66. Calculate AH°for the process Co304(s)3Co(8)+2O2(g) from the following information: Co(s) + O2 (g) → CoO(s) 3C00(s) + ½ O2 (g) → Co3O4 AH*298 =-237.9 kJ AH 298 -177.5 kJ
66. Calculate AH°for the process Co304(s)3Co(8)+2O2(g) from the following information: Co(s) + O2 (g) → CoO(s) 3C00(s) + ½ O2 (g) → Co3O4 AH*298 =-237.9 kJ AH 298 -177.5 kJ
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Chapter16: Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 66E: An important source of copper is from the copper ore, chalcocite, a form of copper(I) sulfide. When...
Related questions
Question
Chem Hw need help with question 66 and question 68
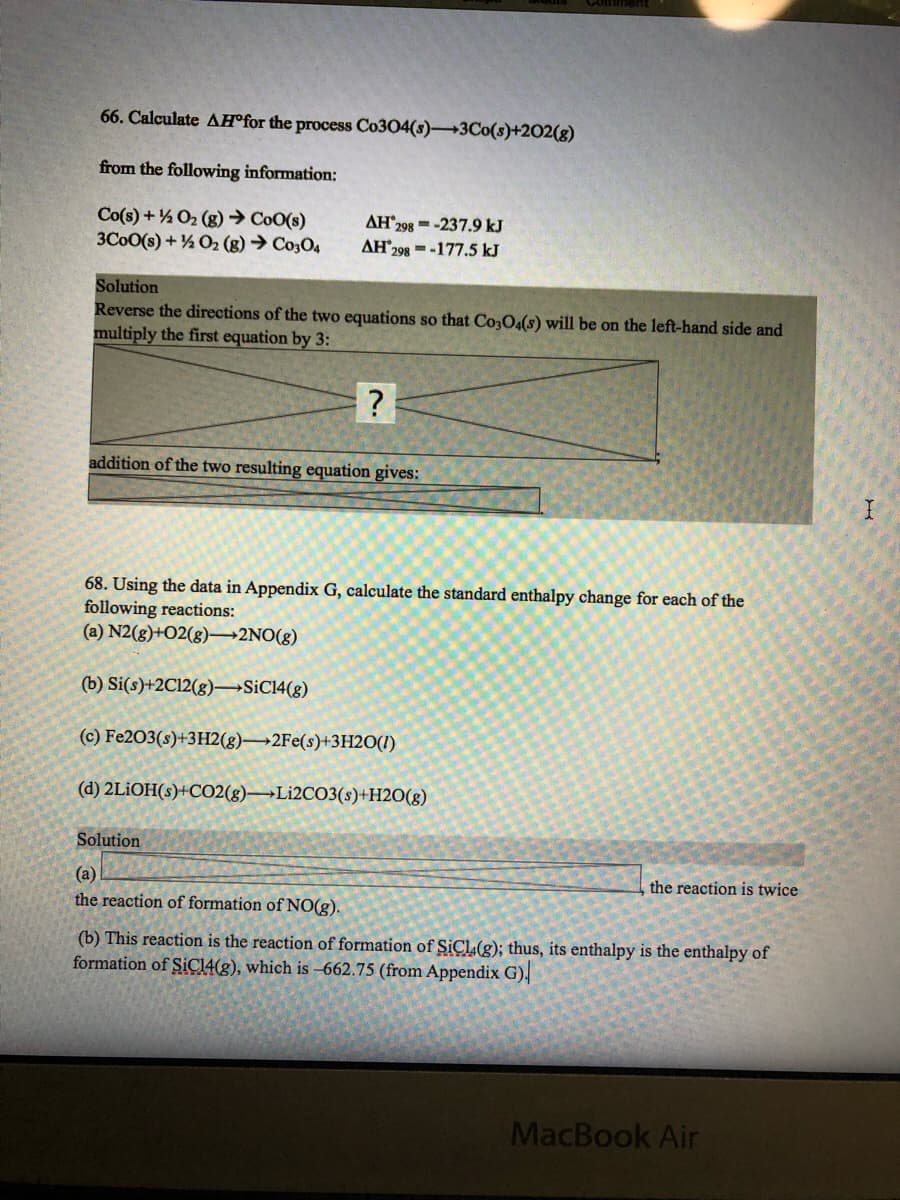
Transcribed Image Text:66. Calculate AH®for the process Co304(s)3Co(s)+202(g)
from the following information:
Co(s) + % O2 (g) → CoO(s)
3C0O(s) + ½ O2 (g) → Co3O4
AH 298 =-237.9 kJ
AH298 =-177.5 kJ
Solution
Reverse the directions of the two equations so that Co3O4(s) will be on the left-hand side and
multiply the first equation by 3:
addition of the two resulting equation gives:
68. Using the data in Appendix G, calculate the standard enthalpy change for each of the
following reactions:
(a) N2(g)+O2(g)–2NO(g)
(b) Si(s)+2C12(g)→SİC14(g)
(c) Fe203(s)+3H2(g)→2FE(s)+3H2O(1)
(d) 2LİOH(s)+CO2(g)→Lİ2CO3(s)+H2O(g)
Solution
(a)
the reaction of formation of NO(g).
the reaction is twice
(b) This reaction is the reaction of formation of SICL(g); thus, its enthalpy is the enthalpy of
formation of SIC14(g), which is -662.75 (from Appendix G),
MacBook Air
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning