1. Describe various inversions of a single slider crank mechanism giving examples.
1. Describe various inversions of a single slider crank mechanism giving examples.
Precision Machining Technology (MindTap Course List)
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781285444543
Author:Peter J. Hoffman, Eric S. Hopewell, Brian Janes
Publisher:Peter J. Hoffman, Eric S. Hopewell, Brian Janes
Chapter8: Computer Numerical Control
Section8.1: Cnc Basics
Problem 7RQ: What is the name for the type of motor used to drive CNC axes that is also capable of recording axis...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:01:53 M 1 or
Vo
LTED
:4G
+ Assignment 1_KoM.pdf
1/2
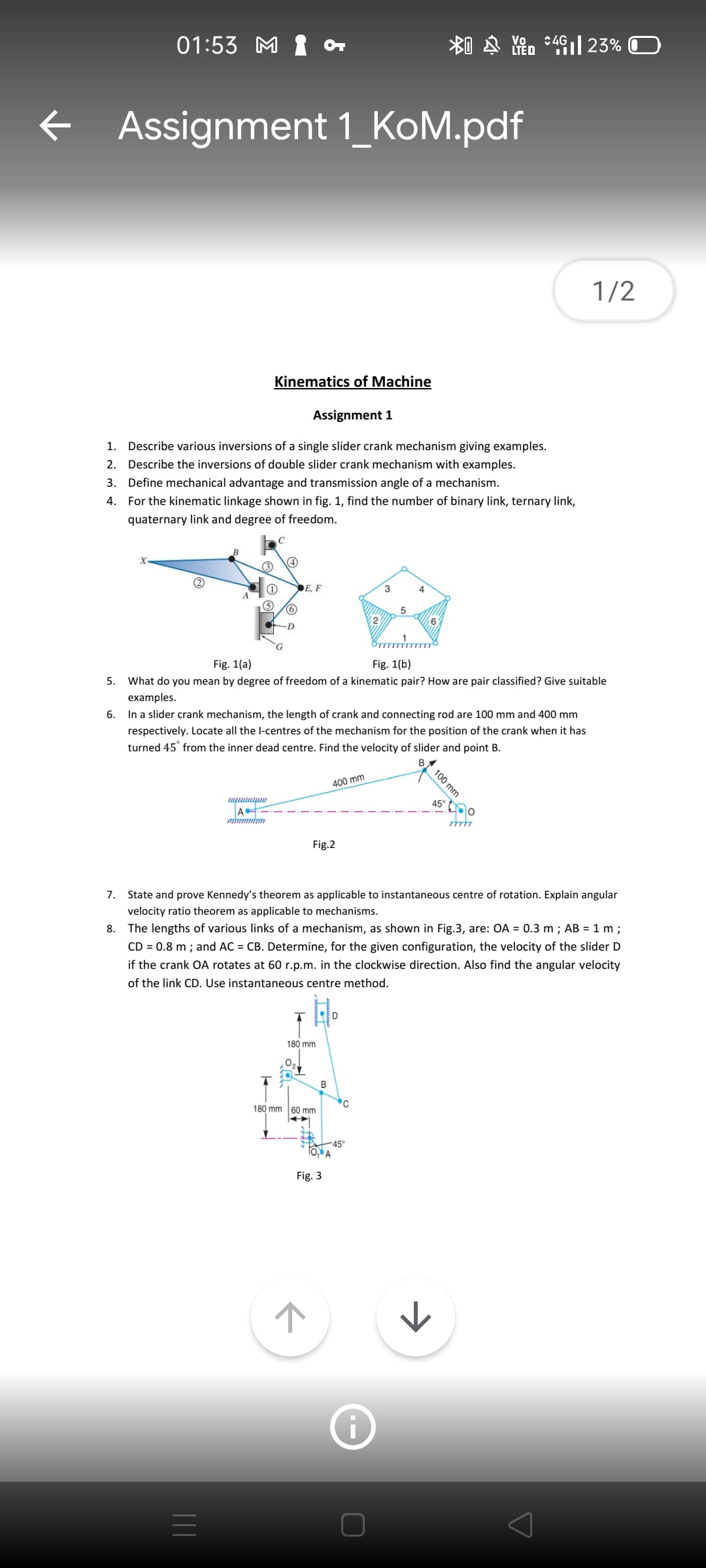
Kinematics of Machine
Assignment 1
1. Describe various inversions of a single slider crank mechanism giving examples.
2. Describe the inversions of double slider crank mechanism with examples.
3. Define mechanical advantage and transmission angle of a mechanism.
4. For the kinematic linkage shown in fig. 1, find the number of binary link, ternary link,
quaternary link and degree of freedom.
C
(1)
DE, F
Fig. 1(a)
Fig. 1(b)
5.
What do you mean by degree of freedom of a kinematic pair? How are pair classified? Give suitable
examples.
6. In a slider crank mechanism, the length of crank and connecting rod are 100 mm and 400 mm
respectively. Locate all the l-centres of the mechanism for the position of the crank when it has
turned 45° from the inner dead centre. Find the velocity of slider and point B.
400 mm
45°
m mim
Fig.2
7.
State and prove Kennedy's theorem as applicable to instantaneous centre of rotation. Explain angular
velocity ratio theorem as applicable to mechanisms.
8. The lengths of various links of a mechanism, as shown in Fig.3, are: OA = 0.3 m ; AB = 1 m ;
CD = 0.8 m ; and AC = CB. Determine, for the given configuration, the velocity of the slider D
if the crank OA rotates at 60 r.p.m. in the clockwise direction. Also find the angular velocity
of the link CD. Use instantaneous centre method.
180 mm
В
180 mm 60 mm
-45°
To, A
Fig. 3
100 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Precision Machining Technology (MindTap Course Li…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285444543
Author:
Peter J. Hoffman, Eric S. Hopewell, Brian Janes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Precision Machining Technology (MindTap Course Li…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285444543
Author:
Peter J. Hoffman, Eric S. Hopewell, Brian Janes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning