1. Which of the following gases diffuse more slowly than oxygen? F2, Ne, N2O, C2H2, NO, Cl2, H2S
2. Calculate the relative rate of diffusion of 1H2 (molar mass 2.0 g/mol) compared with 2H2 (molar mass 4.0 g/mol) and the relative rate of diffusion of O2 (molar mass 32 g/mol) compared with O3 (molar mass 48 g/mol).
3. Can the speed of a given molecule in a gas double at constant temperature? Explain your answer.
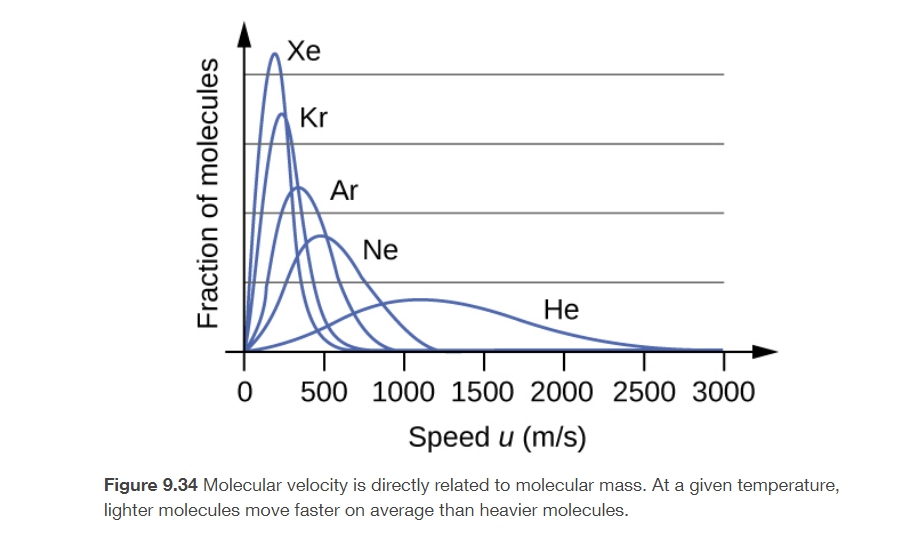
4. The distribution of molecular velocities in a sample of helium is shown in the picture attached. If the sample is cooled, will the distribution of velocities look more like that of H2 or of H2O? Explain your answer.
5. A 1-L sample of CO initially at STP is heated to 546 K, and its volume is increased to 2 L.
6. Under which of the following sets of conditions does a real gas behave most like an ideal gas, and for which conditions is a real gas expected to deviate from ideal behavior? Explain.
(a) high pressure, small volume
(b) high temperature, low pressure
(c) low temperature, high pressure
The rate of diffusion is inversely proportional to square root of molecular mass..
That means as molecular mass increases rate of diffusion decreases.
And ,
Molecular masses of : O2 - 31.998 g/mol
F2 - 37.996 g/ mol
Ne- 20.18 g/mol
N2O- 44.013 g/mol
C2H2- 26.04 g/mol
NO- 30.01 g/mol
Cl2- 70.9 g/mol
H2S- 34.1 g/mol
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps









