3. Prices of diamonds are determined by what is known as the 4 Cs: cut, clarity, color, and carat weight. The prices of diamonds go up as the carat weight increases, but the increase is not smooth. For example, the difference between the size of a 0.99 carat diamond and a 1 carat diamond is undetectable to the naked human eye, but the price of a 1 carat diamond tends to be much higher than the price of a 0.99 diamond. In this question we use two random samples of diamonds, 0.99 carats and 1 carat and compare the average prices of the diamonds. In order to be able to compare equivalent units, we first divide the price for each diamond by 100 times its weight in carats. That is, for a 0.99 carat diamond, we divide the price by 99. For a 1 carat diamond, we divide the price by 100. 0.99 carats 1 carat $44.51 $13.32 Mean $54.42 SD $16.03 23 1558 Find a 95% confidence interval for the difference in Price Per Carat between 0.99 and 1.00 carat diamonds. Interpret the interval in context. If it helps, the degrees of freedom should be 22.951.
3. Prices of diamonds are determined by what is known as the 4 Cs: cut, clarity, color, and carat weight. The prices of diamonds go up as the carat weight increases, but the increase is not smooth. For example, the difference between the size of a 0.99 carat diamond and a 1 carat diamond is undetectable to the naked human eye, but the price of a 1 carat diamond tends to be much higher than the price of a 0.99 diamond. In this question we use two random samples of diamonds, 0.99 carats and 1 carat and compare the average prices of the diamonds. In order to be able to compare equivalent units, we first divide the price for each diamond by 100 times its weight in carats. That is, for a 0.99 carat diamond, we divide the price by 99. For a 1 carat diamond, we divide the price by 100. 0.99 carats 1 carat $44.51 $13.32 Mean $54.42 SD $16.03 23 1558 Find a 95% confidence interval for the difference in Price Per Carat between 0.99 and 1.00 carat diamonds. Interpret the interval in context. If it helps, the degrees of freedom should be 22.951.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter7: Analytic Trigonometry
Section7.6: The Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Problem 92E
Related questions
Question
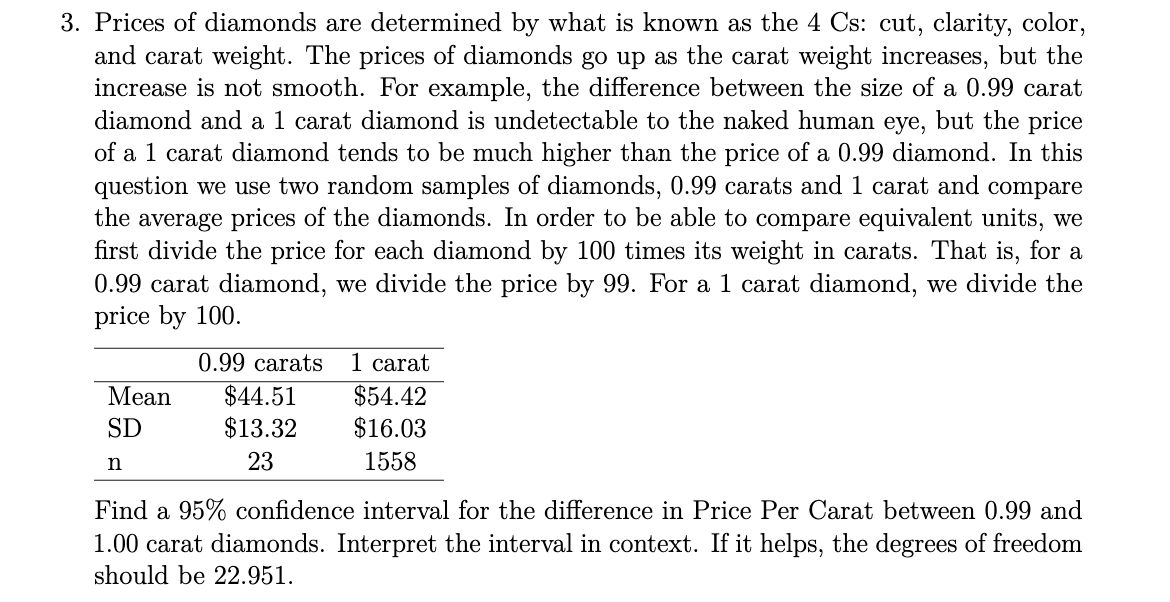
Transcribed Image Text:3. Prices of diamonds are determined by what is known as the 4 Cs: cut, clarity, color,
and carat weight. The prices of diamonds go up as the carat weight increases, but the
increase is not smooth. For example, the difference between the size of a 0.99 carat
diamond and a 1 carat diamond is undetectable to the naked human eye, but the price
of a 1 carat diamond tends to be much higher than the price of a 0.99 diamond. In this
question we use two random samples of diamonds, 0.99 carats and 1 carat and compare
the average prices of the diamonds. In order to be able to compare equivalent units, we
first divide the price for each diamond by 100 times its weight in carats. That is, for a
0.99 carat diamond, we divide the price by 99. For a 1 carat diamond, we divide the
price by 100.
0.99 carats
1 carat
$44.51
$13.32
Мean
$54.42
SD
$16.03
23
1558
Find a 95% confidence interval for the difference in Price Per Carat between 0.99 and
1.00 carat diamonds. Interpret the interval in context. If it helps, the degrees of freedom
should be 22.951.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,