15.18) Determine whether the following statements describe insulin, glucagon, or both insulin and glucagon. a) secreted by pancreas both insulin and glucagon b) released when blood glucose concentration is high insulin c) released when blood glucose concentration is low glucagon d) immediately increases the amount of glucose entering cells insulin e) is a hormone both insulin and glucagon f) lowers blood glucose concentration insulin g) not enough is produced by individuals with type-1 diabetes insulin h) stimulates glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) glucagon EXPLANATION: When insulin binds to liver and muscle cell receptors, it triggers a series of events that result in the activation of an enzyme in the glycogenesis pathway and the inhibition of an enzyme in the glycogenolysis pathway. Glucagon has the opposite effect of insulin on liver cells; it accelerates glycogenolysis and suppresses glycogenesis causes a decrease in blood glucose levels accelerated by insulin • suppressed by glucagon glucose glycogenesis glycogen glycogenolysis causes an increase in blood glucose levels accelerated by glucagon • suppressed by insulin
15.18) Determine whether the following statements describe insulin, glucagon, or both insulin and glucagon. a) secreted by pancreas both insulin and glucagon b) released when blood glucose concentration is high insulin c) released when blood glucose concentration is low glucagon d) immediately increases the amount of glucose entering cells insulin e) is a hormone both insulin and glucagon f) lowers blood glucose concentration insulin g) not enough is produced by individuals with type-1 diabetes insulin h) stimulates glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) glucagon EXPLANATION: When insulin binds to liver and muscle cell receptors, it triggers a series of events that result in the activation of an enzyme in the glycogenesis pathway and the inhibition of an enzyme in the glycogenolysis pathway. Glucagon has the opposite effect of insulin on liver cells; it accelerates glycogenolysis and suppresses glycogenesis causes a decrease in blood glucose levels accelerated by insulin • suppressed by glucagon glucose glycogenesis glycogen glycogenolysis causes an increase in blood glucose levels accelerated by glucagon • suppressed by insulin
Anatomy & Physiology
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Chapter17: The Endocrine System
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 31RQ: Which of the following statements about insulin is true? Insulin acts as a transport protein, cany...
Related questions
Question
I don't get it at all. I struggled with my homework. Can you help me? Can you help me to explain to me, please?
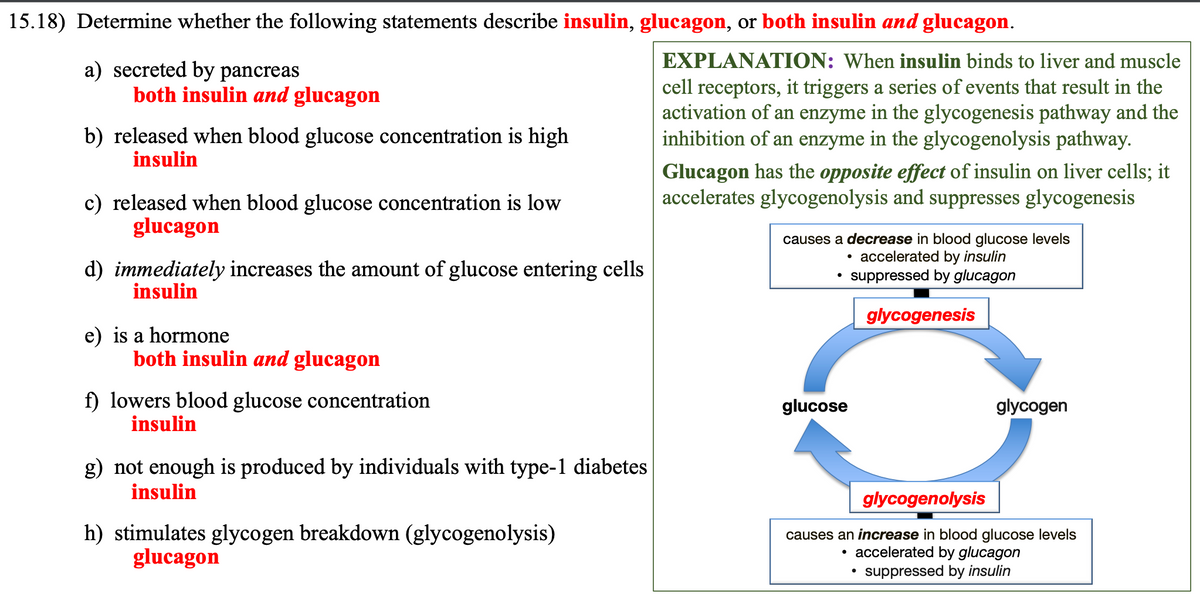
Transcribed Image Text:15.18) Determine whether the following statements describe insulin, glucagon, or both insulin and glucagon.
a) secreted by pancreas
both insulin and glucagon
b) released when blood glucose concentration is high
insulin
c) released when blood glucose concentration is low
glucagon
d) immediately increases the amount of glucose entering cells
insulin
e) is a hormone
both insulin and glucagon
f) lowers blood glucose concentration
insulin
g) not enough is produced by individuals with type-1 diabetes
insulin
h) stimulates glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis)
glucagon
EXPLANATION: When insulin binds to liver and muscle
cell receptors, it triggers a series of events that result in the
activation of an enzyme in the glycogenesis pathway and the
inhibition of an enzyme in the glycogenolysis pathway.
Glucagon has the opposite effect of insulin on liver cells; it
accelerates glycogenolysis and suppresses glycogenesis
causes a decrease in blood glucose levels
• accelerated by insulin
suppressed by glucagon
glucose
glycogenesis
●
glycogen
glycogenolysis
causes an increase in blood glucose levels
• accelerated by glucagon
suppressed by insulin
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College



Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College

