Two round solid bars of different materials are connected in series against rigid (b) supports as shown in Figure 4. Determine the stress in each bar and the support reactions if temperature is increased by 18° C. Bar A da, EA, AA Bar B de, EB, aB LA LB Figure 4 Use the following information. Bar, B: Length, LB Diameter, ds Poisson's Ratio Bar, A: = 25mm = 40 mm 30 mm = 0.32 70 kN/mm2 Coefficient of expansion aa 16.5x10 °C Length, LA Diameter, da Poisson's Ratio 10 mm %3D =0.28 %3D Young's Modulus Es Coefficient of expansion ag 12.4x10 °C 210 kN/mm Young's Modulus EA
Two round solid bars of different materials are connected in series against rigid (b) supports as shown in Figure 4. Determine the stress in each bar and the support reactions if temperature is increased by 18° C. Bar A da, EA, AA Bar B de, EB, aB LA LB Figure 4 Use the following information. Bar, B: Length, LB Diameter, ds Poisson's Ratio Bar, A: = 25mm = 40 mm 30 mm = 0.32 70 kN/mm2 Coefficient of expansion aa 16.5x10 °C Length, LA Diameter, da Poisson's Ratio 10 mm %3D =0.28 %3D Young's Modulus Es Coefficient of expansion ag 12.4x10 °C 210 kN/mm Young's Modulus EA
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Chapter2: Axially Loaded Members
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2.5.18P: A steel wire AB is stretched between rigid supports (see figure). The initial priestess in the wire...
Related questions
Question
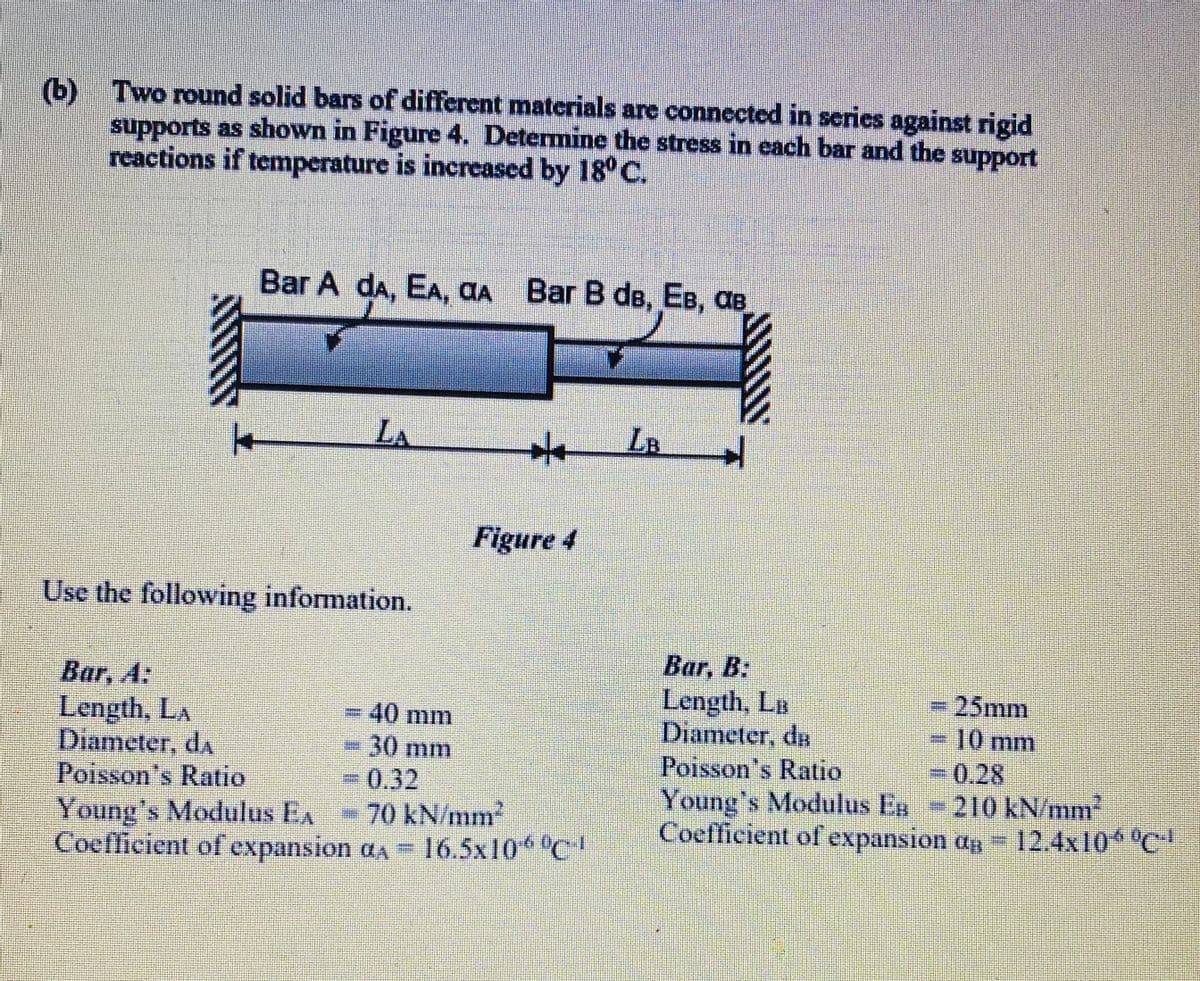
Transcribed Image Text:(b) Two round solid bars of different materials are connected in series against rigid
supports as shown in Figure 4. Determine the stress in each bar and the support
reactions if temperature is increased by 18° C.
Bar A da, EA, AA Bar B de, EB, aB
LA
La
Figure 4
Use the following information.
Bar, A:
Length, LA
Diameter, da
Poisson's Ratio
Young's Modulus EA
Coefficient of expansion aa 16.5x10 C
Bar, B:
Length, LB
Diameter, da
Poisson's Ratio
Young's Modulus En 210 kN/mm
Coefficient of expansion an 12.4x10 °C
25mm
40 mm
30 mm
10 mm
30.28
=0.32
70 kN/mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 11 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning