2. (a) Using table data presented in the text, calculate the focusing power Fmin of the crystalline lens in the case when eye is focused to view distant objects. (b) Knowing that focusing power of the cornea is Feornea = 42 D, calculate minimum focusing power of the eye. (c) Find what if the eye focal length in this case. Eye optical system 1. Optical power of the cornea: Fornea = F, + F = F- optical power of the cornea front surface, D; F - optical power of the cornea back surface, D; R, radius of curvature of the comea front surface, m; Clary fibers R. Vous humor Comea Lene - radius of curvature of the comea back surface, R, Fora m; n1 - ambient refraction index (for air n = 1 and for water n, = 1.33); n - cornea refraction index: n- aqueous humour refraction index. 2. Optical power of the erystalline lens: Ferystalline tens =F +F, = s-a E- optical power of the crystalline lens front surface, D; F, - optical power of the crystalline lens back surface, D; R - radius of curvature of the crystalline lens front surface, m; R, - radius of curvature of the crystalline lens back surface, m; n - aqueous humour refraction index; n, - crystalline lens refraction index; n; - vitreous humor Oplo nerve Agueous humor Rena Scera refraction index. Table - Parameters for the Eye Radius, mm Index of refraction Front Back R = 7.8 Ramar =10 Ramin =6 Aqueous humour and vitreous humor R, = 7.3 R4maz =6 Ramie =5.5 Cornea n, =1.38 n4 =1.4 Crystalline lens (Fmin) Crystalline lens (Fmar) =1.33 3. Optical power of eye: F= Farnaa + Feristalline lens 4. Lens equation: 1 1. 1 Cornea Lens S- lens focal length (m); F- lens optical power (D); p - distance from the object to the lens or object distance (m); g – distance from the image to the lens or image distance (m). 5. Height of image on the retina: h.9 Н Е H - height of image on the retina, m; h - height of object, m; q - image distance (for human eye on the average is equal to 1.5 cm), m; p - distance of the object to optical system of the eye, m. 6. Lens magnification: н H- image height (m); h - object height (m), p - object distance (m); g - image distance (m). 7. Law of refraction: nisine, = nzsinez
2. (a) Using table data presented in the text, calculate the focusing power Fmin of the crystalline lens in the case when eye is focused to view distant objects. (b) Knowing that focusing power of the cornea is Feornea = 42 D, calculate minimum focusing power of the eye. (c) Find what if the eye focal length in this case. Eye optical system 1. Optical power of the cornea: Fornea = F, + F = F- optical power of the cornea front surface, D; F - optical power of the cornea back surface, D; R, radius of curvature of the comea front surface, m; Clary fibers R. Vous humor Comea Lene - radius of curvature of the comea back surface, R, Fora m; n1 - ambient refraction index (for air n = 1 and for water n, = 1.33); n - cornea refraction index: n- aqueous humour refraction index. 2. Optical power of the erystalline lens: Ferystalline tens =F +F, = s-a E- optical power of the crystalline lens front surface, D; F, - optical power of the crystalline lens back surface, D; R - radius of curvature of the crystalline lens front surface, m; R, - radius of curvature of the crystalline lens back surface, m; n - aqueous humour refraction index; n, - crystalline lens refraction index; n; - vitreous humor Oplo nerve Agueous humor Rena Scera refraction index. Table - Parameters for the Eye Radius, mm Index of refraction Front Back R = 7.8 Ramar =10 Ramin =6 Aqueous humour and vitreous humor R, = 7.3 R4maz =6 Ramie =5.5 Cornea n, =1.38 n4 =1.4 Crystalline lens (Fmin) Crystalline lens (Fmar) =1.33 3. Optical power of eye: F= Farnaa + Feristalline lens 4. Lens equation: 1 1. 1 Cornea Lens S- lens focal length (m); F- lens optical power (D); p - distance from the object to the lens or object distance (m); g – distance from the image to the lens or image distance (m). 5. Height of image on the retina: h.9 Н Е H - height of image on the retina, m; h - height of object, m; q - image distance (for human eye on the average is equal to 1.5 cm), m; p - distance of the object to optical system of the eye, m. 6. Lens magnification: н H- image height (m); h - object height (m), p - object distance (m); g - image distance (m). 7. Law of refraction: nisine, = nzsinez
College Physics
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Chapter26: Vision And Optical Instruments
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20PE: The contact lens prescription for a mildly farsighted person is 0.750 D, and the person has a near...
Related questions
Concept explainers
Applications Of Reflection Of Light
When a light ray (termed as the incident ray) hits a surface and bounces back (forms a reflected ray), the process of reflection of light has taken place.
Sign Convention for Mirrors
A mirror is made of glass that is coated with a metal amalgam on one side due to which the light ray incident on the surface undergoes reflection and not refraction.
Question
Can you use the formula in the second picture to answer it, please?

Transcribed Image Text:2. (a) Using table data presented in the text, calculate the focusing power Fmin of the crystalline
lens in the case when eye is focused to view distant objects. (b) Knowing that focusing power of the
cornea is Feornea = 42 D, calculate minimum focusing power of the eye. (c) Find what if the eye
focal length in this case.
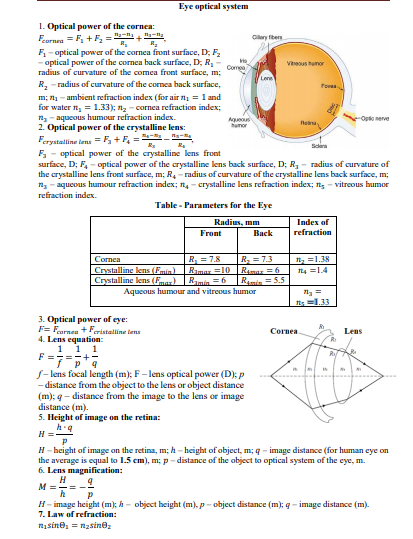
Transcribed Image Text:Eye optical system
1. Optical power of the cornea:
Fornea = F, + F =
F- optical power of the cornea front surface, D; F
- optical power of the cornea back surface, D; R,
radius of curvature of the comea front surface, m;
Clary fibers
R.
Vous humor
Comea
Lene
- radius of curvature of the comea back surface,
R,
Fora
m; n1 - ambient refraction index (for air n = 1 and
for water n, = 1.33); n - cornea refraction index:
n- aqueous humour refraction index.
2. Optical power of the erystalline lens:
Ferystalline tens =F +F, = s-a
E- optical power of the crystalline lens front
surface, D; F, - optical power of the crystalline lens back surface, D; R - radius of curvature of
the crystalline lens front surface, m; R, - radius of curvature of the crystalline lens back surface, m;
n - aqueous humour refraction index; n, - crystalline lens refraction index; n; - vitreous humor
Oplo nerve
Agueous
humor
Rena
Scera
refraction index.
Table - Parameters for the Eye
Radius, mm
Index of
refraction
Front
Back
R = 7.8
Ramar =10
Ramin =6
Aqueous humour and vitreous humor
R, = 7.3
R4maz =6
Ramie =5.5
Cornea
n, =1.38
n4 =1.4
Crystalline lens (Fmin)
Crystalline lens (Fmar)
=1.33
3. Optical power of eye:
F= Farnaa + Feristalline lens
4. Lens equation:
1 1. 1
Cornea
Lens
S- lens focal length (m); F- lens optical power (D); p
- distance from the object to the lens or object distance
(m); g – distance from the image to the lens or image
distance (m).
5. Height of image on the retina:
h.9
Н Е
H - height of image on the retina, m; h - height of object, m; q - image distance (for human eye on
the average is equal to 1.5 cm), m; p - distance of the object to optical system of the eye, m.
6. Lens magnification:
н
H- image height (m); h - object height (m), p - object distance (m); g - image distance (m).
7. Law of refraction:
nisine, = nzsinez
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168185
Author:
William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168185
Author:
William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning