1.4-7 The data shown in the table below were obtained from a tensile test of high-strength steel. The test specimen had a diameter of 13 mm and a gage length of 50 mm (see figure for Prob. 1.4-3). At fracture, the elongation between the gage marks was 3.0 mm and the minimum diameter was 10.7 mm. Plot the conventional stress-strain curve for the steefor the steel and determine the proportional limit, modulus of elastics of elastic- ty (i.e., the slope of the initial part of the stress-strain tress-strain curve), yield stress at 0.1% offset, ultimate stress, percent, elongation in 50 mm, and percent reduction in area. "ess, percent area. TENSILE-TEST DATA FOR PROB. 1.4-7 Elongation (mm) 0.005 Load (kN) 10 0.015 30 0.048 50 0.084 60 0.099 64.5 67.0 0.109 0.119 68.0 0.137 69.0 0.160 70.0 0.229 72.0 0.259 76.0 0.330 84.0 0.584 92.0 0.853 100.0 1.288 112.0 2.814 113.0 Fracture
1.4-7 The data shown in the table below were obtained from a tensile test of high-strength steel. The test specimen had a diameter of 13 mm and a gage length of 50 mm (see figure for Prob. 1.4-3). At fracture, the elongation between the gage marks was 3.0 mm and the minimum diameter was 10.7 mm. Plot the conventional stress-strain curve for the steefor the steel and determine the proportional limit, modulus of elastics of elastic- ty (i.e., the slope of the initial part of the stress-strain tress-strain curve), yield stress at 0.1% offset, ultimate stress, percent, elongation in 50 mm, and percent reduction in area. "ess, percent area. TENSILE-TEST DATA FOR PROB. 1.4-7 Elongation (mm) 0.005 Load (kN) 10 0.015 30 0.048 50 0.084 60 0.099 64.5 67.0 0.109 0.119 68.0 0.137 69.0 0.160 70.0 0.229 72.0 0.259 76.0 0.330 84.0 0.584 92.0 0.853 100.0 1.288 112.0 2.814 113.0 Fracture
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Chapter7: Analysis Of Stress And Strain
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7.7.25P: On the surface of a structural component in a space vehicle, the strains arc monitored by means of...
Related questions
Question
100%
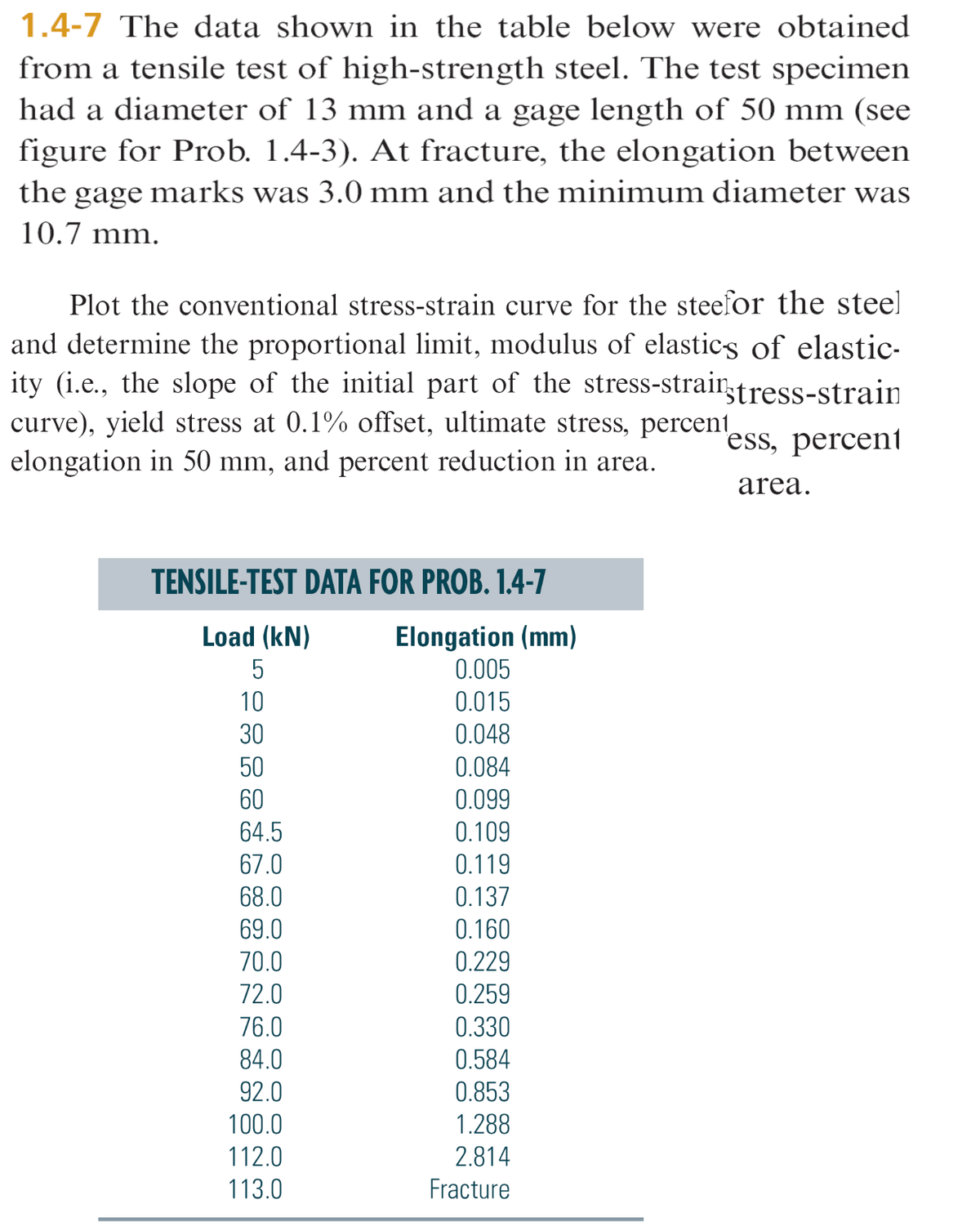
Transcribed Image Text:1.4-7 The data shown in the table below were obtained
from a tensile test of high-strength steel. The test specimen
had a diameter of 13 mm and a gage length of 50 mm (see
figure for Prob. 1.4-3). At fracture, the elongation between
the gage marks was 3.0 mm and the minimum diameter was
10.7 mm.
Plot the conventional stress-strain curve for the steefor the steel
and determine the proportional limit, modulus of elastics of elastic-
ity (i.e., the slope of the initial part of the stress-strain,tress-strain
curve), yield stress at 0.1% offset, ultimate stress, percent,
elongation in 50 mm, and percent reduction in area.
'ess, percent
area.
TENSILE-TEST DATA FOR PROB. 1.4-7
Elongation (mm)
0.005
0.015
0.048
Load (kN)
5
10
30
50
0.084
60
0.099
64.5
0.109
67.0
0.119
68.0
0.137
69.0
0.160
70.0
0.229
72.0
0.259
76.0
0.330
84.0
0.584
92.0
0.853
100.0
1.288
112.0
2.814
113.0
Fracture

Transcribed Image Text:1.5-5 A wire of length L = 2.5 m and diameter d = 1.6 mm
is stretched by tensile forces P = 600 N. The wire is made of
a copper alloy having a stress-strain relationship that may be
described mathematically by the following equation:
124,020e
0 < es 0.03
( σ -MPa)
1 + 300ɛ
in which e is nondimensional and o has units of MPa.
(a) Construct a stress-strain diagram for the material.
(b) Determine the elongation of the wire due to the
forces P.
(c) If the forces are removed, what is the permanent
set of the bar?
(d) If the forces are applied again, what is the propor-
tional limit?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
Expert Answers to Latest Homework Questions
Q: Please answer both questions!!
Q: What is a blue-ocean strategy, what is its appeal, and what is its drawback?
View keyboard…
Q: An additional, and often very important motivating factor for adding new businesses is to complement…
Q: What is the future value, after 36 years, of $375 placed in a savings account today that pays…
Q: Assume the equilibrium wage rate is $6, as shown below.
Wage
$12
Tools
$11
S
$10
$5.50
$6.50
$9
$8…
Q: The table below presents labor market data for three countries. All population values are in…
Q: Draw the major organic product obtained from the following reaction.
CO2 CH
× [+
CO2 CH
Q: Solution? Ple
Q: how is accidental medical events handled in risk managment
Q: Estimate the pH of 0.05 M NaCN(aq) at 25°C. Ka(HCN) = 3.4 × 10−9. Write your answer with two decimal…
Q: Patton Dyes manufactures colorings, primarily for textiles. Information on the work in process…
Q: Draw the major organic product obtained from the following sequence of reactions.
1.2 eq. CH3CH2MgCI…
Q: Compute the specified quantity.
Your total payment on a 5 year loan, which charged 8.5% annual…
Q: How do we know that ZnO when reacting with H3O+ would react with 2 H3O+ and not just 1 H3O+
Q: Frank’s dog, Fido, is 16 inches tall and 30 inches long. Frank wants to draw Fido 4 inches tall.…
Q: how are conditions of patricipations relevent in healthcare risk managment
Q: Please answer all parts!!
Q: Please expalain your work. Thank you!
Q: what are some of the main reasons why some kids may be more vulnerable to being incarcerated in the…
Q: Please explain well. Thank you!
Q: what is Conditions of participation in risk managment