4. Specialization and trade When a country has a comparative advantage in the production of a good, it means that it can produce this good at a lower opportunity cost than its trading partner. Then the country will specialize in the production of this good and trade it for other goods. The following graphs show the production possibilities frontiers (PPFS) for Maldonia and Lamponia. Both countries produce potatoes and sugar, each initially (I.e., before specialization and trade) producing 12 million pounds of potatoes and 6 million pounds of sugar, as indicated by the grey stars marked with the letter A. ? Maldonla Lamponia 32 28 SUGAR (Millions of pounds) 24 30 16 PPF SUGAR (Millions of pounds) 32 28 24 20 16 12 n 12,6 PPF 0 0 4 0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 POTATOES (Millions of pounds) 32 POTATOES (Millions of pounds) while Lamponia has a comparative advantage in the Maldonia has a comparative advantage in the production of production of Suppose that Maldonia and Lamponia specialize in the production of the goods in which each has a comparative advantage. After specialization, the two countries can produce a total of million pounds of sugar and million pounds of potatoes.
4. Specialization and trade When a country has a comparative advantage in the production of a good, it means that it can produce this good at a lower opportunity cost than its trading partner. Then the country will specialize in the production of this good and trade it for other goods. The following graphs show the production possibilities frontiers (PPFS) for Maldonia and Lamponia. Both countries produce potatoes and sugar, each initially (I.e., before specialization and trade) producing 12 million pounds of potatoes and 6 million pounds of sugar, as indicated by the grey stars marked with the letter A. ? Maldonla Lamponia 32 28 SUGAR (Millions of pounds) 24 30 16 PPF SUGAR (Millions of pounds) 32 28 24 20 16 12 n 12,6 PPF 0 0 4 0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 POTATOES (Millions of pounds) 32 POTATOES (Millions of pounds) while Lamponia has a comparative advantage in the Maldonia has a comparative advantage in the production of production of Suppose that Maldonia and Lamponia specialize in the production of the goods in which each has a comparative advantage. After specialization, the two countries can produce a total of million pounds of sugar and million pounds of potatoes.
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305971509
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter3: Interdependence And The Gains Rrom Trade
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5PA
Related questions
Question
Practice Pack
A10
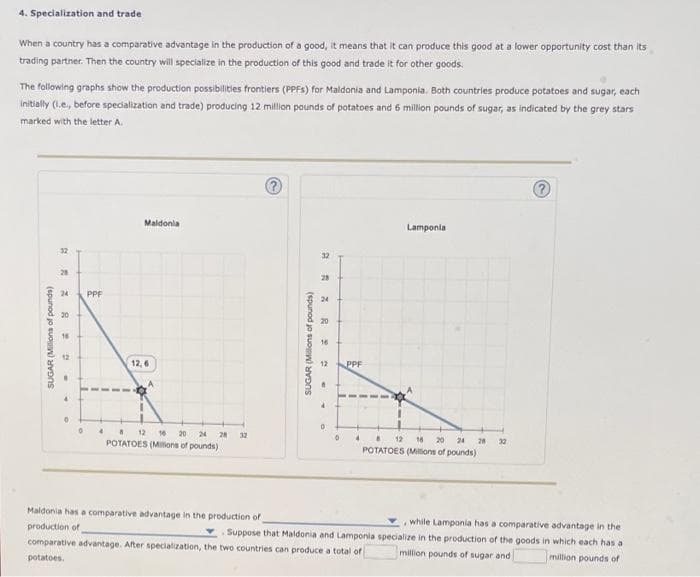
Transcribed Image Text:4. Specialization and trade
When a country has a comparative advantage in the production of a good, it means that it can produce this good at a lower opportunity cost than its
trading partner. Then the country will specialize in the production of this good and trade it for other goods.
The following graphs show the production possibilities frontiers (PPFS) for Maldonia and Lamponia. Both countries produce potatoes and sugar, each
initially (I.e., before specialization and trade) producing 12 million pounds of potatoes and 6 million pounds of sugar, as indicated by the grey stars
marked with the letter A.
?
Maldonia
Lamponia
32
28
24
30
16
SUGAR (Millions of pounds)
PPF
SUGAR (Millions of pounds)
32
28
24
20
16
12
n
0
12,6
0
4
4 8
12 16 20 24 28
32
8 12 16 20 24 28 32
POTATOES (Millions of pounds)
POTATOES (Millions of pounds)
Maldonia has a comparative advantage in the production of
while Lamponia has a comparative advantage in the
production of
Suppose that Maldonia and Lamponia specialize in the production of the goods in which each has a
comparative advantage. After specialization, the two countries can produce a total of
potatoes.
million pounds of sugar and
million pounds of
0
PPF
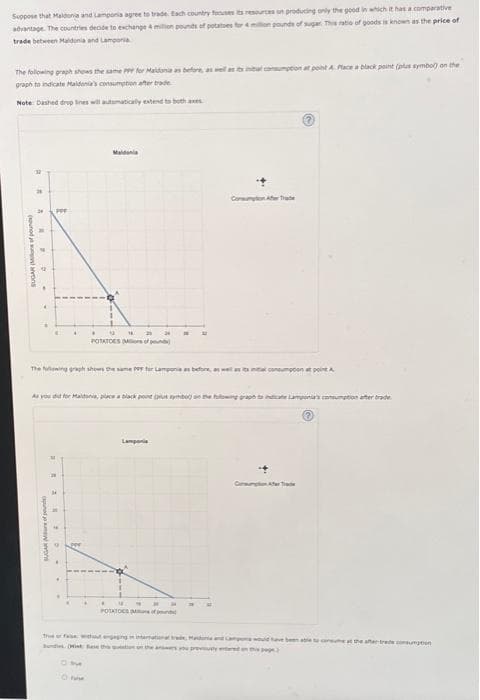
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that Maldonia and Lamponia agree to trade. Each country focuses its resources on producing only the good in which it has a comparative
advantage. The countries decide to exchange 4 million pounds of potatoes for 4 million pounds of sugar. This ratio of goods is known as the price of
trade between Maldonia and Lamponia
consumption at point A Place a black paint (plus symbol) on the
The following graph shows the same PP for Maldonia as before, as well as its
graph to indicate Maldonia's consumption after trade
Note: Dashed drep lines will automatically extend to both as
Maldonia
PPP
SUGAR (of poun
P
Consumption Afer Tra
24
IN
B
POTATOES (Mrs of po
The following graph shows the same for Lamponia as before, as well a
al consumption at point A
As you for Maldi, place a black point us be the following graph to indicate Lamponia's consumption after trade
Lamponi
Afer Trad
.
.
"
POTATOES of
True or fase with engaging in international trade, Madina and Camps would
und Mist Rese the son on the answers y prevyed on this pag
820
SUGAR Mof
able to consume at the after-trade consumption
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Includes step-by-step video
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Learn your way
Includes step-by-step video
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971509
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971509
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165912
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning