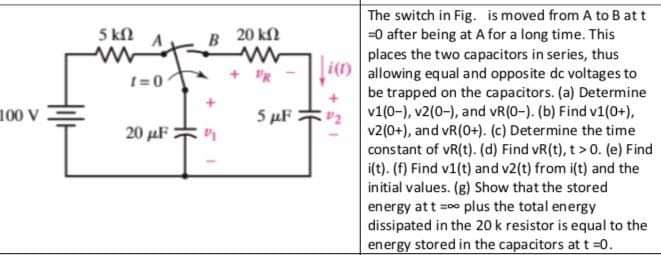
5 k2 B 20 k =0 after being at A for a long time. This places the two capacitors in series, thus O allowing equal and opposite dc voltages to be trapped on the capacitors. (a) Determine v1(0-), v2(0-), and vR(0-). (b) Find v1(0+), v2(0+), and vR(0+). (c) Determine the time constant of vR(t). (d) Find vR(t), t> 0. (e) Find i(t). (f) Find v1(t) and v2(t) from i(t) and the initial values. (g) Show that the stored energy att =00 plus the total energy dissipated in the 20 k resistor is equal to the energy stored in the capacitors at t =0. t=0 5 µF 20 uF
Sinusoids And Phasors
Sinusoids are defined as the mathematical waveforms that are used to describe the nature of periodic oscillations.
Circuit Theory
Electric circuits are a network that comprises of a closed-loop, which helps in providing a return path for the current through a switch. When the switch is activated, the load operates, and the current accepts a path to finish the circuit at a low potential level from the opposing high potential level. Electric circuits theory is a linear analysis that helps in establishing a linear relation of voltage and current for R (resistance), L (inductance), and C (capacitance).
The switch in Fig. is moved from A to B att 0 after being at For a long time. This places the two capacitors in series, thus allowing equal and opposite dc voltages to be trapped on the capacitors. (a) Determine v1(0-), v2(0-), and vR(0-). (b) Find v1(0+).
v2(0+), and vR(0+). (c) Determine the time constant of VR(t). (d) Find vR(t), t> 0. (e) Find i(t). () Find vi(t) and v2(t) from i(t) and the initial values. (g) Show that the stored energy at t = plus the total energy dissipated in the 20 k resistor is equal to the energy stored in the capacitors at t=0
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images


