(4.10a) Each electron in an atom may be characterized by a set of four quantum numbers (n, I, m, m). For each of the following, tell how many different sets of quantum numbers are possible, such that each set contains all the values listed. If it is not possible to write a set of 4 quantum numbers, write N/A (not allowed). a) n = 2, l = 2 b) n = 2, 1 = 0 c) n = 4, 1 = 2, m/ = +3
(4.10a) Each electron in an atom may be characterized by a set of four quantum numbers (n, I, m, m). For each of the following, tell how many different sets of quantum numbers are possible, such that each set contains all the values listed. If it is not possible to write a set of 4 quantum numbers, write N/A (not allowed). a) n = 2, l = 2 b) n = 2, 1 = 0 c) n = 4, 1 = 2, m/ = +3
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter6: The Periodic Table And Atomic Structure
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6.101PAE: 6.101 Laser welding is a technique in which a tightly focused laser beam is used to deposit enough...
Related questions
Question
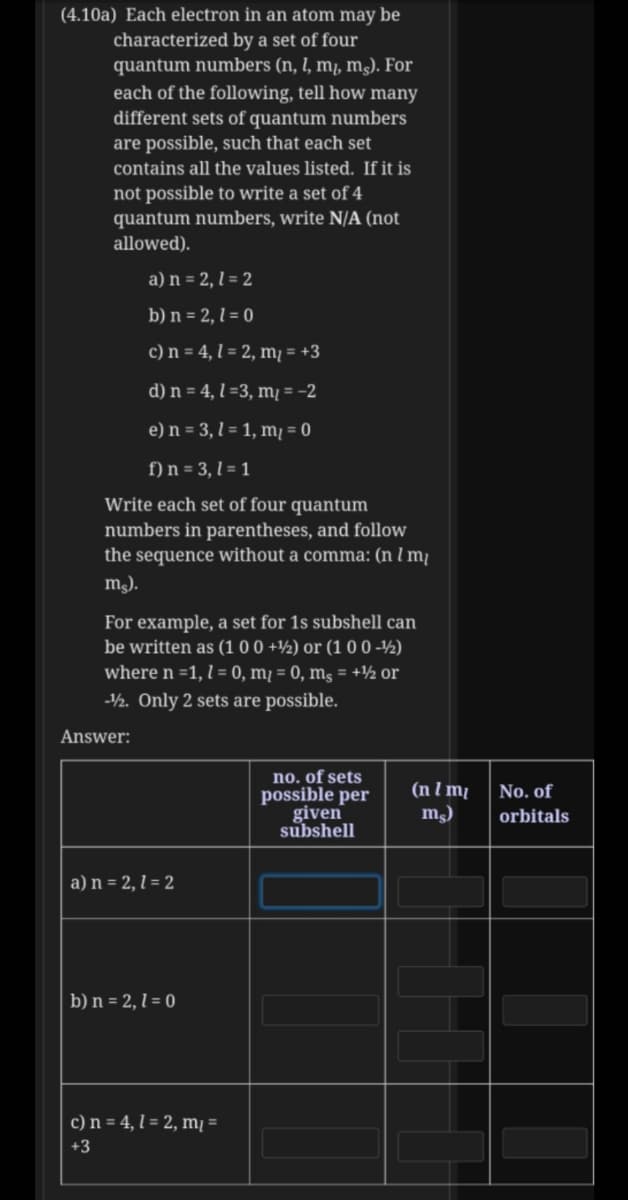
Transcribed Image Text:(4.10a) Each electron in an atom may be
characterized by a set of four
quantum numbers (n, l, m, mɔ. For
each of the following, tell how many
different sets of quantum numbers
are possible, such that each set
contains all the values listed. If it is
not possible to write a set of 4
quantum numbers, write N/A (not
allowed).
a) n = 2, l = 2
b) n = 2, l = 0
c) n = 4, l = 2, m¡ = +3
d) n = 4, l =3, m¡ = -2
e) n = 3, l = 1, m¡ = 0
f) n = 3, l = 1
Write each set of four quantum
numbers in parentheses, and follow
the sequence without a comma: (n l m¡
m).
For example, a set for 1s subshell can
be written as (1 00 +½) or (1 0 0 -½)
where n =1, l = 0, mį = 0, ms = +½ or
-½. Only 2 sets are possible.
Answer:
no. of sets
possible per
given
subshell
(n I m
m)
No. of
orbitals
a) n = 2, l = 2
b) n = 2, l = 0
c) n = 4, l = 2, mį =
+3
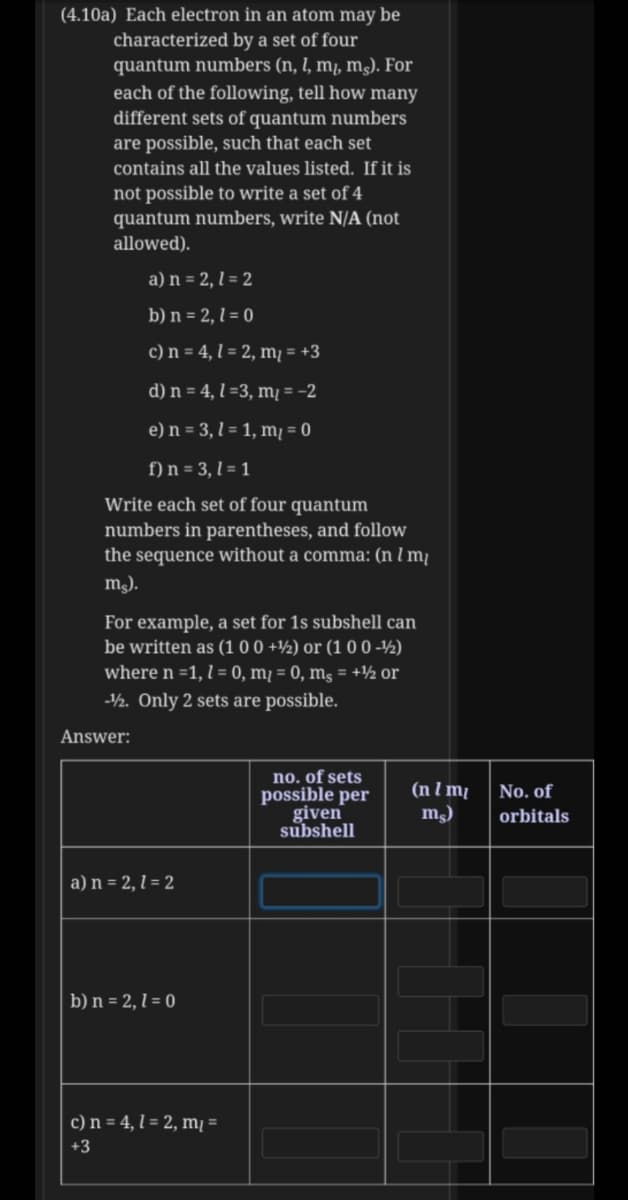
Transcribed Image Text:(4.10a) Each electron in an atom may be
characterized by a set of four
quantum numbers (n, l, m, mɔ. For
each of the following, tell how many
different sets of quantum numbers
are possible, such that each set
contains all the values listed. If it is
not possible to write a set of 4
quantum numbers, write N/A (not
allowed).
a) n = 2, l = 2
b) n = 2, l = 0
c) n = 4, l = 2, m¡ = +3
d) n = 4, l =3, m¡ = -2
e) n = 3, l = 1, m¡ = 0
f) n = 3, l = 1
Write each set of four quantum
numbers in parentheses, and follow
the sequence without a comma: (n l m¡
m).
For example, a set for 1s subshell can
be written as (1 00 +½) or (1 0 0 -½)
where n =1, l = 0, mį = 0, ms = +½ or
-½. Only 2 sets are possible.
Answer:
no. of sets
possible per
given
subshell
(n I m
m)
No. of
orbitals
a) n = 2, l = 2
b) n = 2, 1 = 0
c) n = 4, l = 2, mį =
+3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning