1. Suppose that X,,,X, and Y,.,Y, are random samples from an independent N(2,5) and N(2,30), respectively. Let X and Y denote the sample means and s? denotes the sample variance. (a) Compute P(X >Ỹ+2). (X-2 (b) Find a constant k such that P S =0.95. (c) Find a constant / such that P(Sx >1)=0.90.
1. Suppose that X,,,X, and Y,.,Y, are random samples from an independent N(2,5) and N(2,30), respectively. Let X and Y denote the sample means and s? denotes the sample variance. (a) Compute P(X >Ỹ+2). (X-2 (b) Find a constant k such that P S =0.95. (c) Find a constant / such that P(Sx >1)=0.90.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter10: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section10.8: Probability
Problem 30E
Related questions
Question
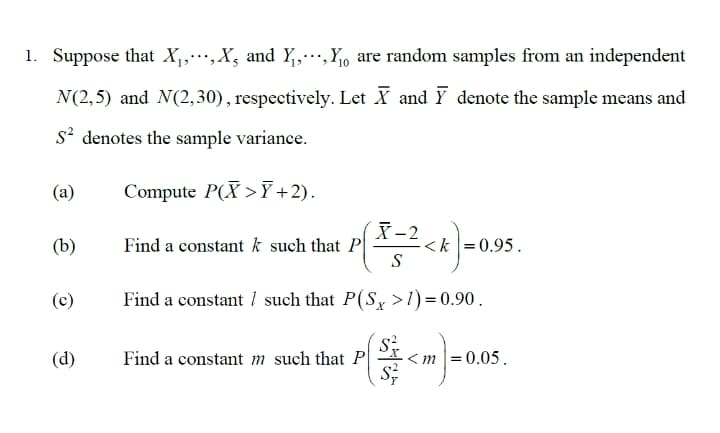
Transcribed Image Text:1. Suppose that X,,…,X, and Y,Y, are random samples from an independent
N(2,5) and N(2,30), respectively. Let X and Y denote the sample means and
s? denotes the sample variance.
(a)
Compute P(X >7+2).
X-2
<k = 0.95.
S
(b)
Find a constant k such that P
(c)
Find a constant 1 such that P(S, >1) = 0.90.
(d)
Find a constant m such that P
< m |= 0.05.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage