1 a) The hot combustion gases of a furnace are separated from the ambient air and its surroundings, which are at 25°C, by a brick wall 0.15 m thick (Figure la). The brick has a thermal conductivity of 1.2 W/m K and a surface emissivity of 0.8. Under steady-state conditions an outer surface temperature of 100°C is measured. Free convection heat transfer to the air adjoining the surface is characterized by a convection coefficient ofh = 20 W/m².K. What is the brick inner surface temperature? b) Consider steady-state conditions for one-dimensional conduction in a plane wall having a thermal conductivity k = 50 W/mk and a thickness L = 0.25 m, with no internal heat generation. Determine i) the heat flux and the unknown quantity for each case; and ii) sketch the temperature distribution, indicating the direction of the heat flux. Case T:(°C) T2(°C) dT/dx (K/m) ġ(W/m²) 1 50 -20 70 160 3 40 -80
1 a) The hot combustion gases of a furnace are separated from the ambient air and its surroundings, which are at 25°C, by a brick wall 0.15 m thick (Figure la). The brick has a thermal conductivity of 1.2 W/m K and a surface emissivity of 0.8. Under steady-state conditions an outer surface temperature of 100°C is measured. Free convection heat transfer to the air adjoining the surface is characterized by a convection coefficient ofh = 20 W/m².K. What is the brick inner surface temperature? b) Consider steady-state conditions for one-dimensional conduction in a plane wall having a thermal conductivity k = 50 W/mk and a thickness L = 0.25 m, with no internal heat generation. Determine i) the heat flux and the unknown quantity for each case; and ii) sketch the temperature distribution, indicating the direction of the heat flux. Case T:(°C) T2(°C) dT/dx (K/m) ġ(W/m²) 1 50 -20 70 160 3 40 -80
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter1: Basic Modes Of Heat Transfer
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.57P
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:1 a) The hot combustion gases of a furnace are separated from the ambient air and its
surroundings, which are at 25°C, by a brick wall 0.15 m thick (Figure la). The brick
has a thermal conductivity of 1.2 W/m K and a surface emissivity of 0.8. Under
steady-state conditions an outer surface temperature of 100°C is measured. Free
convection heat transfer to the air adjoining the surface is characterized by a
convection coefficient ofh = 20 W/m².K. What is the brick inner surface
temperature?
b) Consider steady-state conditions for one-dimensional conduction in a plane wall
having a thermal conductivity k = 50 W/mk and a thickness L = 0.25 m, with no
internal heat generation. Determine
i) the heat flux and the unknown quantity for each case; and
ii) sketch the temperature distribution, indicating the direction of the heat flux.
Case
T:(°C)
T2(°C)
dT/dx (K/m)
ġ(W/m²)
1
50
-20
70
160
3
40
-80
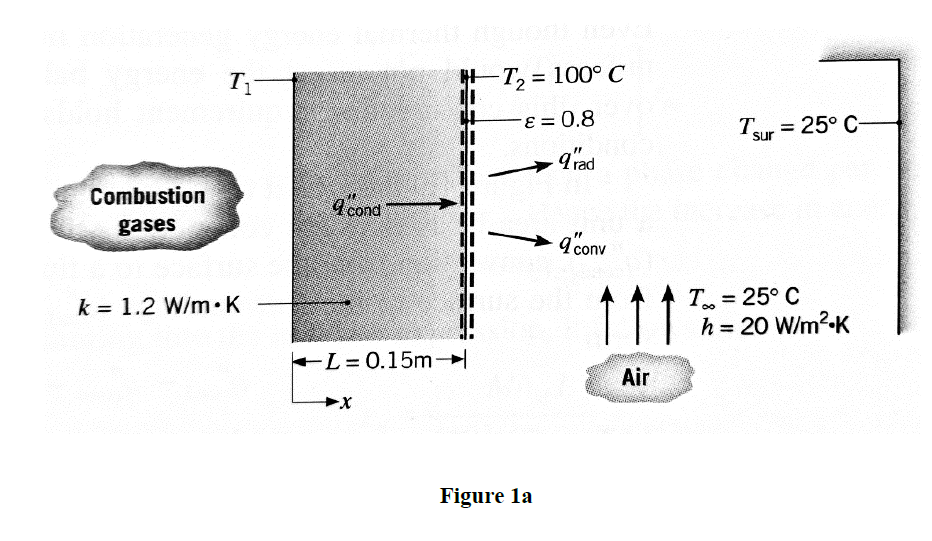
Transcribed Image Text:T1
T, = 100°C
T.
= 25° C-
sur
qad
Combustion
9 cond
gases
9'conv
T = 25° C
h = 20 W/m2-K
k = 1.2 W/m K
L = 0.15m
Air
Figure la
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning