Consider an equilateral triangle Po whose sides have length 1. For each nonnegative integer obtain a polygon Pn+1 from Pn by applying the following steps to each line segment in P. 1. divide the line segment into three segments of equal length. 2. draw an equilateral triangle that has the middle segment from step 1 as its base and po outward. 3. remove the line segment that is the base of the triangle from step 2. See the figure below. As n → o the polygons Po, P1, P2, ... approach the fractal curve shown in the figure belov (d) Show that L, → ∞ as n → o. (e) Find the number of new triangles needed to form P, from Pn-1- (f) Find the area of each new triangle needed to form P, from Pn-1
Consider an equilateral triangle Po whose sides have length 1. For each nonnegative integer obtain a polygon Pn+1 from Pn by applying the following steps to each line segment in P. 1. divide the line segment into three segments of equal length. 2. draw an equilateral triangle that has the middle segment from step 1 as its base and po outward. 3. remove the line segment that is the base of the triangle from step 2. See the figure below. As n → o the polygons Po, P1, P2, ... approach the fractal curve shown in the figure belov (d) Show that L, → ∞ as n → o. (e) Find the number of new triangles needed to form P, from Pn-1- (f) Find the area of each new triangle needed to form P, from Pn-1
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Chapter2: Parallel Lines
Section2.5: Convex Polygons
Problem 41E
Related questions
Question
100%
Sequences and Series - parts d-f
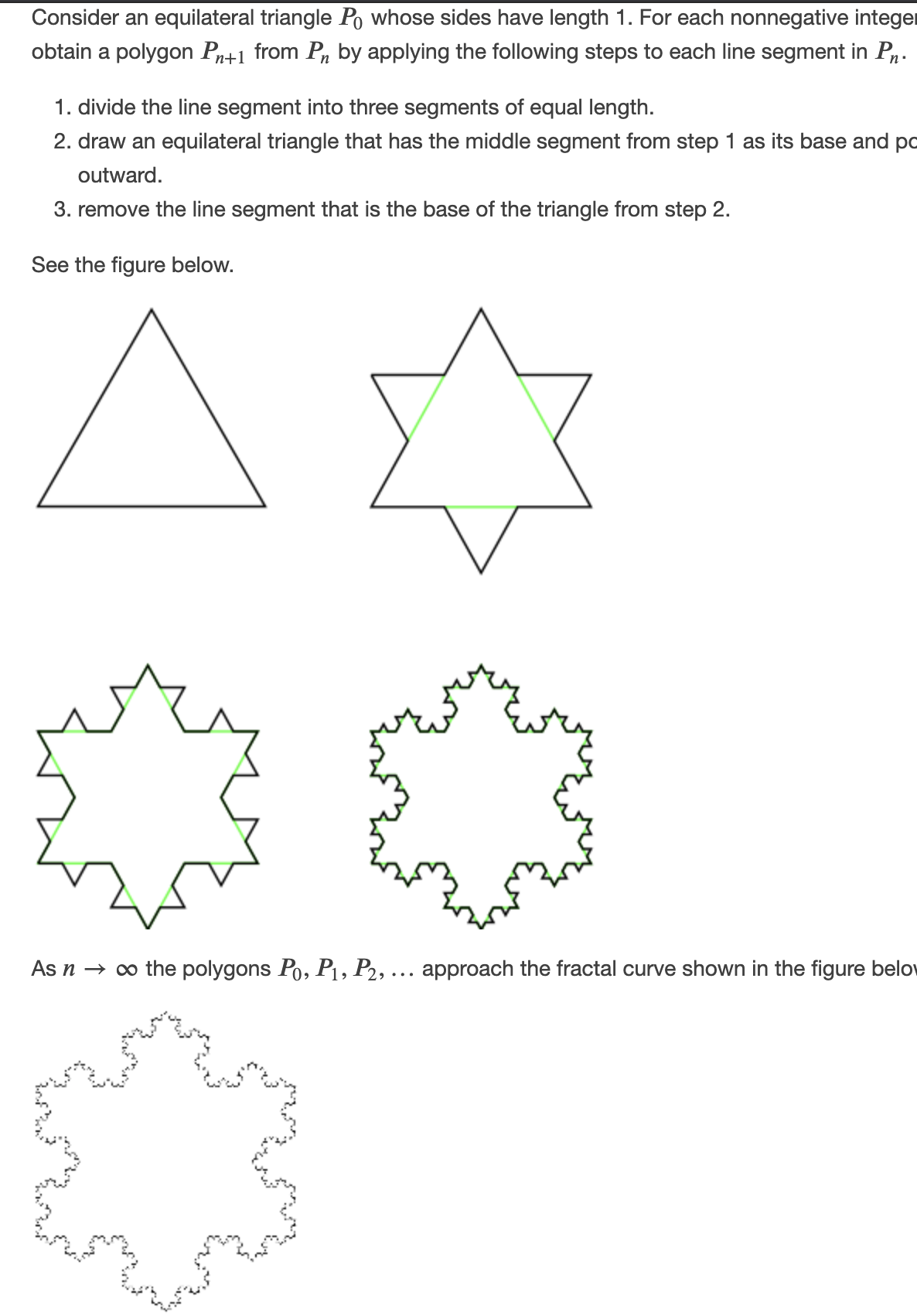
Transcribed Image Text:Consider an equilateral triangle Po whose sides have length 1. For each nonnegative integer
obtain a polygon Pn+1 from Pn by applying the following steps to each line segment in P.
1. divide the line segment into three segments of equal length.
2. draw an equilateral triangle that has the middle segment from step 1 as its base and po
outward.
3. remove the line segment that is the base of the triangle from step 2.
See the figure below.
As n → o the polygons Po, P1, P2, ... approach the fractal curve shown in the figure belov

Transcribed Image Text:(d) Show that L, → ∞ as n → o.
(e) Find the number of new triangles needed to form P, from Pn-1-
(f) Find the area of each new triangle needed to form P, from Pn-1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,