4. From VE=0.1VCC, it is changed to VE= (1/3)VCC and the base resistors are adjusted accordingly to the same Q-point. What may happen? a. Increased stability and increased output VCE swing b. Increased stability but reduced output swing c. Reduced stability but increased output swing d. Reduced stability and reduced output swing Figure 4 Fixed Bias with Emitter Resistor 5. In the voltage divider, what happens if R2 is +Vcc lowered? a. VB is lowered and VC will shift toward VCC b. VB is increased and VC will shift toward VE c. Decreased current flow to the divider circuit • Vat but Q-point will stay the same Ve d. Increased current flow to the divider circuit VE but Q-point will stay the same 6. In the voltage divider, what happens if R1 is lowered? e. VB is lowered and VC will shift toward VCC f. VB is increased and VC will shift toward VE g. Decreased current flow to the divider circuit but Q-point will stay the same h. Increased current flow to the divider circuit but Q-point will stay the same
4. From VE=0.1VCC, it is changed to VE= (1/3)VCC and the base resistors are adjusted accordingly to the same Q-point. What may happen? a. Increased stability and increased output VCE swing b. Increased stability but reduced output swing c. Reduced stability but increased output swing d. Reduced stability and reduced output swing Figure 4 Fixed Bias with Emitter Resistor 5. In the voltage divider, what happens if R2 is +Vcc lowered? a. VB is lowered and VC will shift toward VCC b. VB is increased and VC will shift toward VE c. Decreased current flow to the divider circuit • Vat but Q-point will stay the same Ve d. Increased current flow to the divider circuit VE but Q-point will stay the same 6. In the voltage divider, what happens if R1 is lowered? e. VB is lowered and VC will shift toward VCC f. VB is increased and VC will shift toward VE g. Decreased current flow to the divider circuit but Q-point will stay the same h. Increased current flow to the divider circuit but Q-point will stay the same
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:Robert L. Boylestad
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P: Visit your local library (at school or home) and describe the extent to which it provides literature...
Related questions
Question
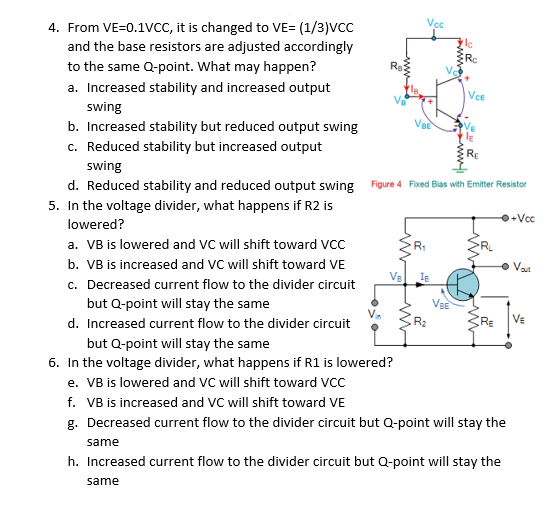
Transcribed Image Text:Vcc
4. From VE=0.1VCC, it is changed to VE= (1/3)VCC
and the base resistors are adjusted accordingly
to the same Q-point. What may happen?
Re
a. Increased stability and increased output
VCE
swing
b. Increased stability but reduced output swing
c. Reduced stability but increased output
swing
d. Reduced stability and reduced output swing Figure 4 Fixed Bias with Emitter Resistor
5. In the voltage divider, what happens if R2 is
+Vcc
lowered?
a. VB is lowered and VC will shift toward VCC
b. VB is increased and VC will shift toward VE
• Vat
VE
c. Decreased current flow to the divider circuit
but Q-point will stay the same
d. Increased current flow to the divider circuit
VE
but Q-point will stay the same
6. In the voltage divider, what happens if R1 is lowered?
e. VB is lowered and VC will shift toward VCC
f. VB is increased and VC will shift toward VE
g. Decreased current flow to the divider circuit but Q-point will stay the
same
h. Increased current flow to the divider circuit but Q-point will stay the
same
wwe
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028229
Author:
Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134746968
Author:
James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028151
Author:
Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,