1. For the closed tank with Bourdon-tube gages tapped into it shown in figure 1, what is the specific gravity of the oil and the pressure reading on gage C?
1. For the closed tank with Bourdon-tube gages tapped into it shown in figure 1, what is the specific gravity of the oil and the pressure reading on gage C?
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
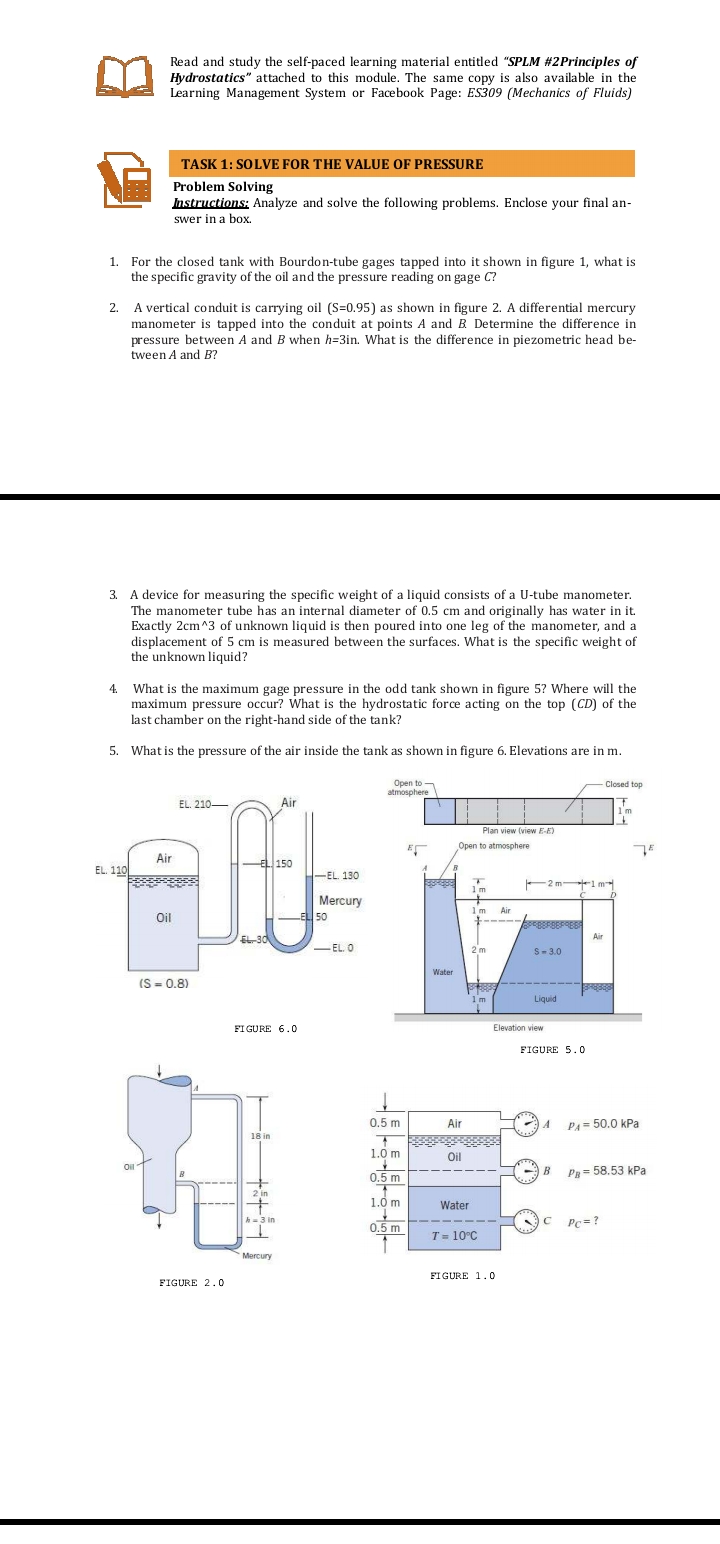
Transcribed Image Text:Read and study the self-paced learning material entitled "SPLM #2Principles of
Hydrostatics" attached to this module. The same copy is also available in the
Learning Management System or Facebook Page: ES309 (Mechanics of Fluids)
TASK 1: SOLVE FOR THE VALUE OF PRESSURE
Problem Solving
Instructions; Analyze and solve the following problems. Enclose your final an-
swer in a box.
1. For the closed tank with Bourdon-tube gages tapped into it shown in figure 1, what is
the specific gravity of the oil and the pressure reading on gage C?
2.
A vertical conduit is carrying oil (S=0.95) as shown in figure 2. A differential mercury
manometer is tapped into the conduit at points A and B Determine the difference in
pressure between A and B when h=3in. What is the difference in piezometric head be-
tween A and B?
3. A device for measuring the specific weight of a liquid consists of a U-tube manometer.
The manometer tube has an internal diameter of 0.5 cm and originally has water in it.
Exactly 2cm^3 of unknown liquid is then poured into one leg of the manometer, and a
displacement of 5 cm is measured between the surfaces. What is the specific weight of
the unknown liquid?
4.
What is the maximum gage pressure in the odd tank shown in figure 5? Where will the
maximum pressure occur? What is the hydrostatic force acting on the top (CD) of the
last chamber on the right-hand side of the tank?
5. What is the pressure of the air inside the tank as shown in figure 6. Elevations are in m.
Open to
atmosphere
Closed top
EL. 210–
Air
1m
Plan view (view E-E)
Open to atmosphere
Air
타 150
EL. 110
H-EL. 130
1m
F2 m 1m
Mercury
50
Air
Oil
EL-30
Air
-EL. O
2m
S-3.0
Water
(S = 0.8)
Liquid
FI GURE 6.0
Elevation view
FIGURE 5.0
0.5 m
Air
A
PA= 50.0 kPa
18 in
1.0 m
Oil
Oil
0.5 m
B
Pg= 58.53 kPa
2 in
1.0 m
Water
C Pc=?
h=3 in
0.5 m
T = 10°C
Mercury
FIGURE 1.0
FIGURE 2.0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY