1. The beakers below contain an aqueous solution of three different acids, HX, HY, and HZ, respectively, and represent the solutions at equilibrium. The initial concentrations of all three solutions were the same. Assume the volume of each solution is the same. HX = 00 HY = O HZ = 00 H,o' = H,o = %3D Answer the following questions. Briefly explain your answers. a. The conjugate base particles are left out of each figure. Draw the appropriate number of conjugate base particles in each beaker above, matching the legend provided for the acid in each beaker. Write the dissociation equation of an acid (HA) in water.
1. The beakers below contain an aqueous solution of three different acids, HX, HY, and HZ, respectively, and represent the solutions at equilibrium. The initial concentrations of all three solutions were the same. Assume the volume of each solution is the same. HX = 00 HY = O HZ = 00 H,o' = H,o = %3D Answer the following questions. Briefly explain your answers. a. The conjugate base particles are left out of each figure. Draw the appropriate number of conjugate base particles in each beaker above, matching the legend provided for the acid in each beaker. Write the dissociation equation of an acid (HA) in water.
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter16: Principles Of Chemical Reactivity: The Chemistry Of Acids And Bases
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 127SCQ
Related questions
Question
100%
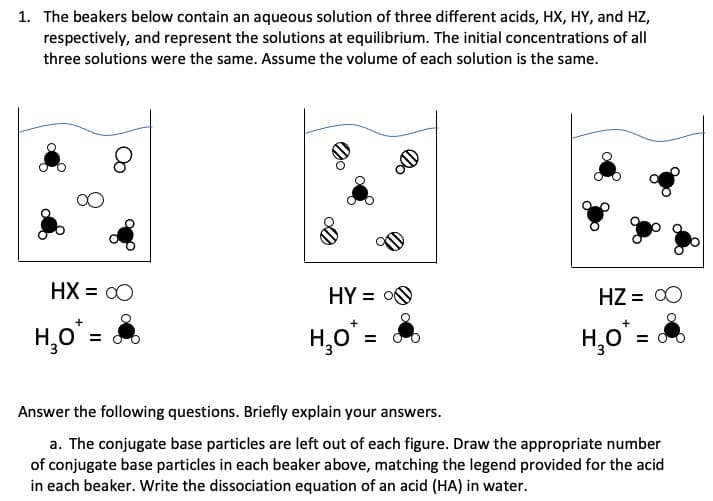
Transcribed Image Text:1. The beakers below contain an aqueous solution of three different acids, HX, HY, and HZ,
respectively, and represent the solutions at equilibrium. The initial concentrations of all
three solutions were the same. Assume the volume of each solution is the same.
HX = 00
HY = O0
HZ = 00
H,o'=
H,o =
H,o'=
Answer the following questions. Briefly explain your answers.
a. The conjugate base particles are left out of each figure. Draw the appropriate number
of conjugate base particles in each beaker above, matching the legend provided for the acid
in each beaker. Write the dissociation equation of an acid (HA) in water.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning