1. Consider the shaded area below the graph of the function y = x² + 1, above the x-axis and between the lines x = -1 and x = 1, illustrated below. -1.5 1 -0.5 2 y = x² + 1 0.5 1 1.5 (a) Use n = 4 rectangles and left endpoints for each rectangle to estimate the shaded area. Notice that you cannot be certain whether this estimate is an overestimate or an underestimate because some rectangles miss shaded area and other rectangles include unshaded area. (b) Use n = 4 rectangles and choose your sampled point to guarantee that you get an overestimate of the shaded area. (c) Use n = 5 rectangles and choose your sampled points to guarantee that you get an underestimate of the shaded area.
1. Consider the shaded area below the graph of the function y = x² + 1, above the x-axis and between the lines x = -1 and x = 1, illustrated below. -1.5 1 -0.5 2 y = x² + 1 0.5 1 1.5 (a) Use n = 4 rectangles and left endpoints for each rectangle to estimate the shaded area. Notice that you cannot be certain whether this estimate is an overestimate or an underestimate because some rectangles miss shaded area and other rectangles include unshaded area. (b) Use n = 4 rectangles and choose your sampled point to guarantee that you get an overestimate of the shaded area. (c) Use n = 5 rectangles and choose your sampled points to guarantee that you get an underestimate of the shaded area.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter7: Analytic Trigonometry
Section7.6: The Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Problem 92E
Related questions
Question
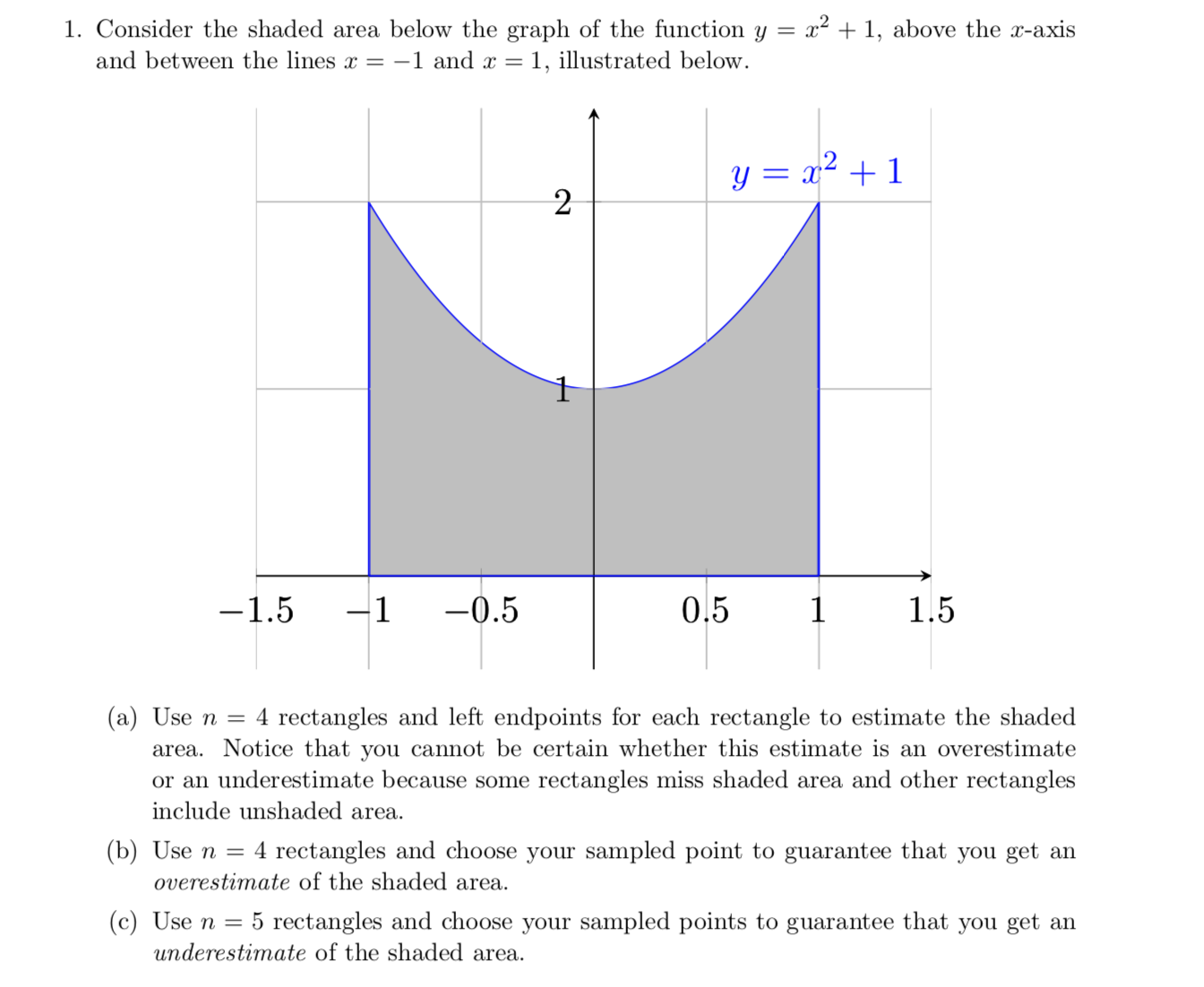
Transcribed Image Text:1. Consider the shaded area below the graph of the function y = x² + 1, above the x-axis
and between the lines x = -1 and x = 1, illustrated below.
y = x2 + 1
-1.5
-1
-0.5
0.5
1.5
(a) Use n =
4 rectangles and left endpoints for each rectangle to estimate the shaded
area. Notice that you cannot be certain whether this estimate is an overestimate
or an underestimate because some rectangles miss shaded area and other rectangles
include unshaded area.
(b) Use n = 4 rectangles and choose your sampled point to guarantee that you get an
overestimate of the shaded area.
(c) Use n = 5 rectangles and choose your sampled points to guarantee that you get an
underestimate of the shaded area.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 7 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning