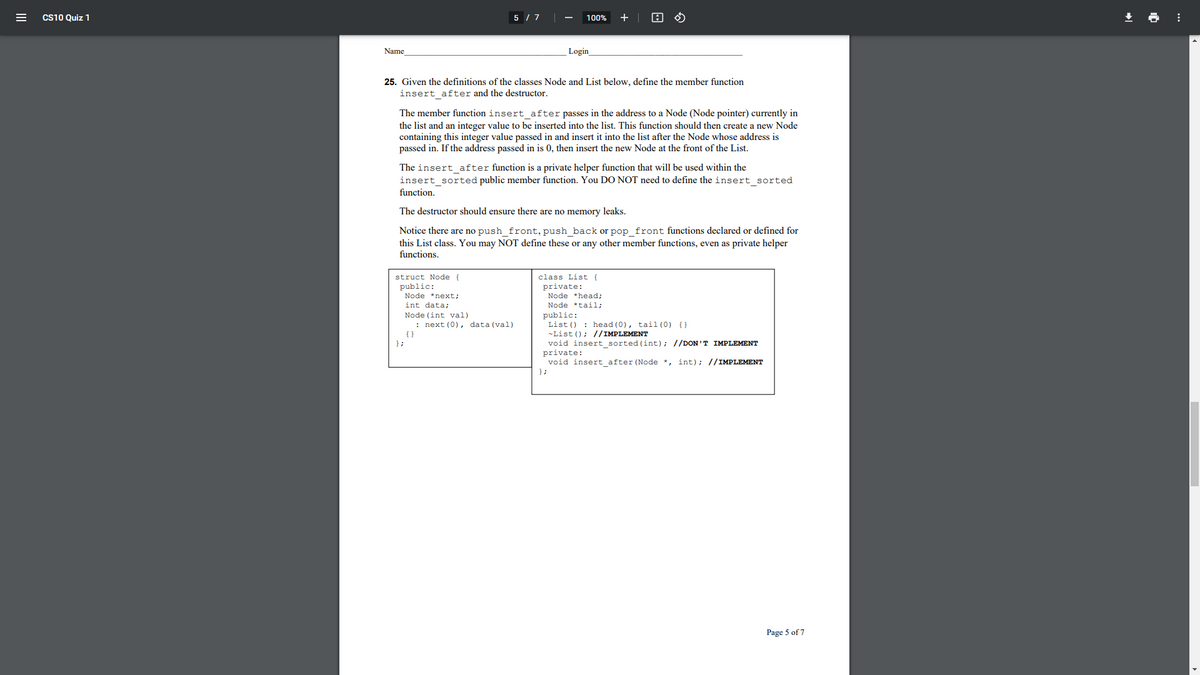
25. Given the definitions of the classes Node and List below, define the member funetion insert_after and the destructor. The member function insert_after passes in the address to a Node (Node pointer) currently in the list and an integer value to be inserted into the list. This funetion should then create a new Node containing this integer value passed in and insert it into the list after the Node whose address is passed in. If the address passed in is 0, then insert the new Node at the front of the List. The insert_after function is a private helper function that will be used within the insert_sorted public member function. You DO NOT need to define the insert_sorted function. The destructor should ensure there are no memory leaks. Notice there are no push_front, push_back or pop_front functions declared or defined for this List class. You may NOT define these or any other member functions, even as private helper functions. struct Node publie: Node nexti int data Node (int val) : next (0), data (val) elass List ( private: Node headi Node tail publiei List () : head (0), tail(0) () -List (): //IMPLEMENT void insert_sorted(int) //DON'T IMPLEMENT private: void insert after (Node , int) //IMPLEMENT
25. Given the definitions of the classes Node and List below, define the member funetion insert_after and the destructor. The member function insert_after passes in the address to a Node (Node pointer) currently in the list and an integer value to be inserted into the list. This funetion should then create a new Node containing this integer value passed in and insert it into the list after the Node whose address is passed in. If the address passed in is 0, then insert the new Node at the front of the List. The insert_after function is a private helper function that will be used within the insert_sorted public member function. You DO NOT need to define the insert_sorted function. The destructor should ensure there are no memory leaks. Notice there are no push_front, push_back or pop_front functions declared or defined for this List class. You may NOT define these or any other member functions, even as private helper functions. struct Node publie: Node nexti int data Node (int val) : next (0), data (val) elass List ( private: Node headi Node tail publiei List () : head (0), tail(0) () -List (): //IMPLEMENT void insert_sorted(int) //DON'T IMPLEMENT private: void insert after (Node , int) //IMPLEMENT
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Chapter1: Computer Networks And The Internet
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem R1RQ: What is the difference between a host and an end system? List several different types of end...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Cs10 Quiz 1
5 / 7
100%
+
Name
Login
25. Given the definitions of the classes Node and List below, define the member function
insert after and the destructor.
The member function insert after passes in the address to a Node (Node pointer) currently in
the list and an integer value to be inserted into the list. This function should then create a new Node
containing this integer value passed in and insert it into the list after the Node whose address is
passed in. If the address passed in is 0, then insert the new Node at the front of the List.
The insert_after function is a private helper function that will be used within the
insert_sorted public member function. You DO NOT need to define the insert_sorted
function.
The destructor should ensure there are no memory leaks.
Notice there are no push_front, push_back or pop_front functions declared or defined for
this List class. You may NOT define these or any other member functions, even as private helper
functions.
struct Node {
public:
class List {
private:
Node *next;
Node *head;
Node *tail;
int data;
public:
List () : head (0), tail (0) {}
-List (); //IMPLEMENT
void insert sorted (int); //DON'T IMPLEMENT
Node (int val)
: next (0), data (val)
};
private:
void insert after (Node *, int); //IMPLEMENT
};
Page 5 of 7
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093422
Author:
Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133750423
Author:
VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:
Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781119368830
Author:
FITZGERALD
Publisher:
WILEY