1. Use Hess's law and Standard Enthalpy of Formation and Entropy to calculate arH"(T); AS“(T) and arG"(T) at 13 caculate equilibrium constant at the same temperature and compare to Table 5 data AH- AS,- AG,"- Keq- 2. Use Graph 8 to calculate arHo( T) and compare to Table 5 data and Hess's Law calculation results. Show your in the space provided. Compare the results of two methods AS,"- AH- Show ALL your calculations in the space provided. Please use handwriting (you may take and upload a picture of all your solutions) or use a proper software showing mathematical operations correctly.
1. Use Hess's law and Standard Enthalpy of Formation and Entropy to calculate arH"(T); AS“(T) and arG"(T) at 13 caculate equilibrium constant at the same temperature and compare to Table 5 data AH- AS,- AG,"- Keq- 2. Use Graph 8 to calculate arHo( T) and compare to Table 5 data and Hess's Law calculation results. Show your in the space provided. Compare the results of two methods AS,"- AH- Show ALL your calculations in the space provided. Please use handwriting (you may take and upload a picture of all your solutions) or use a proper software showing mathematical operations correctly.
Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Chapter16: Spontaneity, Entropy, And Free Energy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1ALQ: For the process A(l) A(g), which direction is favored by changes in energy probability? Positional...
Related questions
Question
Please help answer unanswered parts: Calculations 1 and 2 (at bottom, red boxes)
Equation used was as follows:
C [crystal graphite] + CO2 [gas ] ⇌ 2CO [gas ] ; Formation of carbon monoxide
Equation:
| C [crystal graphite] + | CO2 [gas] + | <---> | 2CO [gas] + | + |
| Standard Enthalpy of Formation and Entropy | ∆fHo(T) (KJ/mol) | So(T) (J/mol.K) |
| C [crystal graphite] | 18.51 | 30.32 |
| CO2 [gas] | -343.41 | 283.87 |
| CO [gas] | -78.69 | 243.42 |
![201
Graph 6. Final composition vs Temperature (put both curves on Graph 7. AG vs Temperature
the same graph by inserting three columns and clicking
Scatter with Smooth Lines)
202
203
204
205
206
Ink vs 1/T
207
1.000E+01
208
5.000E+00
209
210
0,000E+00
211
5.000E-04.000E-04.000E-04.100E-01.300E-03.500E-01700E-01.900E-03
-5.000E+00
212
213
-1.000E+01
214
-1.500E+01
y=-20627x+21.11
215
R = 0.9999
216
-2.000E+01
217
-2.500E+01
218
1/T, к
219
220
221
Graph 8. Ink vs IT (Vant Hoff's equation)
222
223
CALCULATIONS
Show your calculations in the space provided. Add more space if necessary Including the space to the right or the next page.
Please use handwriting (you may take and insert a picture of your solutions) or
a proper software showing mathematical operations correctly. YOU ARE ENCOURAGED TO USE EXCEL IN CALCULATIONS
If you used Excel in calculations, show how you coded the cells.
224
225
226
227
228
Hints:
1. Use Hess's law and Standard Enthalpy of Formation and Entropy to calculate arH"(T); AS"(T) and ArG"(T) at 1300 IHess's Law:
caculate equilibrium constant at the same temperature and compare to Table 5 data
229
230
231
ΔΗ"eaction =Σn: ΔΗproducts) - Ση: ΔΗ'peactants )
(reactants)
232
AH,"=
AS,"=
AG,"=
Keg-
AS°reaction-En+ AS°Iproducts) - En+ AS°Ireactants)
233
2. Use Graph 8 to calculate ArHo[ T) and compare to Table 5 data and Hess's Law calculation results. Show your calc van't Hoff equation
in the space provided. Compare the results of two methods
234
235
AH,"=
In KAH. |1], 4s
+
AS
236
AS,"=
R=8.3145J-K'mol!.
R IT
R
237
238
Show ALL your calculations in the space provided.
y=
b
a
+
239
The trendline coefficient on the Excel graph will give you the value of a and y-intercept -b
Please use handwriting (you may take and uploada picture of all your solutions) or use a proper software showing
mathematical operations correctly.
240
ASan
b =kn
R
ΔΗ
241
a =
R
242
243
Solve both equations fot thermodynamic functions
Compare the results of two methods
244](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F435327ce-ad1d-47b0-9d05-42b05e19b7ae%2F94885b5a-eaef-4177-9421-7d4360e8a641%2Fkpodp2m_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:201
Graph 6. Final composition vs Temperature (put both curves on Graph 7. AG vs Temperature
the same graph by inserting three columns and clicking
Scatter with Smooth Lines)
202
203
204
205
206
Ink vs 1/T
207
1.000E+01
208
5.000E+00
209
210
0,000E+00
211
5.000E-04.000E-04.000E-04.100E-01.300E-03.500E-01700E-01.900E-03
-5.000E+00
212
213
-1.000E+01
214
-1.500E+01
y=-20627x+21.11
215
R = 0.9999
216
-2.000E+01
217
-2.500E+01
218
1/T, к
219
220
221
Graph 8. Ink vs IT (Vant Hoff's equation)
222
223
CALCULATIONS
Show your calculations in the space provided. Add more space if necessary Including the space to the right or the next page.
Please use handwriting (you may take and insert a picture of your solutions) or
a proper software showing mathematical operations correctly. YOU ARE ENCOURAGED TO USE EXCEL IN CALCULATIONS
If you used Excel in calculations, show how you coded the cells.
224
225
226
227
228
Hints:
1. Use Hess's law and Standard Enthalpy of Formation and Entropy to calculate arH"(T); AS"(T) and ArG"(T) at 1300 IHess's Law:
caculate equilibrium constant at the same temperature and compare to Table 5 data
229
230
231
ΔΗ"eaction =Σn: ΔΗproducts) - Ση: ΔΗ'peactants )
(reactants)
232
AH,"=
AS,"=
AG,"=
Keg-
AS°reaction-En+ AS°Iproducts) - En+ AS°Ireactants)
233
2. Use Graph 8 to calculate ArHo[ T) and compare to Table 5 data and Hess's Law calculation results. Show your calc van't Hoff equation
in the space provided. Compare the results of two methods
234
235
AH,"=
In KAH. |1], 4s
+
AS
236
AS,"=
R=8.3145J-K'mol!.
R IT
R
237
238
Show ALL your calculations in the space provided.
y=
b
a
+
239
The trendline coefficient on the Excel graph will give you the value of a and y-intercept -b
Please use handwriting (you may take and uploada picture of all your solutions) or use a proper software showing
mathematical operations correctly.
240
ASan
b =kn
R
ΔΗ
241
a =
R
242
243
Solve both equations fot thermodynamic functions
Compare the results of two methods
244
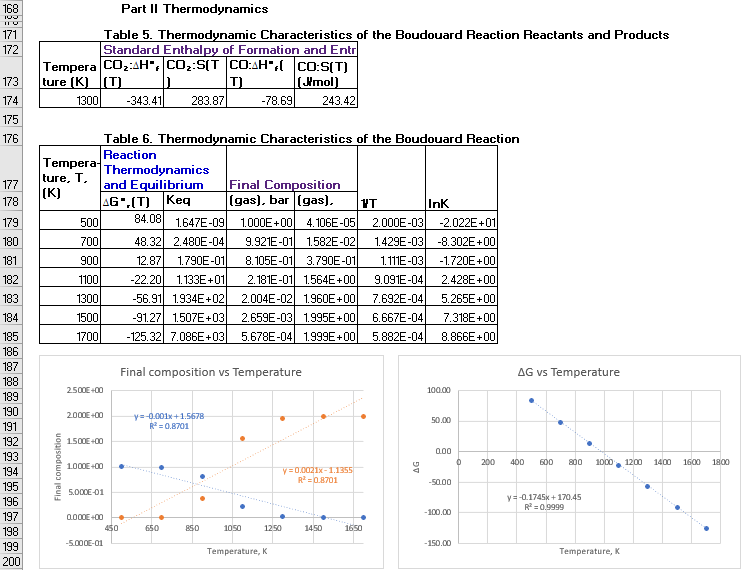
Transcribed Image Text:168
Part II Thermodynamics
171
Table 5. Thermodynamic Characteristics of the Boudouard Reaction Reactants and Products
Standard Enthalpy of Formation and Entr
Tempera COz:AH", CO::S(T CO:AH",( Co:S(T)
(Imol)
243.42
172
173
ture (K) (T)
T)
174
1300
-343.41
283.87
-78.69
175
176
Table 6. Thermodynamic Characteristics of the Boudouard Reaction
Reaction
Тempera
ture, T.
(K)
Thermodynamics
and Equilibrium
A6".(T) Keq
Final Composition
(gas), bar (gas).
177
178
VT
InK
179
500
84.08
1.647E-09
1.000E+00 4. 106E-05
2.000E-03
-2.022E+01
180
700
48.32 2.480E-04
9.921E-01
1.582E-02
1.429E-03
-8.302E+00
181
900
12.87
1.790E-01
8.105E-01
3.790E-01
1.111E-03
-1.720E +00
2.181E-01 1.564E+00
2.004E-02 1.960E+00
182
1100
-22.20
1.133E+01
9.091E-04
2.428E+00
-56.91 1.934E+02
-91.27 1.507E+03
-125.32 7.086E+03
183
1300
7.692E-04
5.265E+00
184
1500
2.659E-03 1.995E+00
6.667E-04
7.318E +00
185
1700
5.678E-04 1.999E+00
5.882E-04
8.866E +00
186
187
Final composition vs Temperature
AG vs Temperature
188
2500E +00
100.00
189
190
2.000E+00
y=-0.001x+1.5678
R = 0.8701
50.00
191
192
1500E +00
0.00
193
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1600
1800
1000E+00
y=0.0021x-1.1355
R =0.8701
194
-50.00
195
5.000E-01
y=-0.1745k + 170.45
R = 0,9999
196
-100.00
197
0.000E +00
198
450
650
BSO
1050
1250
1450
1650
-5.000E-01
-150.00
199
Temperature, K
Temperature, K
200
Final composition
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning