3. Profit maximization using total cost and total revenue curves Suppose Rian operates a handicraft pop-up retail shop that sells cardigans. Assume a perfectly competitive market structure for cardigans with a market price equal to $25 per cardigan. The following graph shows Rian's total cost curve. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for cardigans for quantities zero through seven (including zero and seven) that Rian produces. 200 175 150 Total Cost 125 100 75 50 25 0 A + A -25 0 2 A 5 6 7 8 3 4 QUANTITY (Cardigans) Total Revenue Profit Calculate Rian's marginal revenue and marginal cost for the first seven cardigans they produce, and plot them on the following graph. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot marginal revenue and the orange points (square symbol) to plot marginal cost at each quantity. 35 15 5 0 D 1 2 3 4 5 7 8 QUANTITY (Cardigans) Marginal Revenue -0- Marginal Cost Rian's profit is maximized when they produce a total of , an amount cardigans. At this quantity, the marginal cost of the final cardigan they produce is , an amount than the price received for each cardigan they sell. At this point, the marginal cost of producing one more cardigan (the first cardigan beyond the profit maximizing quantity) is $ than the price received for each cardigan they sell. Therefore, Rian's profit-maximizing quantity occurs at the point of Intersection between the curves. Because Rian is a price taker, the previous condition is equivalent to
3. Profit maximization using total cost and total revenue curves Suppose Rian operates a handicraft pop-up retail shop that sells cardigans. Assume a perfectly competitive market structure for cardigans with a market price equal to $25 per cardigan. The following graph shows Rian's total cost curve. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for cardigans for quantities zero through seven (including zero and seven) that Rian produces. 200 175 150 Total Cost 125 100 75 50 25 0 A + A -25 0 2 A 5 6 7 8 3 4 QUANTITY (Cardigans) Total Revenue Profit Calculate Rian's marginal revenue and marginal cost for the first seven cardigans they produce, and plot them on the following graph. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot marginal revenue and the orange points (square symbol) to plot marginal cost at each quantity. 35 15 5 0 D 1 2 3 4 5 7 8 QUANTITY (Cardigans) Marginal Revenue -0- Marginal Cost Rian's profit is maximized when they produce a total of , an amount cardigans. At this quantity, the marginal cost of the final cardigan they produce is , an amount than the price received for each cardigan they sell. At this point, the marginal cost of producing one more cardigan (the first cardigan beyond the profit maximizing quantity) is $ than the price received for each cardigan they sell. Therefore, Rian's profit-maximizing quantity occurs at the point of Intersection between the curves. Because Rian is a price taker, the previous condition is equivalent to
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781337091992
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter13: Firms In Competitive Markets
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8PA
Related questions
Question
None
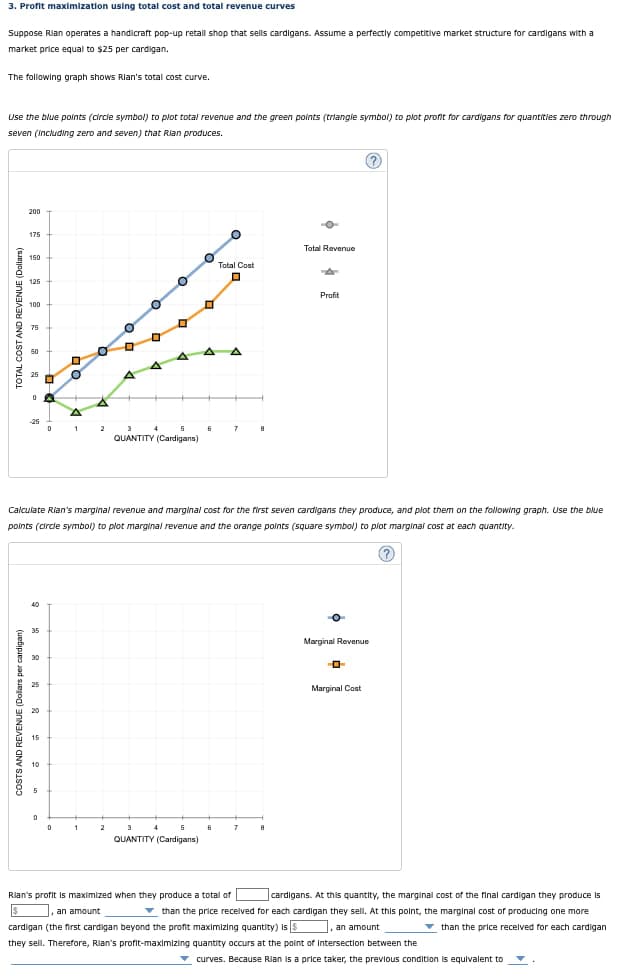
Transcribed Image Text:3. Profit maximization using total cost and total revenue curves
Suppose Rian operates a handicraft pop-up retail shop that sells cardigans. Assume a perfectly competitive market structure for cardigans with a
market price equal to $25 per cardigan.
The following graph shows Rian's total cost curve.
Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for cardigans for quantities zero through
seven (including zero and seven) that Rian produces.
200
175
150
Total Cost
125
100
75
50
25
0 A
+
A
-25
0
2
A
5
6
7
8
3
4
QUANTITY (Cardigans)
Total Revenue
Profit
Calculate Rian's marginal revenue and marginal cost for the first seven cardigans they produce, and plot them on the following graph. Use the blue
points (circle symbol) to plot marginal revenue and the orange points (square symbol) to plot marginal cost at each quantity.
35
15
5
0
D
1
2
3
4
5
7
8
QUANTITY (Cardigans)
Marginal Revenue
-0-
Marginal Cost
Rian's profit is maximized when they produce a total of
, an amount
cardigans. At this quantity, the marginal cost of the final cardigan they produce is
, an amount
than the price received for each cardigan they sell. At this point, the marginal cost of producing one more
cardigan (the first cardigan beyond the profit maximizing quantity) is $
than the price received for each cardigan
they sell. Therefore, Rian's profit-maximizing quantity occurs at the point of Intersection between the
curves. Because Rian is a price taker, the previous condition is equivalent to
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning