2. Linear Momentum/Work and Energy: A bullet of mass 15 grams is tıred into a block of mass 985 grams, which is attacnea to an uncompressed spring of force constant k = 1.000×10° The velocity of the bullet is parallel to the long dimension of the spring. The spring is anchored to a very massive support and the block rests on a frictionless surface. After the bullet embeds itself in the block, the block and bullet move as one object compressing the spring by 12 cm before coming -- momentarily -- to rest. You may neglect the mass of the spring. Compute the speed of the bullet just before impact.
2. Linear Momentum/Work and Energy: A bullet of mass 15 grams is tıred into a block of mass 985 grams, which is attacnea to an uncompressed spring of force constant k = 1.000×10° The velocity of the bullet is parallel to the long dimension of the spring. The spring is anchored to a very massive support and the block rests on a frictionless surface. After the bullet embeds itself in the block, the block and bullet move as one object compressing the spring by 12 cm before coming -- momentarily -- to rest. You may neglect the mass of the spring. Compute the speed of the bullet just before impact.
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter8: Momentum And Collisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 57P: A 5.00-g bullet moving with an initial speed of v = 400 m/s is fired into and passes through a...
Related questions
Question
Please show formula's used and do step for step, please don't cut out any algebra
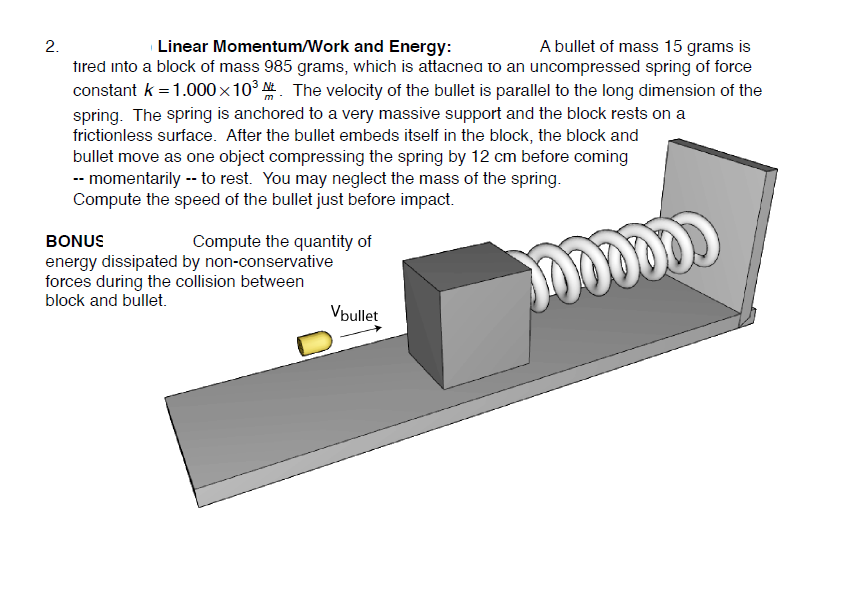
Transcribed Image Text:Linear Momentum/Work and Energy:
A bullet of mass 15 grams is
tıred into a block of mass 985 grams, which is attacnea to an uncompressed spring of force
constant k = 1.000×10° The velocity of the bullet is parallel to the long dimension of the
spring. The spring is anchored to a very massive support and the block rests on a
frictionless surface. After the bullet embeds itself in the block, the block and
bullet move as one object compressing the spring by 12 cm before coming
-- momentarily -- to rest. You may neglect the mass of the spring.
Compute the speed of the bullet just before impact.
BONUS
Compute the quantity of
energy dissipated by non-conservative
forces during the collision between
block and bullet.
Vbullet
2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill