2 N H₂C H3C :0: H H3C The aldol reaction is a carbonyl condensation reaction between two carbonyl partners and involves a combination of nucleophilic addition and a-substitution steps. One partner is converted into an enolate ion nucleophile and adds to the electrophilic carbonyl group of the second partner. In the classic aldol reaction, the carbonyl partners are aldehydes or ketones, although aldehydes are more reactive. The product is a B-hydroxy carbonyl compound. H OH == base XT Under reaction conditions slightly more vigorous than those employed for the aldol reaction, the B-hydroxyl group is eliminated in an E1cB dehydration to give an a,ß-unsaturated carbonyl compound. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism. Arrow-pushing Instructions H₂C heat H H H3C H + H₂O
2 N H₂C H3C :0: H H3C The aldol reaction is a carbonyl condensation reaction between two carbonyl partners and involves a combination of nucleophilic addition and a-substitution steps. One partner is converted into an enolate ion nucleophile and adds to the electrophilic carbonyl group of the second partner. In the classic aldol reaction, the carbonyl partners are aldehydes or ketones, although aldehydes are more reactive. The product is a B-hydroxy carbonyl compound. H OH == base XT Under reaction conditions slightly more vigorous than those employed for the aldol reaction, the B-hydroxyl group is eliminated in an E1cB dehydration to give an a,ß-unsaturated carbonyl compound. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism. Arrow-pushing Instructions H₂C heat H H H3C H + H₂O
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Chapter18: Functional Derivatives Of Carboxylic Acids
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 18.70P
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:2
Moin
H3C
H
H₂C
C⇒x=
base
:0:
OH
Hori
H3C
H.
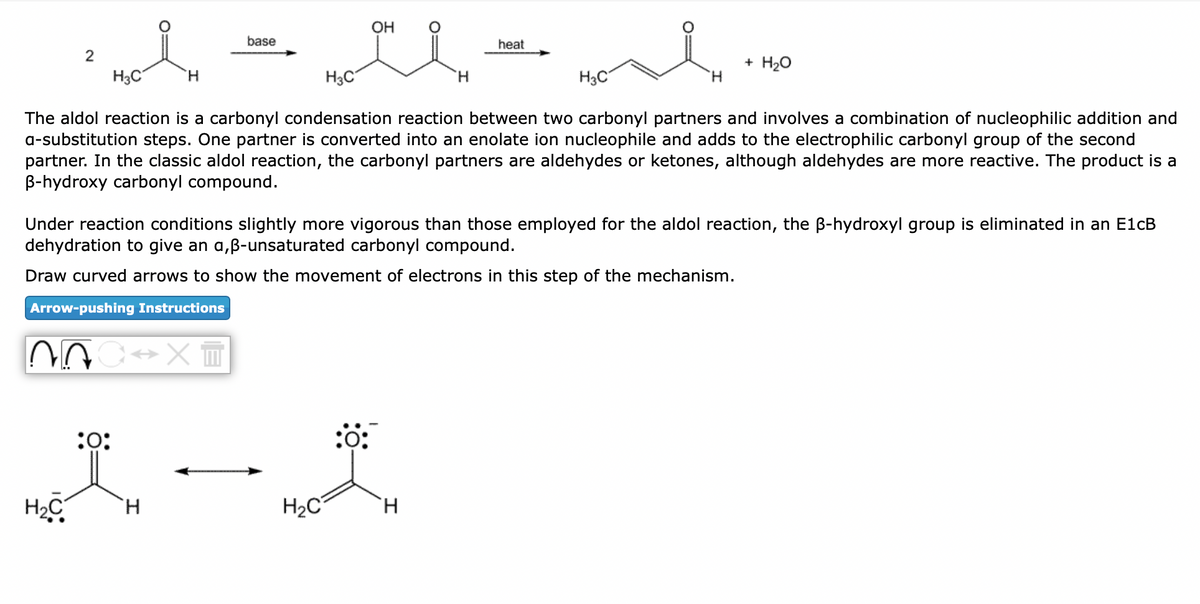
The aldol reaction is a carbonyl condensation reaction between two carbonyl partners and involves a combination of nucleophilic addition and
a-substitution steps. One partner is converted into an enolate ion nucleophile and adds to the electrophilic carbonyl group of the second
partner. In the classic aldol reaction, the carbonyl partners are aldehydes or ketones, although aldehydes are more reactive. The product is a
B-hydroxy carbonyl compound.
Under reaction conditions slightly more vigorous than those employed for the aldol reaction, the ß-hydroxyl group is eliminated in an E1cB
dehydration to give an a,ß-unsaturated carbonyl compound.
Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism.
Arrow-pushing Instructions
H₂C
Ἡ
:0:
heat
H
Home
H3C
+ H₂O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
