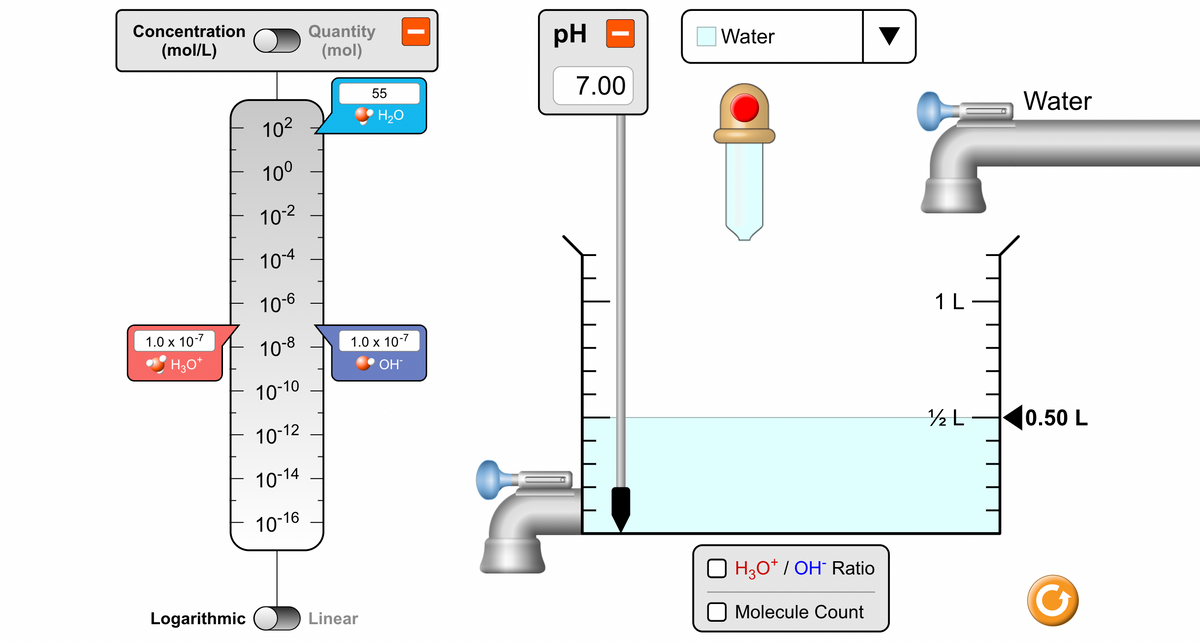
3. What is the meaning of pH? Choose the "micro" screen Micro from the options at the bottom of the page. A. What are two quantities of the three molecules or ions measured by the scale on the left? B. Toggle the top scale to concentration. What are the units of concentration? C. The switch below the scale (on the bottom) should read logarithmic. What is the range of values for concentration (use scientific notation!)? Change these values to standard notation (without the exponent) Which is the largest number on the scale (in scientific notation)? Which is the smallest number on the scale (in scientific notation) D. The substances in the boxes are H₂O, H3O+ and OH. Relate these three substances in a balanced chemical equation. E. Change the solutions and look at the concentration values. Which concentration level always stays constant? F. How are the concentration values of the other two substances related? G. Now, pick out two acidic solutions and two basic solutions from the previous chart. Indicate which is higher, the H3O+ concentration or the OH- concentration. Acidic/basic/neutral solution Which is higher, H3O+ or OH-? Acidic Acidic Basic Basic H. Change the logarithmic scale to linear. What do you notice about the position of the boxes on the scale? Why is a logarithmic scale preferred when measuring the concentration of H3O+ and OH-?
Ionic Equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium and ionic equilibrium are two major concepts in chemistry. Ionic equilibrium deals with the equilibrium involved in an ionization process while chemical equilibrium deals with the equilibrium during a chemical change. Ionic equilibrium is established between the ions and unionized species in a system. Understanding the concept of ionic equilibrium is very important to answer the questions related to certain chemical reactions in chemistry.
Arrhenius Acid
Arrhenius acid act as a good electrolyte as it dissociates to its respective ions in the aqueous solutions. Keeping it similar to the general acid properties, Arrhenius acid also neutralizes bases and turns litmus paper into red.
Bronsted Lowry Base In Inorganic Chemistry
Bronsted-Lowry base in inorganic chemistry is any chemical substance that can accept a proton from the other chemical substance it is reacting with.

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps









