1. A sanding block is being pushed up a vertical wall by a force F that is being applied at an angle of ? = 33.0° to the vertical as shown in the diagram. The block is moving up the wall at a constant speed. The mass of the block is 0.523 kg and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the wall is 0.937. Calculate the magnitude of the force F. To receive full marks, you must include a diagram showing the physical situation and your choice of coordinate system.
1. A sanding block is being pushed up a vertical wall by a force F that is being applied at an angle of ? = 33.0° to the vertical as shown in the diagram. The block is moving up the wall at a constant speed. The mass of the block is 0.523 kg and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the wall is 0.937. Calculate the magnitude of the force F. To receive full marks, you must include a diagram showing the physical situation and your choice of coordinate system.
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Chapter5: Displacement And Force In Two Dimensions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 72A
Related questions
Question
1. A sanding block is being pushed up a vertical wall by a force F that is being applied at an angle of ? = 33.0° to the vertical as shown in the diagram. The block is moving up the wall at a constant speed. The mass of the block is 0.523 kg and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the wall is 0.937. Calculate the magnitude of the force F. To receive full marks, you must include a diagram showing the physical situation and your choice of coordinate system.
2. A 46.7-kg person, initially at rest, throws a 0.143-kg snowball forward with a horizontal speed of 33.5 m/s. A second person, with a mass of 47.5 kg, catches the snowball. Both people are on skates. The first person is initially at rest, as mentioned, and the second person is initially moving with a speed of 1.45 m/s toward the first person. Disregard air resistance and the friction between the skates and the ice. Take the direction in which the snowball is thrown to be the positive direction. Indicate the directions of the final velocities with the signs of your answers. To receive full marks, you must include a diagram showing the physical situation.
(a) Calculate the velocity of the first person immediately after they throw the snowball.
(b) Calculate the velocity of the second person immediately after they catch the snowball.
(a) thrower (first person) m/s (Give your answer to at least three decimal places.)(b) catcher (second person) m/s (Give your answer to at least three decimal places.)
3. A tire is tied to a rope that is tied to the branch of a tree so that the tire swings in a circular trajectory of radius h1 = 15.31 m. A child takes the tire to the top of a platform that is a height h2 = 12.60 m above the ground, sits in the tire, and swings from rest from the platform. The combined mass of the tire and child is 36 kg. The rope is taut when the child leaves the platform and you may neglect the mass of the rope. At the bottom of the circular trajectory, the child and tire are a height h3 = 0.99 m above the ground. To receive full marks, you must include a diagram showing the physical situation.
(a) Calculate the speed of the child/tire at the bottom of the circular trajectory. m/s
(b) Calculate the maximum tension in the rope as the child/tire swing back and forth. N --
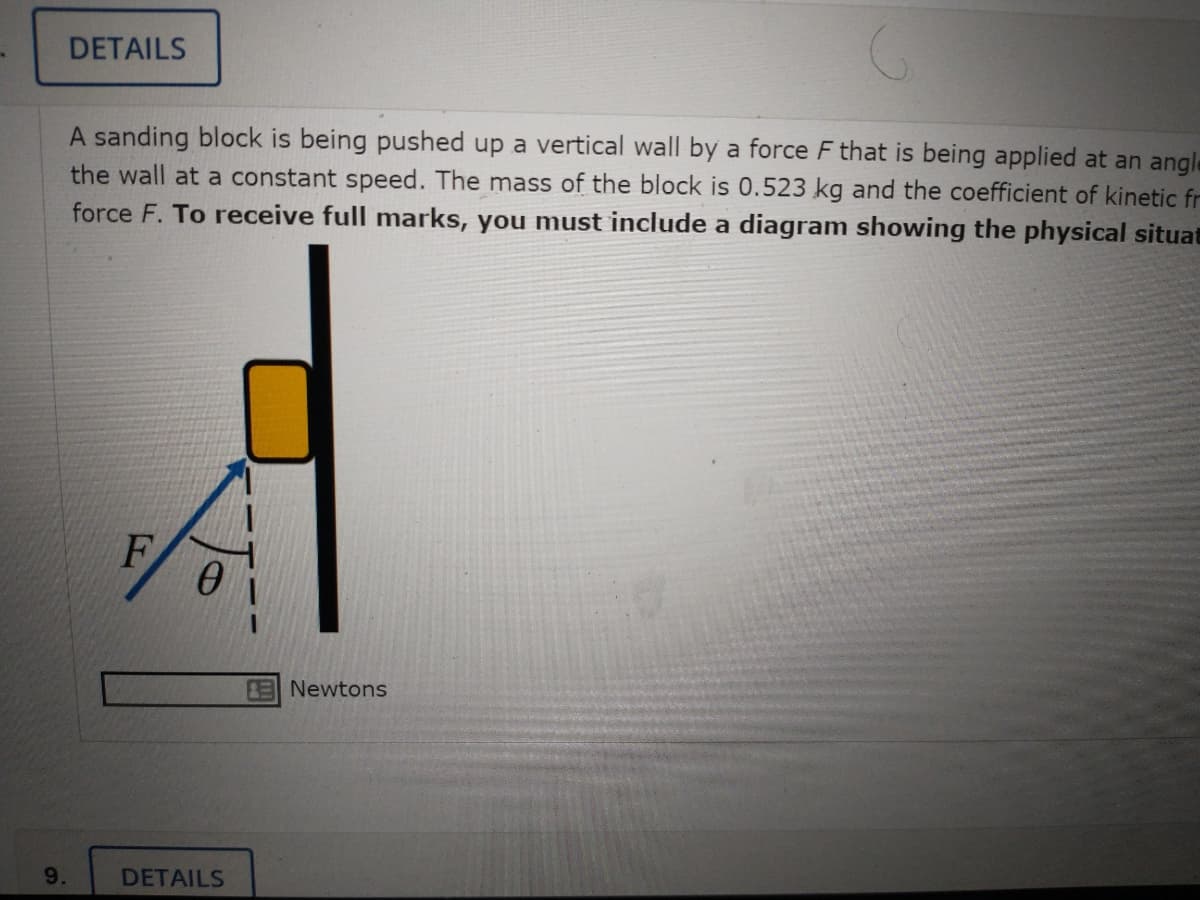
Transcribed Image Text:DETAILS
A sanding block is being pushed up a vertical wall by a force F that is being applied at an angle
the wall at a constant speed. The mass of the block is 0.523 kg and the coefficient of kinetic fr
force F. To receive full marks, you must include a diagram showing the physical situat
F
ENewtons
9.
DETAILS
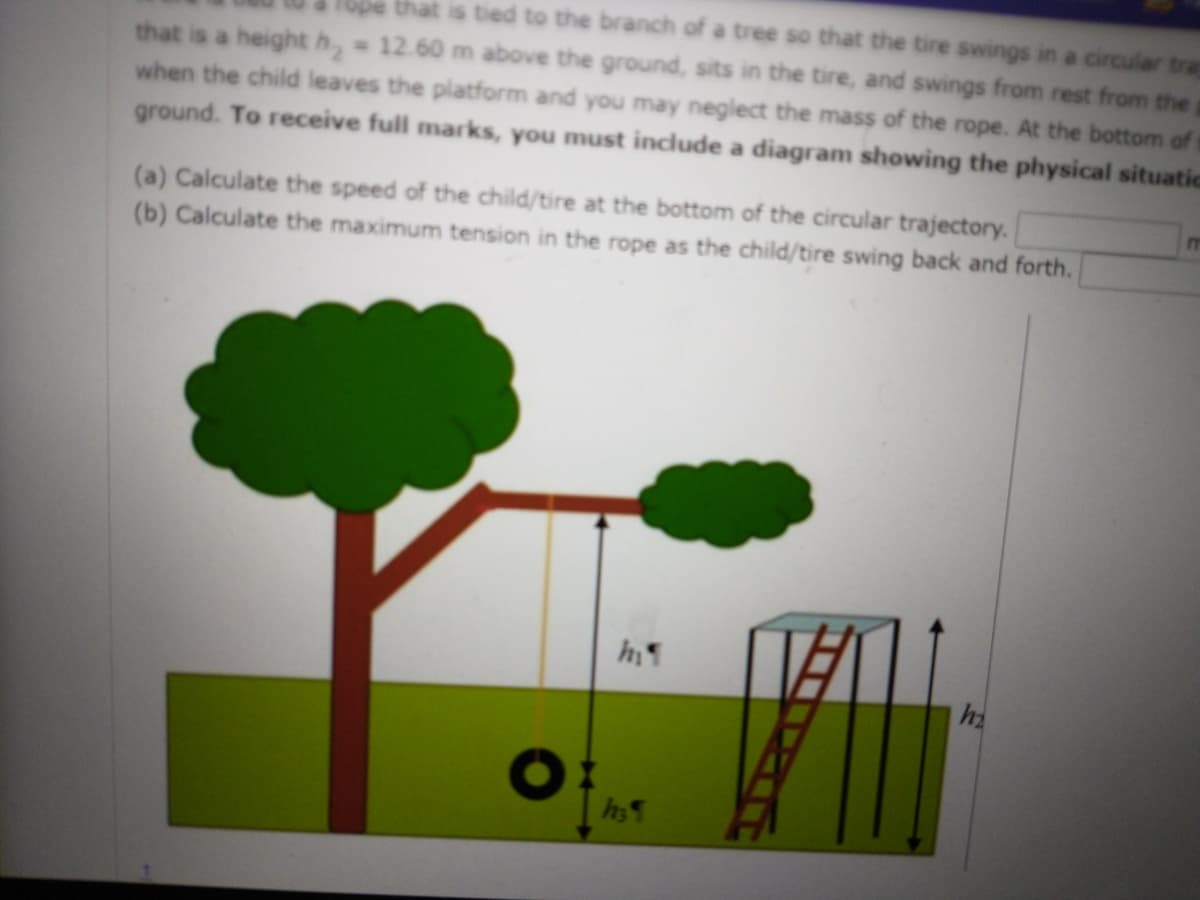
Transcribed Image Text:18be that is tied to the branch of a tree so that the tire swings in a circular tra
that is a height h, 12.60 m above the ground, sits in the tire, and swings from rest from the
when the child leaves the platform and you may neglect the mass of the rope. At the bottom of
ground. To receive full marks, you must include a diagram showing the physical situatic
(a) Calculate the speed of the child/tire at the bottom of the circular trajectory.
(b) Calculate the maximum tension in the rope as the child/tire swing back and forth.
h
h
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning