critical values for the Student's t-distribution.
THIV IVVI VIMUVUV IVA
Since the test statistic is
IV
The test statistic is t =
MITM IV
ܝ
The critical value(s) is(are) 1.663.
(Round to three decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
greater than t + ny – 2,0 ²
reject Ho.
c. Can you reject the null hypothesis, using a probability of Type I error x = 0.05, if the sample standard deviation from process 1 is 32 and from process 2 is
34?
SEVILTIMI provv/
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Solution
Follow-up Question
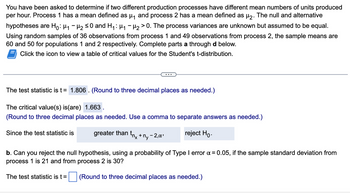
Transcribed Image Text:You have been asked to determine if two different production processes have different mean numbers of units produced
per hour. Process 1 has a mean defined as µ₁ and process 2 has a mean defined as µ₂. The null and alternative
hypotheses are Ho: H₁ H₂ ≤0 and H₁: μ₁ −μ₂ > 0. The process variances are unknown but assumed to be equal.
Using random samples of 36 observations from process 1 and 49 observations from process 2, the sample means are
60 and 50 for populations 1 and 2 respectively. Complete parts a through d below.
Click the icon to view a table of critical values for the Student's t-distribution.
The test statistic is t = 1.806. (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
The critical value(s) is(are) 1.663.
(Round to three decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)
reject Ho.
Since the test statistic is
greater than
The test statistic is t =
tnx + My-
-2,α¹
b. Can you reject the null hypothesis, using a probability of Type I error x = 0.05, if the sample standard deviation from
process 1 is 21 and from process 2 is 30?
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Solution
Recommended textbooks for you

Calculus For The Life Sciences
Calculus
ISBN:
9780321964038
Author:
GREENWELL, Raymond N., RITCHEY, Nathan P., Lial, Margaret L.
Publisher:
Pearson Addison Wesley,

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Calculus For The Life Sciences
Calculus
ISBN:
9780321964038
Author:
GREENWELL, Raymond N., RITCHEY, Nathan P., Lial, Margaret L.
Publisher:
Pearson Addison Wesley,

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill