Biology (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Chapter10: Chromosomes, Mitosis, And Meiosis
Section10.2: The Cell Cycle And Mitosis
Problem 5LO
Related questions
Question
Can you please help me solve all these questions? Please please?
Transcribed Image Text:E Select
Font
Paragraph
Styles
Editing
Voice
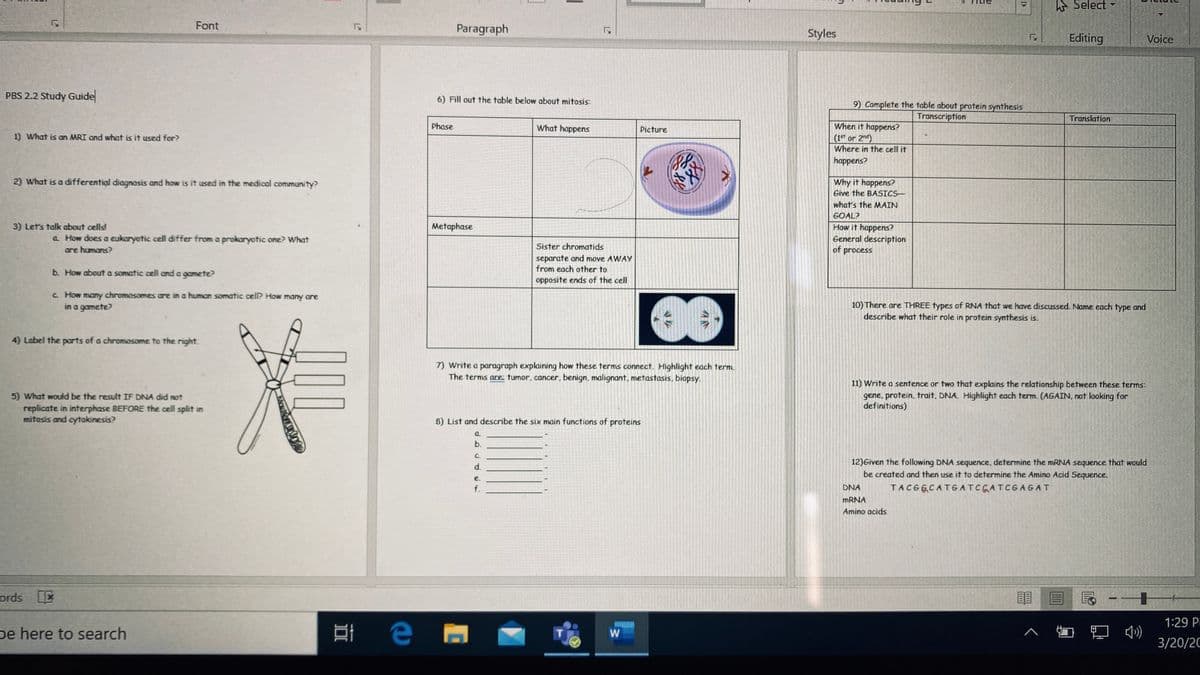
PBS 2.2 Study Guide
6) Fill out the table below about mitosis:
9) Complete the table about protein synthesis
Transcription
Translation
When it happens?
(1" or 2nd)
Where in the cell it
Phase
What happens
Picture
1) What is
MRI and what is it used for?
happeris?
2) What is a differential diagnosis and how is it used in the medical community?
Why it happens?
Give the BASICS-
what's the MAIN
GOAL?
How it happens?
General description
of process
3) Let's talk about cells!
Metaphase
a How does a eukaryotic cell differ from a prokaryotic one? What
Sister chromatids
are humans?
separate and move AWAY
from each other to
b. How about a somatic cell and a gamete?
opposite ends of the cell
C How many chromosomes are in a human somatic cell? How many are
in a gamete?
10) There are THREE types of RNA that we have discussed. Name each type and
describe what their role in protein synthesis is.
4) Label the parts of a chromosome to the right.
7) Write a paragraph explaining how these terms connect. Highlight each term.
The terms are tumor, cancer. benign, malignant, metastasis, biopsy.
5) What would be the result IF DNA did not
replicate in interphase BEFORE the cell split in
mitosis and cytokinesis?
11) Write a sentence or two that explains the relationship between these terms:
gene, protein, trait, DNA. Highlight each term. (AGAIN, not laoking for
definitions)
8) List and describe the six main functions of proteins
b.
C.
12)Given the following DNA sequence, determine the MRNA sequence that would
be created and then use it to determine the Amino Acid Sequence.
d.
e.
f.
DNA
TACGECATGATCGATCGAGAT
MRNA
Amino acids
ords
E
目
1:29 P
pe here to search
W
3/20/20
Transcribed Image Text:rd
Font
Paragraph
Styles
Editing
Voice
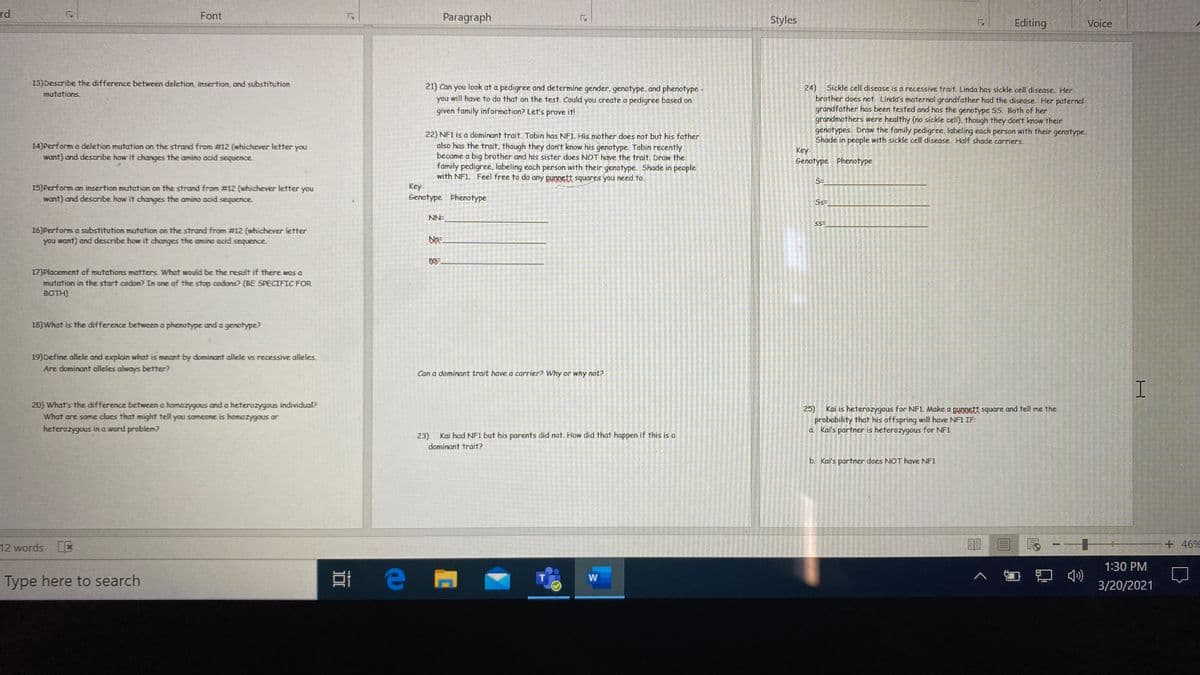
13)Describe the difference between deletion, insertion, and substitution
21) Can you look at a pedigree and determine gender, genotype, and phenotype -
you will have to do that on the test. Could you create a pedigree based on
24)
Sickle cell disease is a recessive trait. Linda has sickle cell disease. Her
brother does not. Linda's maternal grandfather had the disease. Her paternal
grandfather has been tested and has the genotype 55. Both of her
grandmothers were healthy (no sickle cell). though they don't know their
genotypes. Draw the family pedigree, labeling each person with their genotype.
Shade in people with sickle cell disease. Half shade carriers.
Key
Genotype Phenotype
mutations
given family information? Let's prove it!
22) NF1 is a dominant trait. Tobin has NF1. His mother does not but his father
also has the trait, though they don't know his genotype. Tobin recently
became a big brother and his sister does NOT have the trait. Draw the
family pedigree., labeling each person with their genotype. Shade in people
with NF1 Feel free to do any pungett squares you need to.
14)Perform a deletion mutation on the strand from #12 (whichever letter you
want) and describe how it changes the amino acid sequence.
5=
15) Perform an insertion mutation on the strand from #12 (whichever letter you
want) and describe how it changes the amino acid sequence.
Key:
Genotype Phenotype
Ss=
NN=
16)Perform a substitution mutation on the strand from #12 (whichever letter
you want) and describe how it changes the amino acid sequence.
17)Placement of mutations matters. What would be the result if there was a
mutation in the start codon? In one of the stop codons? (BE SPECIFIC FOR
BOTH)
18)What is the difference between a phenotype and a genotype?
19) Define allele and explain what is meant by dominant allele vs recessive alleles.
Are dominant alleles always better?
Can a dominant trait have a carrier? Why or why not?
20) What's the difference between a homozygous and a heterozygous individual?
What are some clues that might tell you sameone is homozygous or
Kai is heterozygous for NF1 Make a pungett square and tell me the
probability that his offspring will have NF1 IF:
a Kai's partner is heterozygous for NF1
25)
heterozygous in a word problem?
23)
Kai had NF1 but his parents did not. How did that happen if this is a
dominant trait?
b. Kai's partmer does NOT have NF1
12 words L*
+ 46%
1:30 PM
Type here to search
3/20/2021
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781337392938
Author:
Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305112100
Author:
Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781337392938
Author:
Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305112100
Author:
Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
