*20-24. The end C of the plate rests on the horizontal plane, while end points A and B are restricted to move along the grooved slots. If at the instant shown A is moving downward with a constant velocity of va = 4 ft/s, determine the angular velocity of the plate and the velocities of points B and C. 0.4 ft 0.8 ft 1 ft vA 2 ft 2 ft
*20-24. The end C of the plate rests on the horizontal plane, while end points A and B are restricted to move along the grooved slots. If at the instant shown A is moving downward with a constant velocity of va = 4 ft/s, determine the angular velocity of the plate and the velocities of points B and C. 0.4 ft 0.8 ft 1 ft vA 2 ft 2 ft
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
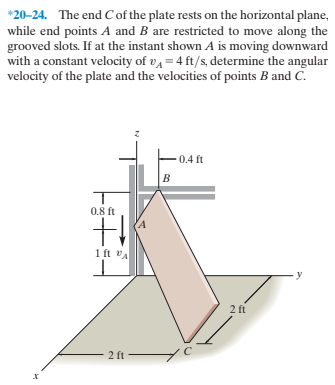
Transcribed Image Text:*20-24. The end C of the plate rests on the horizontal plane,
while end points A and B are restricted to move along the
grooved slots. If at the instant shown A is moving downward
with a constant velocity of va = 4 ft/s, determine the angular
velocity of the plate and the velocities of points B and C.
0.4 ft
0.8 ft
1 ft vA
2 ft
2 ft
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 10 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY