3-55 Consider a double-fluid manometer attached to an air pipe shown in Fig. P3-55. If the specific gravity of one fluid is 13.55, determine the specific gravity of the other fluid for the indicated absolute pressure of air. Take the atmospheric pressure to be 100 kPa. Answer: 1.34 Air P = 76 kPa 40 cm SG, 22 cm SG, = 13.55
3-55 Consider a double-fluid manometer attached to an air pipe shown in Fig. P3-55. If the specific gravity of one fluid is 13.55, determine the specific gravity of the other fluid for the indicated absolute pressure of air. Take the atmospheric pressure to be 100 kPa. Answer: 1.34 Air P = 76 kPa 40 cm SG, 22 cm SG, = 13.55
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Chapter8: Centroids And Distributed Loads
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8.122P: The 12-ft wide quarter-circular gate AB is hinged at A. Determine the contact force between the gate...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
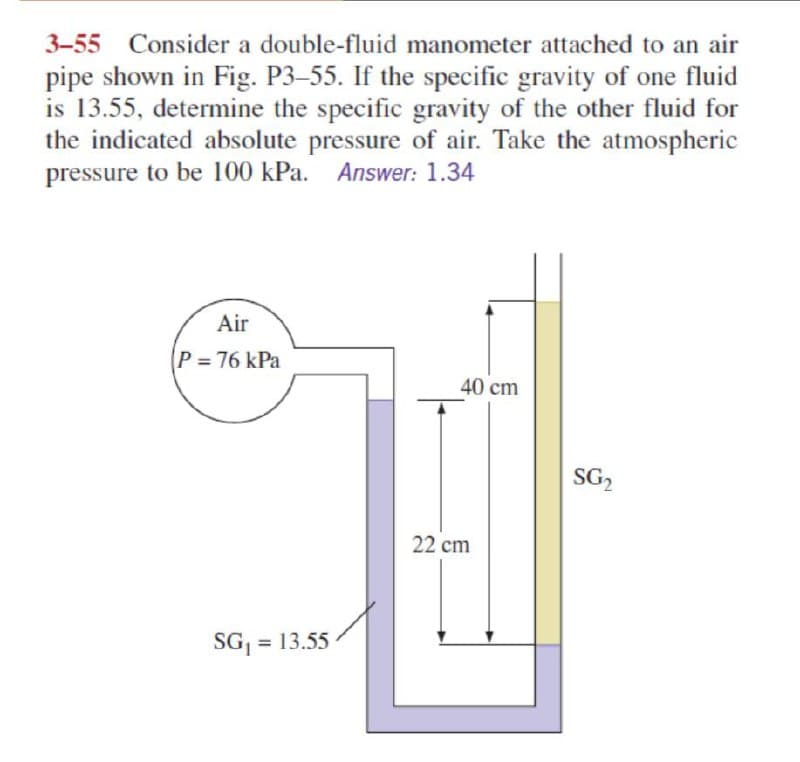
Transcribed Image Text:3-55 Consider a double-fluid manometer attached to an air
pipe shown in Fig. P3-55. If the specific gravity of one fluid
is 13.55, determine the specific gravity of the other fluid for
the indicated absolute pressure of air. Take the atmospheric
pressure to be 100 kPa. Answer: 1.34
Air
P = 76 kPa
40 cm
SG2
22 cm
SG = 13.55
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L