14. A sphere with the same mass and radius as the original cylinder, but a smaller rotational inertia, is released from rest from the top of the ramp. K, and K. are the sphere's and the cylinder's total kinetic energy at the bottom of the ramp, respectively. How do K, and K̟ compare, and why? (A) K, < K, because the sphere will gain less rotational kinetic energy. (B) K, < K., because the sphere has a greater acceleration and therefore has less time to gain kinetic energy. (C) K, = K, because both objects accelerate at %3D the same rate. (D) K, = K̟, because the gravitational force %3D does equal work on each object as it rolls down the ramp.
14. A sphere with the same mass and radius as the original cylinder, but a smaller rotational inertia, is released from rest from the top of the ramp. K, and K. are the sphere's and the cylinder's total kinetic energy at the bottom of the ramp, respectively. How do K, and K̟ compare, and why? (A) K, < K, because the sphere will gain less rotational kinetic energy. (B) K, < K., because the sphere has a greater acceleration and therefore has less time to gain kinetic energy. (C) K, = K, because both objects accelerate at %3D the same rate. (D) K, = K̟, because the gravitational force %3D does equal work on each object as it rolls down the ramp.
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Chapter11: Angular Momentum
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 27P: A solid cylinder of radius 10.0 cm rolls down an incline with slipping. The angle of the incline is...
Related questions
Question
#14 AP Physics 1 question attached.
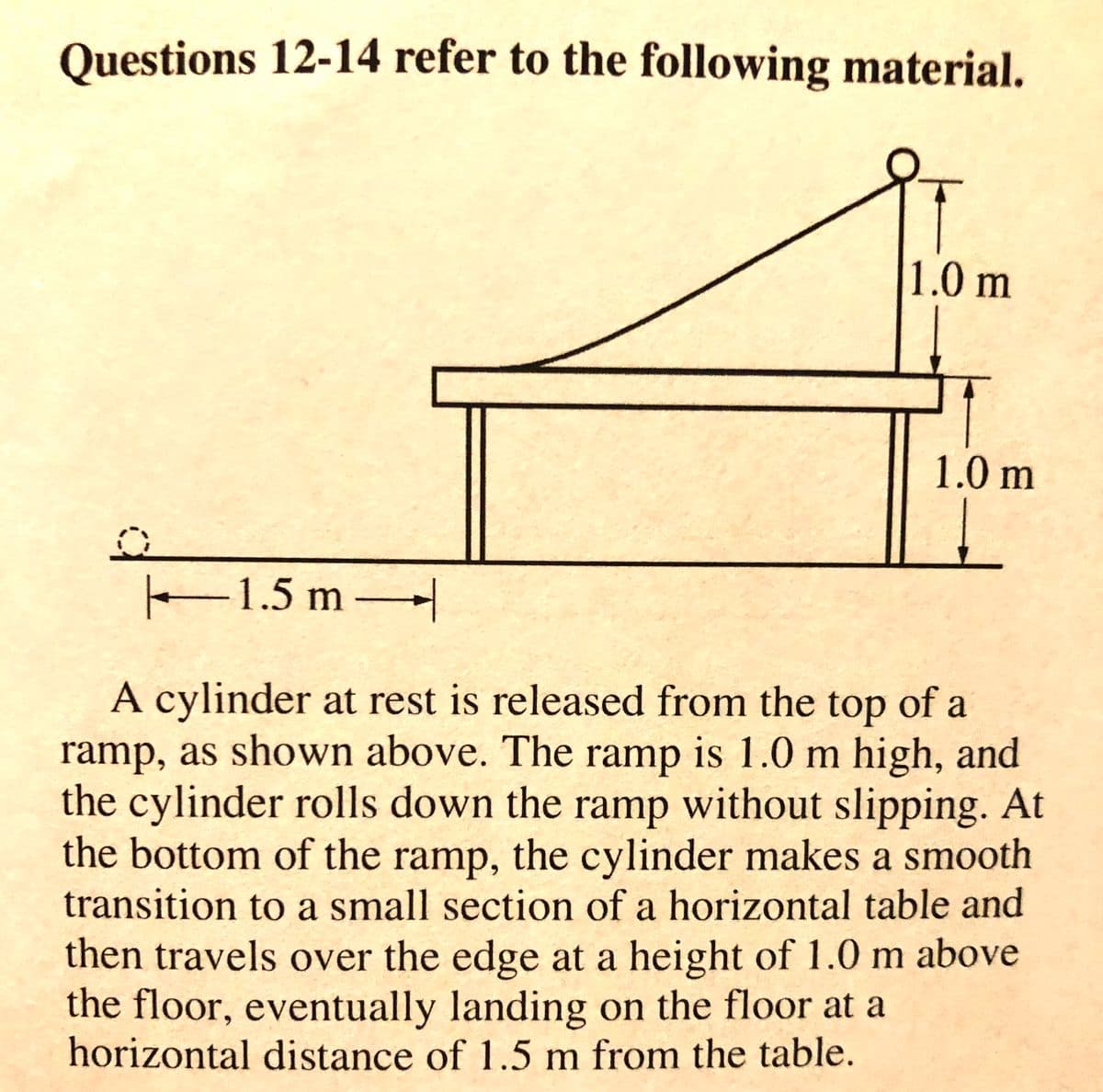
Transcribed Image Text:Questions 12-14 refer to the following material.
1.0 m
1.0 m
1.5 m
A cylinder at rest is released from the top of a
ramp, as shown above. The ramp is 1.0 m high, and
the cylinder rolls down the ramp without slipping. At
the bottom of the ramp, the cylinder makes a smooth
transition to a small section of a horizontal table and
then travels over the edge at a height of 1.0 m above
the floor, eventually landing on the floor at a
horizontal distance of 1.5 m from the table.

Transcribed Image Text:14. A sphere with the same mass and radius as the
original cylinder, but a smaller rotational inertia,
is released from rest from the top of the ramp. K,
and K, are the sphere's and the cylinder's total
kinetic energy at the bottom of the ramp,
respectively. How do K, and K. compare, and
why?
(A) K, < K because the sphere will gain less
rotational kinetic energy.
(B) K, < K, because the sphere has a greater
acceleration and therefore has less time to
gain kinetic energy.
(C) K, = K, because both objects accelerate at
%3D
the same rate.
(D) K = K¸, because the gravitational force
does equal work on each object as it rolls
down the ramp.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College