21 Time-dependent force AS-kg mass moves under the influence of a force F (4i-3¢])N, where r is the time in seconds (1 N = I newton). It starts at rest from the origin at t=0. Find: (a) its velocity; (b) its position; and (c)rxv, for any later time.
21 Time-dependent force AS-kg mass moves under the influence of a force F (4i-3¢])N, where r is the time in seconds (1 N = I newton). It starts at rest from the origin at t=0. Find: (a) its velocity; (b) its position; and (c)rxv, for any later time.
Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
5th Edition
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Chapter3: Oscillations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3.40P: An automobile with a mass of 1000 kg, including passengers, settles 1.0 cm closer to the road for...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:97
K/s ll
O &e 7:23
۱۰۳۹ من ۱۰۶۰
PROBLEMS
77
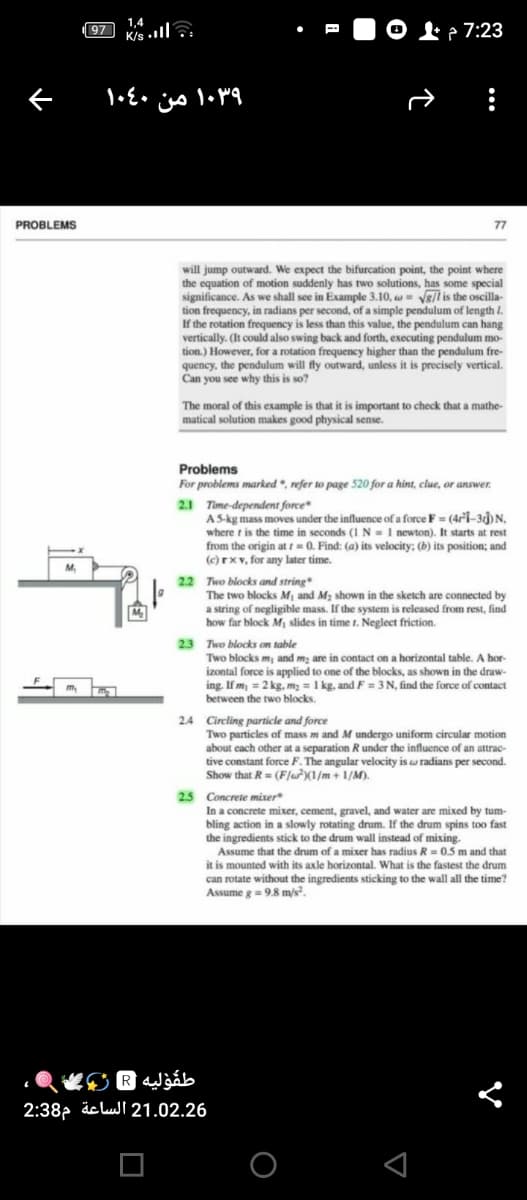
will jump outward. We expect the bifurcation point, the point where
the equation
significance. As we shall see in Example 3.10, w= Vg/l is the oscilla-
tion frequency, in radians per second, of a simple pendulum of length I.
If the rotation frequency is less than this value, the pendulum can hang
vertically. (It could also swing back and forth, executing pendulum mo-
tion.) However, for a rotation frequency higher than the pendulum fre-
quency, the pendulum will fly outward, unless it is precisely vertical.
Can you see why this is so?
motion suddenly has two solutions, has some special
The moral of this example is that it is important to check that a mathe-
matical solution makes good physical sense.
Problems
For problems marked *, refer so page 520 for a hint, clue, or answer.
2.1 Time-dependent force*
A S-kg mass moves under the influence of a force F (4ri-3j)N,
where t is the time in seconds (1 N = 1 newton). It starts at rest
from the origin at t = 0. Find: (a) its velocity; (b) its position; and
(c) rxv, for any later time.
22 Two blocks and string
The two blocks M and M2 shown in the sketch are connected by
a string of negligible mass. If the system is released from rest, find
how far block M, slides in time t. Neglect friction.
M.
2.3 Two blocks on table
Two blocks m, and m; are in contact on a horizontal table. A hor-
izontal force is applied to one of the blocks, as shown in the draw-
ing. If m, = 2 kg, m, = 1 kg, and F = 3N, find the force of contact
between the two blocks.
2.4 Circling particle and force
Two particles of mass m and M undergo uniform circular motion
about each other at a separation R under the influence of an attrac-
tive constant force F. The angular velocity is w radians per second.
Show that R= (F/)(1/m+ 1/M).
2.5 Concrete mixer
In a concrete mixer, cement, gravel, and water are mixed by tum-
bling action in a slowly rotating drum. If the drum spins too fast
the ingredients stick to the drum wall instead of mixing.
Assume that the drum of a mixer has radius R = 0.5 m and that
it is mounted with its axle horizontal. What is the fastest the drum
can rotate without the ingredients sticking to the wall all the time?
Assume g=9.8 m/s.
طفولیه B
2:38, äclull 21.02.26
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning