14. Use Exhibit 2. Which of the following statements is (are) correct? (x) In autarky, the relative price of hats, in terms of caps, in Canada is greater than the relative price of hats in Mexico. (y) Mexico has both an absolute advantage and comparative advantage in the production of hats, and it would be willing to trade with Canada at terms of trade equal to 20 caps for 12 hats. (z) Canada does not have an absolute advantage in either caps or hats but it has a comparative advantage in caps and it would be willing to trade with Mexico at terms of trade equal to 20 caps for 12 hats. А. (х), (у) and (2) B. (x) and (y) only C. (x) and (z) only D. (y) and (z) only E. (y) only Exhibit 2 Output per labor hour Caps Hats Canada 8 Меxico 9
14. Use Exhibit 2. Which of the following statements is (are) correct? (x) In autarky, the relative price of hats, in terms of caps, in Canada is greater than the relative price of hats in Mexico. (y) Mexico has both an absolute advantage and comparative advantage in the production of hats, and it would be willing to trade with Canada at terms of trade equal to 20 caps for 12 hats. (z) Canada does not have an absolute advantage in either caps or hats but it has a comparative advantage in caps and it would be willing to trade with Mexico at terms of trade equal to 20 caps for 12 hats. А. (х), (у) and (2) B. (x) and (y) only C. (x) and (z) only D. (y) and (z) only E. (y) only Exhibit 2 Output per labor hour Caps Hats Canada 8 Меxico 9
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
7th Edition
ISBN:9781285165912
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter3: Interdependence And The Gains From Trade
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9PA
Related questions
Question
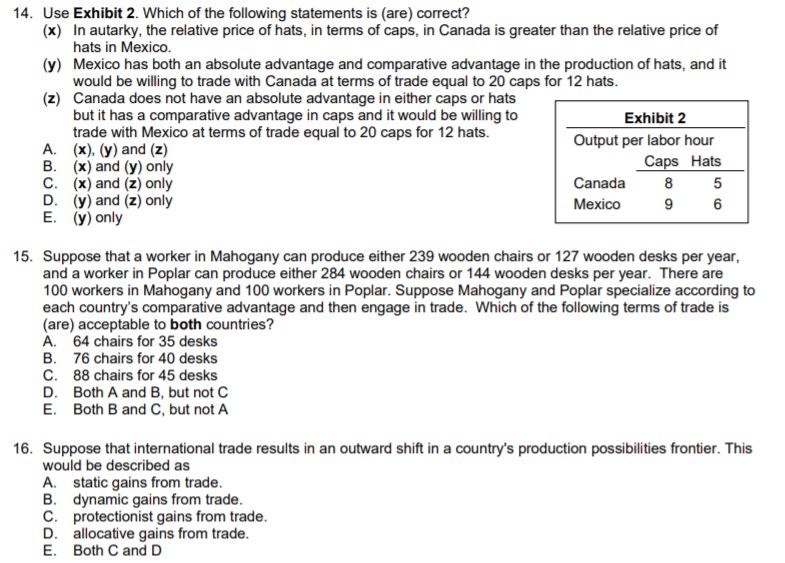
Transcribed Image Text:14. Use Exhibit 2. Which of the following statements is (are) correct?
(x) In autarky, the relative price of hats, in terms of caps, in Canada is greater than the relative price of
hats in Mexico.
(y) Mexico has both an absolute advantage and comparative advantage in the production of hats, and it
would be willing to trade with Canada at terms of trade equal to 20 caps for 12 hats.
(z) Canada does not have an absolute advantage in either caps or hats
but it has a comparative advantage in caps and it would be willing to
trade with Mexico at terms of trade equal to 20 caps for 12 hats.
A. (x), (y) and (z)
B. (x) and (y) only
C. (x) and (z) only
D. (y) and (z) only
E. (y) only
Exhibit 2
Output per labor hour
Caps Hats
Canada
8
5
Mexico
6
15. Suppose that a worker in Mahogany can produce either 239 wooden chairs or 127 wooden desks per year,
and a worker in Poplar can produce either 284 wooden chairs or 144 wooden desks per year. There are
100 workers in Mahogany and 100 workers in Poplar. Suppose Mahogany and Poplar specialize according to
each country's comparative advantage and then engage in trade. Which of the following terms of trade is
(are) acceptable to both countries?
A. 64 chairs for 35 desks
B. 76 chairs for 40 desks
C. 88 chairs for 45 desks
D. Both A and B, but not C
E. Both B and C, but not A
16. Suppose that international trade results in an outward shift in a country's production possibilities frontier. This
would be described as
A. static gains from trade.
B. dynamic gains from trade.
C. protectionist gains from trade.
D. allocative gains from trade.
E. Both C and D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165912
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165912
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
