1) Proteins undergo a process called thermal denaturation. This is a process where the protein unfolds (denaturates) as the temperature is increased. (This has important practical consequences for protein based pharmaceuticals). Later this semester we will see that proteins can also denaturate if they are cooled too much. For now we will consider heat denaturation: Protein (folded) → Protein(unfolded) . For a certain protein Adenaturation H is 418.0 k.J mol¬! and Adenaturation S = 1.30 k.J K-1 mol-1. Assume that these values of Adenaturation H and Adenaturation S are independent of temperature (this is actually a bad assumption in real life). A) Calculate AdenaturationG at 310 K. Do you expect the thermal denaturation of the protein to be spontaneous? B) Does the entropy change favor the folded state or the unfolded state at 310 K? C) At what temperature is AdenaturationG zero? We usually call this temperature the “melting temperature" of the protein.
1) Proteins undergo a process called thermal denaturation. This is a process where the protein unfolds (denaturates) as the temperature is increased. (This has important practical consequences for protein based pharmaceuticals). Later this semester we will see that proteins can also denaturate if they are cooled too much. For now we will consider heat denaturation: Protein (folded) → Protein(unfolded) . For a certain protein Adenaturation H is 418.0 k.J mol¬! and Adenaturation S = 1.30 k.J K-1 mol-1. Assume that these values of Adenaturation H and Adenaturation S are independent of temperature (this is actually a bad assumption in real life). A) Calculate AdenaturationG at 310 K. Do you expect the thermal denaturation of the protein to be spontaneous? B) Does the entropy change favor the folded state or the unfolded state at 310 K? C) At what temperature is AdenaturationG zero? We usually call this temperature the “melting temperature" of the protein.
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Chapter11: States Of Matter; Liquids And Solids
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11.145QP
Related questions
Question
NOT a graded assignment. From my understanding it is just (Delta G) = (Delta H) - (T)(Delta S) for part A. I am confused about the "unfolding" part and the last part.
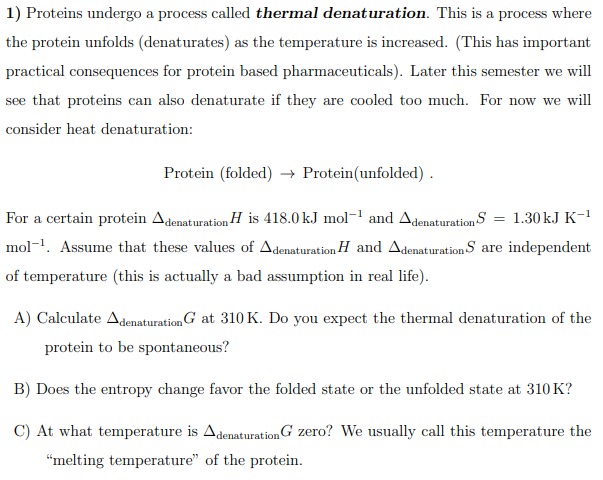
Transcribed Image Text:1) Proteins undergo a process called thermal denaturation. This is a process where
the protein unfolds (denaturates) as the temperature is increased. (This has important
practical consequences for protein based pharmaceuticals). Later this semester we will
see that proteins can also denaturate if they are cooled too much. For now we will
consider heat denaturation:
Protein (folded) → Protein(unfolded) .
For a certain protein Adenaturation H is 418.0 kJ mol-' and Adenaturation S = 1.30kJ K-1
mol-1. Assume that these values of Adenaturation H and Adenaturation S are independent
of temperature (this is actually a bad assumption in real life).
A) Calculate AdenaturationG at 310 K. Do you expect the thermal denaturation of the
protein to be spontaneous?
B) Does the entropy change favor the folded state or the unfolded state at 310 K?
C) At what temperature is AdenaturationG zero? We usually call this temperature the
"melting temperature" of the protein.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax