3. Using logic to compare samples with different sources of variation Two hypothetical outcomes for the same repeated-measures experiment are shown. Outcome A Treatment II III 100 110 120 101 111 122 102 112 123 103 113 121 Participant I A B C D D Outcome B Participant I A B C Treatment II 100 101 101 105 105 106 110 110 110 115 116 115 III
3. Using logic to compare samples with different sources of variation Two hypothetical outcomes for the same repeated-measures experiment are shown. Outcome A Treatment II III 100 110 120 101 111 122 102 112 123 103 113 121 Participant I A B C D D Outcome B Participant I A B C Treatment II 100 101 101 105 105 106 110 110 110 115 116 115 III
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
12th Edition
ISBN:9781305652231
Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Chapter8: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section8.CT: Chapter Test
Problem 24CT: Show the sample space of the experiment: toss a fair coin three times.
Related questions
Question
Need help
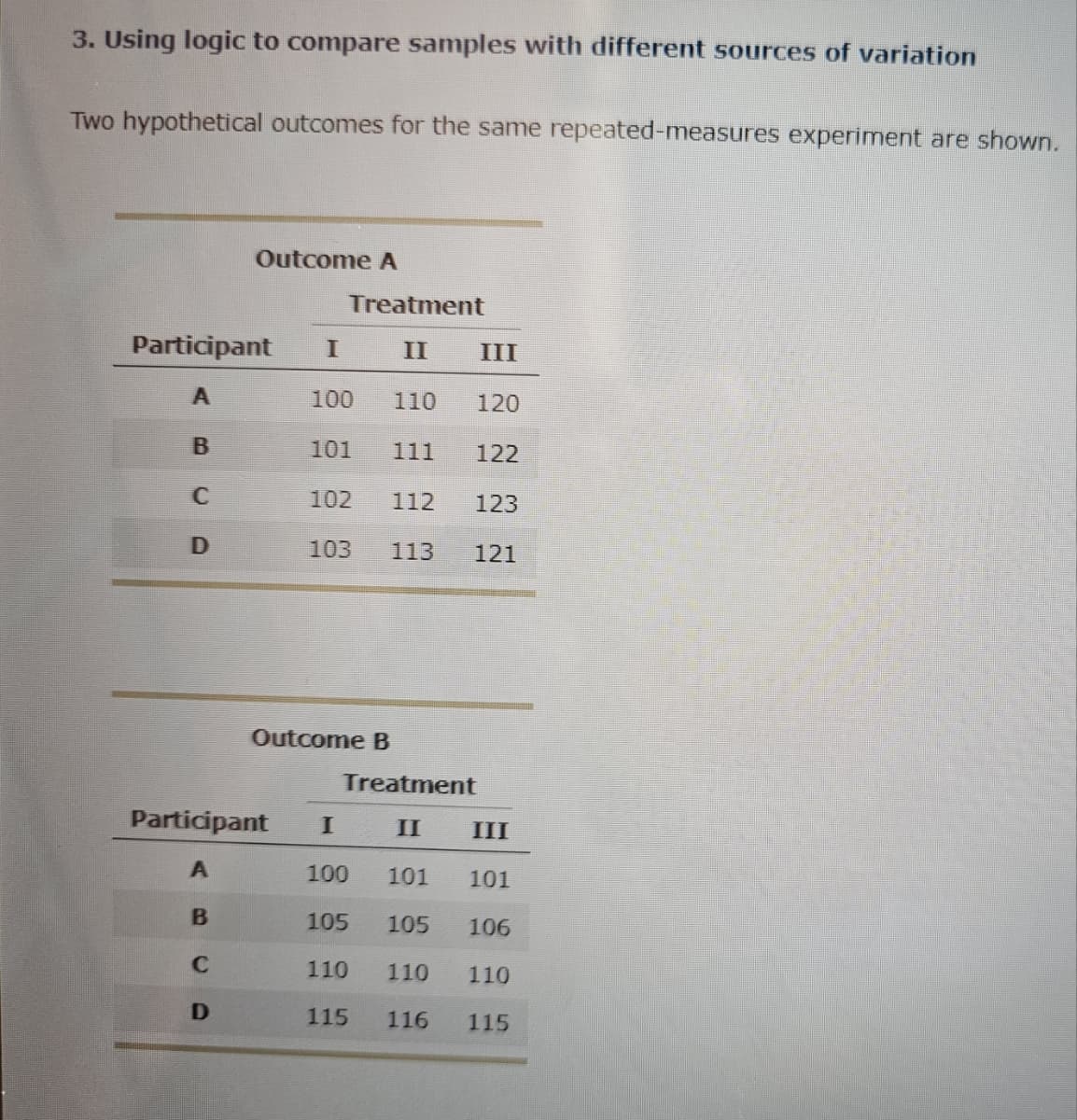
Transcribed Image Text:3. Using logic to compare samples with different sources of variation
Two hypothetical outcomes for the same repeated-measures experiment are shown.
Participant I
A
B
C
D
Outcome A
B
C
D
Treatment
II
III
100 110 120
101 111
Participant I
A
102
103 113
Outcome B
122
112 123
121
Treatment
II
105
100 101 101
105 106
110
115
III
110 110
115
116

Transcribed Image Text:For each outcome, consider the scores and note how they vary from treatment to treatment and from participant to participant (without making any
calculations). Then answer the following questions by comparing outcome A to outcome B.
Outcome A appears to have
Outcome A appears to have
between-treatments variance than (as) outcome B.
between-subjects variance than (as) outcome B.
Assuming that the variability caused by random and unsystematic factors is the same in the two outcomes, you can predict that outcome A has
F-ratio than (as) outcome B.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill


College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill
