2x²y dx = (3x³ + y³) dy du
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question
Can someone please help me solve these problems .21 and 33.
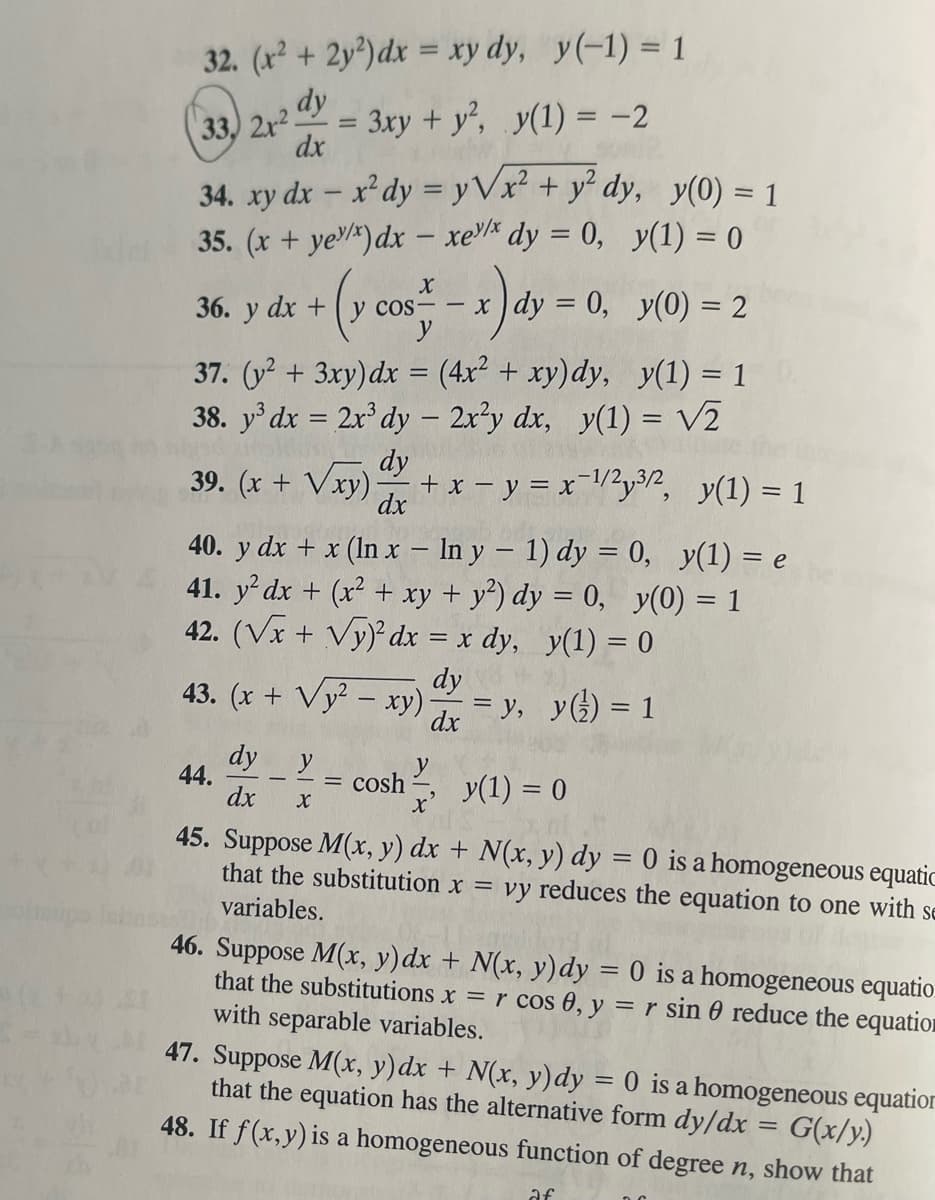
Transcribed Image Text:32. (x² + 2y²) dx = xy dy, y(-1) = 1
dy
33, 2x2- 3xy + y², y(1) = -2
dx
34. xy dx - x² dy = yVx² + y² dy,
35. (x + ye/x) dx - xe/* dy = 0,
X
- (y cos - - x) dy
cos-x dy = 0,
36. y dx +
y(1) = 0
y(0) = 2
37. (y² + 3xy) dx = (4x² + xy)dy,
y(1) = 1
38. y³ dx = 2x³ dy – 2x²y dx, y(1) = √₂
39. (x + √xy)
=
dy
dx
dy y
dx
X
44.
40. y dx + x (lnx - In y - 1) dy = 0, y(1) = e
41. y² dx + (x² + xy + y²) dy = 0, y(0) = 1
42. (√x + √y)² dx = x dy, y(1) = 0
dy
43. (x + √y² - xy).
dx
+ x - y = x-¹1/²y³/2, y(1) = 1
y(0) = 1
cosh
= y, y(¹) = 1
y
y(1) = 0
X
45. Suppose M(x, y) dx + N(x, y) dy = 0 is a homogeneous equatic
that the substitution x = vy reduces the equation to one with se
variables.
46. Suppose M(x, y) dx + N(x, y) dy = 0 is a homogeneous equatio
that the substitutions x = r cos 0, y = r sin 0 reduce the equatio
with separable variables.
47. Suppose M(x, y)dx + N(x, y) dy = 0 is a homogeneous equation
that the equation has the alternative form dy/dx
G(x/y.)
48. If f(x,y) is a homogeneous function of degree n, show that
af
=

Transcribed Image Text:In Problems 11-30 solve the given differential equation by using an
appropriate substitution.
M.
(x - y) dx + x dy = 0
013) x dx + (y - 2x) dy = 0
(15) (y² + yx) dx = x² dy = 0
y - x
dy
17. =
dx
y + x
19. -y dx + (x + √xy)dy = 0
21.) 2x2y dx = (3x³ + y³) dy
dy
dx X
23.
25. y
=
dx
dy
y+201
X
y
у
2MOITAUO
pups 021
= x + 4ye
27. y + x cot
(x +
e-2x/y
117) d
31. xy² dy
dx
bittin
dx - x dy = 0
12. (x + y) dx + x dy = 0
14. y dx = 2(x + y) dy
16. (y² + yx) dx + x² dy = 0
dy x + 3y
3x + y
18. =
dx
dy
20. x - y = √x² + y²
dx
22. (x4 + y4) dx - 2x³y dy = 0
dy y
x²
dx
X
= y³ - x³, y(1) = 2
24.
28.
29. (x² + xy - y²) dx + xy dy = 0
30. (x² + xy + 3y2) dx = (x² + 2xy) dy = 0
-
=
dy
dx X
+
26. (x²e-v/x + y²) dx = xy dy
is an
y²
= In
+1
X
In Problems 31-44 solve the given differential equation subject to the
indicated initial condition.
Expert Solution
Step 1
There are mentioned two question according to our guidelines i solving first one (question 21) please re post for another one .
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

