1. For each of the following graphs, discuss with your team and think of a motion that would create the graph. Be sure that you can accurately describe the velocity and acceleration for each motion. 2. Your team will be assigned two motions. Write a detailed description of the motions, with enough detail so that someone can follow your instructions and recreate the graph. C 20 20 20 15 15 10 10 10 1 2 3. time (s) 4 5 1 rime (1) time (5) A. Constant position = 5 cm from origin. Velocity = 0, acceleration = 0. B. Constant velocity = +2 cm/s, acceleration = 0, initial position = 5 cm. C. Constant velocity = -3 cm/s, acceleration = 0, initial position = 20 cm. E F 20 20 15 15 10 10 5. 2 tine (s) 1. time (s) 4 4. time (s) D. Velocity changes from 0 to +5 cm/s. Acceleration is positive, and constant (if the position vs. time curve is parabolic.) Initial position = 3 cm. E. Velocity and acceleration are both changing and alternating from positive to negative, initial position = 10 cm, alternates from 15 cm to 5 cm. F. Starting from origin, nearly constant velocity of about+17 cm/s for the first second, then changes to negative velocity. Acceleration changes from zero (first second), to negative, to positive (at about 2 seconds). Object "disappears or data is lost from 3-4 seconds.
1. For each of the following graphs, discuss with your team and think of a motion that would create the graph. Be sure that you can accurately describe the velocity and acceleration for each motion. 2. Your team will be assigned two motions. Write a detailed description of the motions, with enough detail so that someone can follow your instructions and recreate the graph. C 20 20 20 15 15 10 10 10 1 2 3. time (s) 4 5 1 rime (1) time (5) A. Constant position = 5 cm from origin. Velocity = 0, acceleration = 0. B. Constant velocity = +2 cm/s, acceleration = 0, initial position = 5 cm. C. Constant velocity = -3 cm/s, acceleration = 0, initial position = 20 cm. E F 20 20 15 15 10 10 5. 2 tine (s) 1. time (s) 4 4. time (s) D. Velocity changes from 0 to +5 cm/s. Acceleration is positive, and constant (if the position vs. time curve is parabolic.) Initial position = 3 cm. E. Velocity and acceleration are both changing and alternating from positive to negative, initial position = 10 cm, alternates from 15 cm to 5 cm. F. Starting from origin, nearly constant velocity of about+17 cm/s for the first second, then changes to negative velocity. Acceleration changes from zero (first second), to negative, to positive (at about 2 seconds). Object "disappears or data is lost from 3-4 seconds.
College Physics
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Chapter2: Kinematics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 45PE: A dolphin in an aquatic show jumps straight up out of the water at a velocity of 13.0 m/s. (a) List...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
D, E, and F
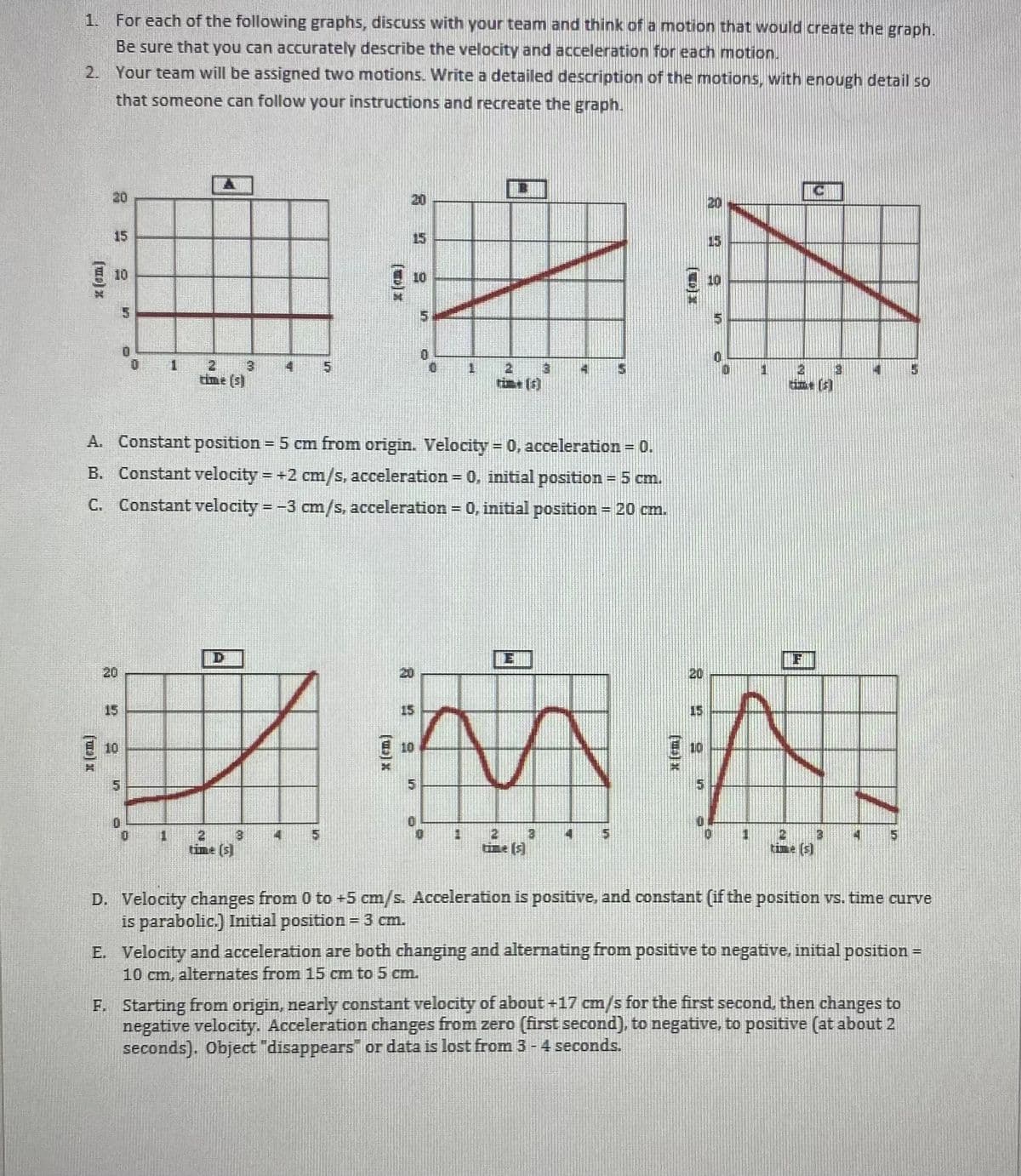
Transcribed Image Text:1. For each of the following graphs, discuss with your team and think of a motion that would create the graph.
Be sure that you can accurately describe the velocity and acceleration for each motion.
2. Your team will be assigned two motions. Write a detailed description of the motions, with enough detail so
that someone can follow your instructions and recreate the graph.
20
15
10
time (s)
A. Constant position = 5 cm from origin. Velocity = 0, acceleration = 0.
B. Constant velocity = +2 cm/s, acceleration = 0, initial position = 5 cm.
C. Constant velocity = -3 cm/s, acceleration 0, initial position = 20 cm.
%3D
20
15
15
E 10
10
21
12
tim: (5)
D. Velocity changes from 0 to +5 cm/s. Acceleration is positive, and constant (if the position vs. time curve
is parabolic.) Initial position = 3 cm.
E. Velocity and acceleration are both changing and alternating from positive to negative, initial position =
10 cm, alternates from 15 cm to 5 cm.
F. Starting from origin, nearly constant velocity of about+17 cm/s for the first second, then changes to
negative velocity. Acceleration changes from zero (first second), to negative, to positive (at about 2
seconds). Object "disappears or data is lost from 3 -4 seconds.
* (sm)
富
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University