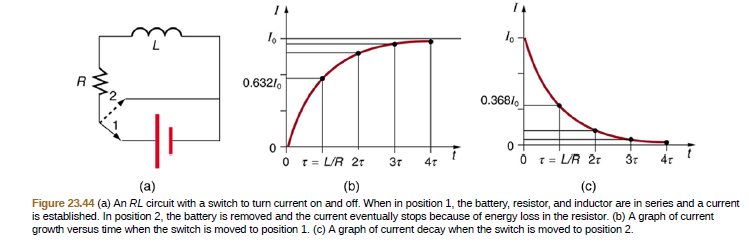
0.6321. 0.368/, O 1= LUR 21 (c) 3r O r= LIR 21 (b) 3т 47 4r (a) Figure 23.44 (a) An RL circuit with a switch to turn current on and off. When in position 1, the battery, resistor, and inductor are in series and a current is established. In position 2, the battery is removed and the current eventually stops because of energy loss in the resistor. (b) A graph of current growth versus time when the switch is moved to position 1. (c) A graph of current decay when the switch is moved to position 2.
0.6321. 0.368/, O 1= LUR 21 (c) 3r O r= LIR 21 (b) 3т 47 4r (a) Figure 23.44 (a) An RL circuit with a switch to turn current on and off. When in position 1, the battery, resistor, and inductor are in series and a current is established. In position 2, the battery is removed and the current eventually stops because of energy loss in the resistor. (b) A graph of current growth versus time when the switch is moved to position 1. (c) A graph of current decay when the switch is moved to position 2.
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter33: Inductors And Ac Circuits
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 69PQ
Related questions
Question
The 5.00 A current through a 1.50 H inductor is dissipated by a 2.00 Ω resistor in a circuit like that as shown with the switch in position 2. (a) What is the initial energy in the inductor? (b) How long will it take the current to decline to 5.00% of its initial value? (c) Calculate the average power
dissipated, and compare it with the initial power dissipated by the resistor.
Transcribed Image Text:0.6321.
0.368/,
O 1= LUR 21
(c)
3r
O r= LIR 21
(b)
3т
47
4r
(a)
Figure 23.44 (a) An RL circuit with a switch to turn current on and off. When in position 1, the battery, resistor, and inductor are in series and a current
is established. In position 2, the battery is removed and the current eventually stops because of energy loss in the resistor. (b) A graph of current
growth versus time when the switch is moved to position 1. (c) A graph of current decay when the switch is moved to position 2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning