1. A very common way to introduce an aldehyde group on an aromatic or alkenyl group is to react the appropriate organometallic reagent with N.N-dimethylformamide. Thinking about the intermediate formed by nucleophilic addition, why do you think that this might stop after addition and not immediately undergo substitution to give the aldehyde that would then react further. Also, please draw this initial addition intermediate for the following reaction as well as the final product. OMe
1. A very common way to introduce an aldehyde group on an aromatic or alkenyl group is to react the appropriate organometallic reagent with N.N-dimethylformamide. Thinking about the intermediate formed by nucleophilic addition, why do you think that this might stop after addition and not immediately undergo substitution to give the aldehyde that would then react further. Also, please draw this initial addition intermediate for the following reaction as well as the final product. OMe
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Andrei Straumanis
Chapter16: Synthesis Workshop 1
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 32CTQ
Related questions
Question
4
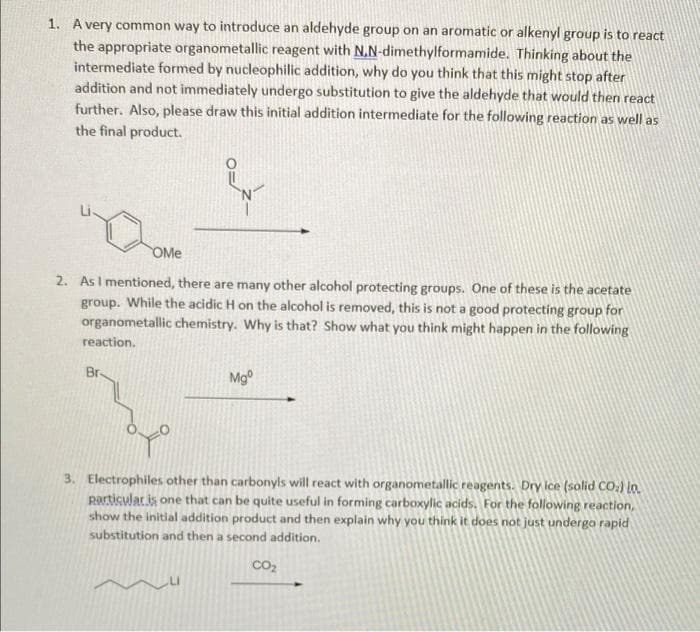
Transcribed Image Text:1. A very common way to introduce an aldehyde group on an aromatic or alkenyl group is to react
the appropriate organometallic reagent with N.N-dimethylformamide. Thinking about the
intermediate formed by nucleophilic addition, why do you think that this might stop after
addition and not immediately undergo substitution to give the aldehyde that would then react
further. Also, please draw this initial addition intermediate for the following reaction as well as
the final product.
OMe
2. AsI mentioned, there are many other alcohol protecting groups. One of these is the acetate
group. While the acidic H on the alcohol is removed, this is not a good protecting group for
organometallic chemistry. Why is that? Show what you think might happen in the following
reaction.
Br-
Mg°
3. Electrophiles other than carbonyls will react with organometallic reagents. Dry lce (solid CO.) lo.
Rartisulatis one that can be quite useful in forming carboxylic acids. For the following reaction,
show the initial addition product and then explain why you think it does not just underga rapid
substitution and then a second addition.
Co2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning