. Fiscal and Monetary policy actions in the short run. Take an example 2. Changes in the AD-AS model and the Phillips curve. Take an example 3. Velocity of money rather than quantity driving prices. Take an example.
1. Fiscal and
2. Changes in the AD-AS model and the Phillips curve. Take an example
3. Velocity of money rather than quantity driving prices. Take an example.
The government can use expansionary or contractionary fiscal policy to change aggregate demand. Expansionary fiscal policy will increase the aggregate demand in the country while contractionary fiscal policy will decrease the aggregate demand in the country, an example of such when the government increases taxes in the country it decreases aggregate demand, decreases in aggregate demand causes a decrease in GDP.
The government can use expansionary or contractionary monetary policy, for example, suppose the central bank of a country purchases bonds, it will increase the money supply in the country that will cause the interest rate to fall and fall in the interest rate will result in an increase in demand.
Philips curve shows the inverse relationship between the unemployment rate and the inflation rate in the short run. In the long-run Philips, the curve becomes vertical and equal to the natural rate of unemployment.
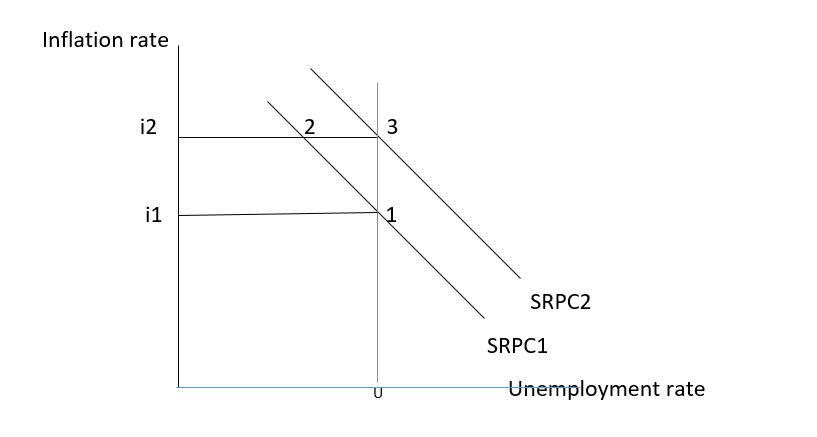
In the above diagram suppose that economy is at point 1 where the unemployment rate is U and the inflation rate is i1. At point 2 unemployment rate while inflation rate rises to i2, Movement along the SRPC (point 1 to point2) indicates aggregate demand has changed and shift of SRPC from point 2 to point 3 indicates a change in aggregate supply.
- An increase in aggregate demand causes inflation Point 1 to point B.
- An increase in aggregate demand prompt firms to produce more thus unemployment rate changes. Movement from point 2 to 3.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images









