3.32 0.5 mol hydrogen at 300 K, 2 mol nitrogen and oxygen present in the ratio of 3:1, and 0.3 mol of CO are mixed. The nitrogen–oxygen mixture was initially present at 400 K and the initial temperature of CO was 500 K. Fifty per cent of the CO present reacts. If the final temperature o the system raises to 1200 K under adiabatic conditions, and if the standard heat of formation of CO, is two times that of CO, calculate the standard heat of formation of CO. The mean heat capacities in J/mol K are 32.5 for O2, 31.1 for N2, 29.0 for H2, 31.0 for CO, and 49.0 for CO2.
3.32 0.5 mol hydrogen at 300 K, 2 mol nitrogen and oxygen present in the ratio of 3:1, and 0.3 mol of CO are mixed. The nitrogen–oxygen mixture was initially present at 400 K and the initial temperature of CO was 500 K. Fifty per cent of the CO present reacts. If the final temperature o the system raises to 1200 K under adiabatic conditions, and if the standard heat of formation of CO, is two times that of CO, calculate the standard heat of formation of CO. The mean heat capacities in J/mol K are 32.5 for O2, 31.1 for N2, 29.0 for H2, 31.0 for CO, and 49.0 for CO2.
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
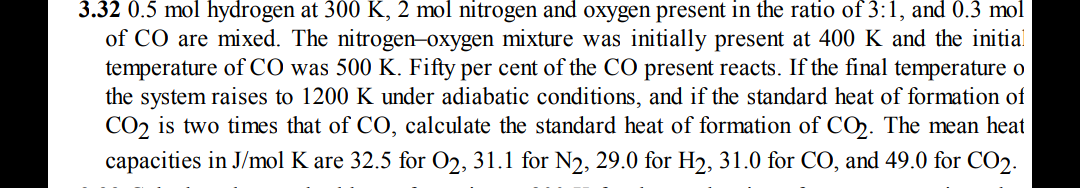
Transcribed Image Text:3.32 0.5 mol hydrogen at 300 K, 2 mol nitrogen and oxygen present in the ratio of 3:1, and 0.3 mol
of CO are mixed. The nitrogen–oxygen mixture was initially present at 400 K and the initial
temperature of CO was 500 K. Fifty per cent of the CO present reacts. If the final temperature o
the system raises to 1200 K under adiabatic conditions, and if the standard heat of formation of
CO, is two times that of CO, calculate the standard heat of formation of CO. The mean heat
capacities in J/mol K are 32.5 for O2, 31.1 for N2, 29.0 for H2, 31.0 for CO, and 49.0 for CO2.

Expert Solution
Step by step
Solved in 10 steps with 12 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The